Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > For a particular material, the Hall coefficie...
Start Learning for Free
For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material is
- a)intrinsic semiconductor
- b)extrinsic semiconductor
- c)metal
- d)insulator
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. T...
Introduction:
The Hall coefficient is a parameter that determines the nature of a material's charge carriers and their mobility in the presence of an external magnetic field. It is denoted by the symbol RH.
Hall Coefficient:
The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the electric field created by the Hall effect to the product of the current density and the magnetic field. Mathematically, it is given by the equation: RH = E/(J × B), where RH is the Hall coefficient, E is the electric field, J is the current density, and B is the magnetic field.
Interpretation of the Hall Coefficient:
The sign of the Hall coefficient determines the type of charge carriers in a material. If the Hall coefficient is positive, it indicates that the majority of charge carriers are positive (holes), while a negative Hall coefficient indicates that the majority of charge carriers are negative (electrons).
Hall Coefficient of Zero:
When the Hall coefficient of a material is zero, it means that the electric field created by the Hall effect is zero, even in the presence of a magnetic field. This implies that there is no deflection of charge carriers in the material when subjected to a magnetic field, resulting in no voltage difference across the material.
Explanation:
If the Hall coefficient is zero, it indicates that the material does not have any free charge carriers that can be deflected by the magnetic field. In other words, the material does not conduct electricity. This behavior is characteristic of insulating materials.
Insulating materials have a large energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band, which makes it difficult for charge carriers to move freely. As a result, these materials have very low conductivity and no free charge carriers that can contribute to the Hall effect.
Therefore, for a material with a Hall coefficient of zero, the correct option is 'D' - insulator.
The Hall coefficient is a parameter that determines the nature of a material's charge carriers and their mobility in the presence of an external magnetic field. It is denoted by the symbol RH.
Hall Coefficient:
The Hall coefficient is defined as the ratio of the electric field created by the Hall effect to the product of the current density and the magnetic field. Mathematically, it is given by the equation: RH = E/(J × B), where RH is the Hall coefficient, E is the electric field, J is the current density, and B is the magnetic field.
Interpretation of the Hall Coefficient:
The sign of the Hall coefficient determines the type of charge carriers in a material. If the Hall coefficient is positive, it indicates that the majority of charge carriers are positive (holes), while a negative Hall coefficient indicates that the majority of charge carriers are negative (electrons).
Hall Coefficient of Zero:
When the Hall coefficient of a material is zero, it means that the electric field created by the Hall effect is zero, even in the presence of a magnetic field. This implies that there is no deflection of charge carriers in the material when subjected to a magnetic field, resulting in no voltage difference across the material.
Explanation:
If the Hall coefficient is zero, it indicates that the material does not have any free charge carriers that can be deflected by the magnetic field. In other words, the material does not conduct electricity. This behavior is characteristic of insulating materials.
Insulating materials have a large energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band, which makes it difficult for charge carriers to move freely. As a result, these materials have very low conductivity and no free charge carriers that can contribute to the Hall effect.
Therefore, for a material with a Hall coefficient of zero, the correct option is 'D' - insulator.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. T...
Hall coefficient is defined as:
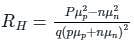
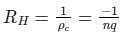
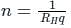
We can find the electron concentration as:
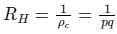
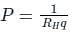
ρc = charge density
σn = nμnq and σp = pμpq
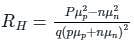
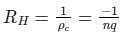
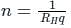
We can find the electron concentration as:
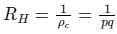
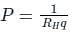
ρc = charge density
σn = nμnq and σp = pμpq
- Hall coefficient depends on the hole and electron concentration, and also on the mobility of carriers.
- In an insulator, the gap between the conduction band and the valence band is very high.
- Conductivity will be almost zero in the insulator
- As conductivity zero in insulator then mobility also almost zero.
- So, the hall coefficient will be zero almost for the insulator.
Attention Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Similar Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Doubts
For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice For a particular material, the Hall coefficient is found to be zero. The material isa)intrinsic semiconductorb)extrinsic semiconductorc)metald)insulatorCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























