Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The transfer function of a linear system is t...
Start Learning for Free
The transfer function of a linear system is the
- a)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)
- b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and input
- c)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output V...
Transfer function:
- The transfer function of a control system is defined as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output variable to Laplace transform of the input variable assuming all initial conditions to be zero.
- It is also defined as the Laplace transform of the impulse response.
If the input is represented by R(s) and the output is represented by C(s), then the transfer function will be:
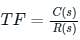
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output V...
Transfer function is a fundamental concept in linear systems theory. It is a mathematical representation of the relationship between the input and output of a linear time-invariant (LTI) system. The transfer function is commonly denoted as H(s), where s is the complex variable representing the Laplace transform domain.
Ratio of Laplace Transforms
The correct option for the transfer function of a linear system is c) Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros. This means that the transfer function H(s) is defined as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output (Y(s)) to the Laplace transform of the input (X(s)).
H(s) = Y(s) / X(s)
This definition implies that the transfer function captures the complete dynamic behavior of the system by taking into account the initial conditions. It describes how the system responds to different input signals in the frequency domain.
Benefits of Transfer Function
The transfer function is a powerful tool for analyzing and designing linear systems. Here are a few key benefits of using transfer functions:
1. System Analysis: By manipulating the transfer function algebraically, we can derive important system properties such as poles, zeros, stability, and frequency response. These properties provide insights into the system's behavior and performance.
2. System Design: Transfer functions allow us to design controllers and filters to achieve desired system responses. By modifying the transfer function, we can shape the system's frequency response and improve its performance.
3. System Simulation: Transfer functions can be easily implemented in simulation tools to model and analyze the system's behavior. This enables engineers to test different scenarios and evaluate the system's performance before implementing it in real-world applications.
4. System Identification: Transfer functions can also be used in system identification, where the goal is to estimate the transfer function of an unknown system based on input-output data. This is crucial for understanding and modeling complex systems.
Conclusion
In summary, the transfer function of a linear system is defined as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output to the Laplace transform of the input with all initial conditions zero. It provides a concise and powerful representation of the system's behavior in the frequency domain. By analyzing and manipulating the transfer function, engineers can gain valuable insights into the system's properties, design controllers, simulate system behavior, and identify unknown systems.
Ratio of Laplace Transforms
The correct option for the transfer function of a linear system is c) Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros. This means that the transfer function H(s) is defined as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output (Y(s)) to the Laplace transform of the input (X(s)).
H(s) = Y(s) / X(s)
This definition implies that the transfer function captures the complete dynamic behavior of the system by taking into account the initial conditions. It describes how the system responds to different input signals in the frequency domain.
Benefits of Transfer Function
The transfer function is a powerful tool for analyzing and designing linear systems. Here are a few key benefits of using transfer functions:
1. System Analysis: By manipulating the transfer function algebraically, we can derive important system properties such as poles, zeros, stability, and frequency response. These properties provide insights into the system's behavior and performance.
2. System Design: Transfer functions allow us to design controllers and filters to achieve desired system responses. By modifying the transfer function, we can shape the system's frequency response and improve its performance.
3. System Simulation: Transfer functions can be easily implemented in simulation tools to model and analyze the system's behavior. This enables engineers to test different scenarios and evaluate the system's performance before implementing it in real-world applications.
4. System Identification: Transfer functions can also be used in system identification, where the goal is to estimate the transfer function of an unknown system based on input-output data. This is crucial for understanding and modeling complex systems.
Conclusion
In summary, the transfer function of a linear system is defined as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output to the Laplace transform of the input with all initial conditions zero. It provides a concise and powerful representation of the system's behavior in the frequency domain. By analyzing and manipulating the transfer function, engineers can gain valuable insights into the system's properties, design controllers, simulate system behavior, and identify unknown systems.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The transfer function of a linear system is thea)Ratio of the output Vo(t) and input Vi(t)b)Ratio of the derivatives of the output and inputc)Ratio of the Laplace transform of the output and that of the input with all initial conditions zeros.d)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























