Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric ...
Start Learning for Free
Hall effect can be used to measure
- a)electric field intensity
- b)magnetic field intensity
- c)carrier concentration
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic...
Hall Voltage states that if a specimen (metal or semiconductor) carrying a current I is placed in transverse magnetic field B, an electric field is induced in the direction perpendicular to both I and B.
Hall Voltage is given by:
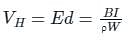
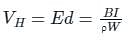
ρ = Charge density
Hall coefficient can be written as:
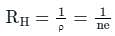
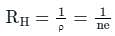
Where,
ρ = charge density = σ / μ
n = charge concentration
σ = conductivity
μ = mobility constant
Hence, the Hall coefficient becomes
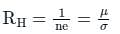
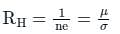
The Hall effect provides information on the sign, concentration, and mobility of charge carriers in the normal state.
A positive sign for the Hall coefficient indicates that the majority carriers are holes and the semiconductor is P-type.
A negative sign for the Hall coefficient indicates that the majority carriers are electrons and the semiconductor is N-type.
Applications of Hall-effect:
Hall effect can be used to find:
1. Carrier concentration
2. Type of semiconductor
3. Conductivity
4. Mobility
It cannot be used to find a magnetic field.
Common Confusion Point:
Looking at the formula one can think that the magnetic field can be calculated but in the HALL Experiment, perpendicular MAGNETIC field and electric field are applied on the material and other parameters are measured.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic...
Understanding the Hall Effect
The Hall effect is a phenomenon observed when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the flow of electric current in a conductor or semiconductor. This effect is utilized to measure various properties of materials, particularly in determining carrier concentration.
How the Hall Effect Works
- When an electric current flows through a conductor in the presence of a magnetic field, it experiences a force (Lorentz force) due to the magnetic field.
- This force causes charge carriers (electrons or holes) to accumulate on one side of the conductor, creating a voltage difference known as the Hall voltage.
Carrier Concentration Measurement
- The Hall voltage is directly related to the number of charge carriers in the material.
- The relationship can be described by the equation:
\[ V_H = \frac{IB}{nq} \]
where:
- \( V_H \) = Hall voltage
- \( I \) = current
- \( B \) = magnetic field strength
- \( n \) = charge carrier concentration
- \( q \) = charge of the carriers
- By measuring the Hall voltage and knowing the values of the current and magnetic field, one can calculate the carrier concentration (\( n \)), making this a precise method for determining the density of charge carriers in a material.
Applications in Electronics
- The Hall effect is widely used in semiconductor research and development.
- It helps in characterizing materials, assessing the quality of semiconductors, and developing devices like Hall effect sensors.
In summary, the Hall effect is a powerful tool to measure carrier concentration, making option 'C' the correct choice in the context of this question.
The Hall effect is a phenomenon observed when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the flow of electric current in a conductor or semiconductor. This effect is utilized to measure various properties of materials, particularly in determining carrier concentration.
How the Hall Effect Works
- When an electric current flows through a conductor in the presence of a magnetic field, it experiences a force (Lorentz force) due to the magnetic field.
- This force causes charge carriers (electrons or holes) to accumulate on one side of the conductor, creating a voltage difference known as the Hall voltage.
Carrier Concentration Measurement
- The Hall voltage is directly related to the number of charge carriers in the material.
- The relationship can be described by the equation:
\[ V_H = \frac{IB}{nq} \]
where:
- \( V_H \) = Hall voltage
- \( I \) = current
- \( B \) = magnetic field strength
- \( n \) = charge carrier concentration
- \( q \) = charge of the carriers
- By measuring the Hall voltage and knowing the values of the current and magnetic field, one can calculate the carrier concentration (\( n \)), making this a precise method for determining the density of charge carriers in a material.
Applications in Electronics
- The Hall effect is widely used in semiconductor research and development.
- It helps in characterizing materials, assessing the quality of semiconductors, and developing devices like Hall effect sensors.
In summary, the Hall effect is a powerful tool to measure carrier concentration, making option 'C' the correct choice in the context of this question.
Attention Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Similar Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Doubts
Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Hall effect can be used to measurea)electric field intensityb)magnetic field intensityc)carrier concentrationd)none of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























