JEE Exam > JEE Questions > The bond lengths and bond angles in the mole...
Start Learning for Free
The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:
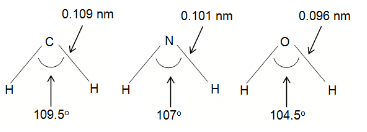
This variation in bond angle is a result of
(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases
(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule
(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron pair
- a)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- b)(i) and (ii)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(i)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia...
In methane, ammonia and water, the central atom is sp3 hybridised and expected bond angle is 109.5°.
However, the bond angle changes due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons.
This is because: lone pair-lone pair repulsions > lone pair-bond pair repulsions > bond pair-bond pair repulsions.
Methane (no lone pair) has a regular tetrahedral geometry with bond angle of 109.5°.
Ammonia (one lone pair) has a pyramidal geometry with bond angle of 107°.
Water (two lone pairs) has an angular bent geometry with bond angle of 104.5°.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Question Description
The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The bond lengths and bond angles in the molecules of methane, ammonia and water are given below:This variation in bond angle is a result of(i) the increasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms as the bond length decreases(ii) the number of non-bonding electron pairs in the molecule(iii) a non-bonding electron pair having a greater repulsive force than a bonding electron paira)(i), (ii) and (iii)b)(i) and (ii)c)(ii) and (iii)d)(i)Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



























