Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Questions > A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circu...
Start Learning for Free
A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximately
- a)24 kΩ
- b)12 kΩ
- c)7 kΩ
- d)14 kΩ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and rever...
Clamper Circuit and Non-Ideal Diode
A clamper circuit is an electronic circuit that is used to shift the DC level of a waveform. It consists of a diode, a capacitor, and a resistor. When the diode is forward biased, the capacitor charges to the peak value of the input signal and stores this voltage level. When the diode is reverse biased, the capacitor discharges through the resistor, maintaining the stored voltage level.
However, in practical applications, diodes are not ideal and have some resistance associated with them. In this case, the forward resistance and reverse resistance of the diode are given as 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively.
Determining the Correct Resistor Value
To correct the circuit, a resistor needs to be connected in parallel to compensate for the non-ideal characteristics of the diode. The value of this resistor can be calculated using the following steps:
1. Identify the desired voltage level: The desired voltage level is the DC level that needs to be shifted to zero volts. In this case, the desired voltage level is zero volts.
2. Calculate the resistance required to shift the voltage level: The resistance required can be determined using Ohm's Law. The voltage across the resistor is the desired voltage level (zero volts), and the current through the resistor is the current flowing through the diode when it is reverse biased.
Using Ohm's Law: V = IR
Rearranging the formula: R = V/I
The current flowing through the diode when it is reverse biased can be calculated using the reverse resistance of the diode. Given that the reverse resistance is 250 kilo ohms and the voltage across the resistor is zero volts, the current can be calculated as:
I = V/R = 0/(250,000) = 0 A
Therefore, the resistance required to shift the voltage level to zero volts is zero ohms.
3. Determine the value of the resistor to be connected in parallel: To compensate for the non-ideal characteristics of the diode, a resistor with a value equal to the reverse resistance of the diode needs to be connected in parallel. In this case, the reverse resistance of the diode is 250 kilo ohms.
However, the circuit designer has already used a 10 kilo ohm resistor in the circuit. To find the equivalent resistance when the two resistors are connected in parallel, the formula for calculating the equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel is used:
R_parallel = (R1 * R2) / (R1 + R2)
Plugging in the values, we get:
R_parallel = (10,000 * 250,000) / (10,000 + 250,000)
= 2,500,000,000 / 260,000
= 9615.38 ohms
Therefore, the value of the resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit is approximately 9615.38 ohms, which is closest to option 'A' - 24 kΩ.
A clamper circuit is an electronic circuit that is used to shift the DC level of a waveform. It consists of a diode, a capacitor, and a resistor. When the diode is forward biased, the capacitor charges to the peak value of the input signal and stores this voltage level. When the diode is reverse biased, the capacitor discharges through the resistor, maintaining the stored voltage level.
However, in practical applications, diodes are not ideal and have some resistance associated with them. In this case, the forward resistance and reverse resistance of the diode are given as 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively.
Determining the Correct Resistor Value
To correct the circuit, a resistor needs to be connected in parallel to compensate for the non-ideal characteristics of the diode. The value of this resistor can be calculated using the following steps:
1. Identify the desired voltage level: The desired voltage level is the DC level that needs to be shifted to zero volts. In this case, the desired voltage level is zero volts.
2. Calculate the resistance required to shift the voltage level: The resistance required can be determined using Ohm's Law. The voltage across the resistor is the desired voltage level (zero volts), and the current through the resistor is the current flowing through the diode when it is reverse biased.
Using Ohm's Law: V = IR
Rearranging the formula: R = V/I
The current flowing through the diode when it is reverse biased can be calculated using the reverse resistance of the diode. Given that the reverse resistance is 250 kilo ohms and the voltage across the resistor is zero volts, the current can be calculated as:
I = V/R = 0/(250,000) = 0 A
Therefore, the resistance required to shift the voltage level to zero volts is zero ohms.
3. Determine the value of the resistor to be connected in parallel: To compensate for the non-ideal characteristics of the diode, a resistor with a value equal to the reverse resistance of the diode needs to be connected in parallel. In this case, the reverse resistance of the diode is 250 kilo ohms.
However, the circuit designer has already used a 10 kilo ohm resistor in the circuit. To find the equivalent resistance when the two resistors are connected in parallel, the formula for calculating the equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel is used:
R_parallel = (R1 * R2) / (R1 + R2)
Plugging in the values, we get:
R_parallel = (10,000 * 250,000) / (10,000 + 250,000)
= 2,500,000,000 / 260,000
= 9615.38 ohms
Therefore, the value of the resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit is approximately 9615.38 ohms, which is closest to option 'A' - 24 kΩ.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and rever...
We have a formula to get the value of resistor to be used in a clamper circuit and it is given by R = 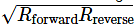
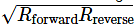
This gives value of R as 7.07 kΩ.
Since 10 kΩ resistor is being used, to make effective resistance as 7.07 kΩ, a resistor of value 24.18 kΩ has to be connected in parallel.
Attention Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Similar Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Doubts
A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus. Information about A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A non-ideal diode is used in a clamper circuit. The forward and reverse resistances of the diode are 200 ohms and 250 kilo ohms, respectively. The circuit designer has designed the circuit using a 10 kilo ohm resistor. The value of resistor to be connected in parallel to correct the circuit would be approximatelya)24 kΩb)12 kΩc)7 kΩd)14 kΩCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























