Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Highe...
Start Learning for Free
As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT has
- a)Higher switching losses but lower conduction losses
- b)Higher switching losses and higher conduction losses
- c)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction losses
- d)Lower switching losses but higher conduction losses
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lo...
Concept:
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lo...
Higher switching losses but lower conduction losses
----------------------------------
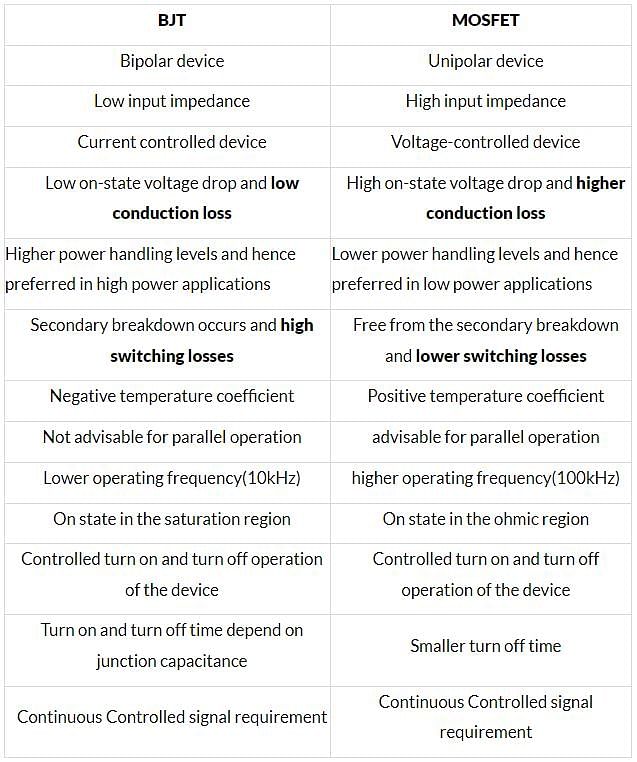
Switching losses refer to the energy dissipated during the transition of a device from on-state to off-state or vice versa. Conduction losses, on the other hand, refer to the energy dissipated during the on-state operation of a device.
BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) and power MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) are two commonly used power devices in electronic circuits. Each of them has different characteristics and performance parameters, which determine their switching and conduction losses.
Switching Losses:
Switching losses in power devices occur during the transition between on-state and off-state. These losses are mainly due to the charging and discharging of the internal capacitances of the device, as well as the voltage and current spikes that occur during the switching process.
- BJT: When a BJT switches from off-state to on-state, there is a significant amount of charge stored in the base region that needs to be removed before the transistor fully turns on. This leads to a longer turn-on time and higher switching losses compared to MOSFETs. Therefore, a BJT has higher switching losses.
- MOSFET: Power MOSFETs have a very low gate-to-source capacitance, which allows for faster turn-on and turn-off times. This results in lower switching losses compared to BJTs.
Conduction Losses:
Conduction losses occur during the on-state operation of a power device when it conducts current from the source to the drain (for MOSFET) or from the collector to the emitter (for BJT).
- BJT: Bipolar junction transistors have a relatively higher on-state voltage drop (VCE(sat)) compared to MOSFETs. This leads to higher conduction losses in BJTs.
- MOSFET: Power MOSFETs have a lower on-state resistance (RDS(on)), resulting in lower conduction losses compared to BJTs.
Conclusion:
Based on the above comparisons, it can be concluded that a BJT has higher switching losses but lower conduction losses compared to a power MOSFET. However, it is important to note that the specific characteristics and performance parameters of each device can vary depending on the specific model and technology used. Therefore, it is always recommended to consult the datasheets and specifications of the devices for accurate information regarding their switching and conduction losses.
----------------------------------
Switching losses refer to the energy dissipated during the transition of a device from on-state to off-state or vice versa. Conduction losses, on the other hand, refer to the energy dissipated during the on-state operation of a device.
BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) and power MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) are two commonly used power devices in electronic circuits. Each of them has different characteristics and performance parameters, which determine their switching and conduction losses.
Switching Losses:
Switching losses in power devices occur during the transition between on-state and off-state. These losses are mainly due to the charging and discharging of the internal capacitances of the device, as well as the voltage and current spikes that occur during the switching process.
- BJT: When a BJT switches from off-state to on-state, there is a significant amount of charge stored in the base region that needs to be removed before the transistor fully turns on. This leads to a longer turn-on time and higher switching losses compared to MOSFETs. Therefore, a BJT has higher switching losses.
- MOSFET: Power MOSFETs have a very low gate-to-source capacitance, which allows for faster turn-on and turn-off times. This results in lower switching losses compared to BJTs.
Conduction Losses:
Conduction losses occur during the on-state operation of a power device when it conducts current from the source to the drain (for MOSFET) or from the collector to the emitter (for BJT).
- BJT: Bipolar junction transistors have a relatively higher on-state voltage drop (VCE(sat)) compared to MOSFETs. This leads to higher conduction losses in BJTs.
- MOSFET: Power MOSFETs have a lower on-state resistance (RDS(on)), resulting in lower conduction losses compared to BJTs.
Conclusion:
Based on the above comparisons, it can be concluded that a BJT has higher switching losses but lower conduction losses compared to a power MOSFET. However, it is important to note that the specific characteristics and performance parameters of each device can vary depending on the specific model and technology used. Therefore, it is always recommended to consult the datasheets and specifications of the devices for accurate information regarding their switching and conduction losses.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice As compared to power MOSFET, a BJT hasa)Higher switching losses but lower conduction lossesb)Higher switching losses and higher conduction lossesc)Lower switching losses and Lower conduction lossesd)Lower switching losses but higher conduction lossesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























