Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > What is the nature of power factor if surge i...
Start Learning for Free
What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?
- a)Unity
- b)Lagging
- c)Leading
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less ...
The Nature of Power Factor when Surge Impedance Loading is Less than Load
When considering the nature of power factor in electrical systems, it is important to understand the concept of surge impedance loading (SIL). SIL is a measure of how much power a transmission line can carry, and it is determined by the line's electrical characteristics, such as its resistance, inductance, and capacitance. The surge impedance loading is typically expressed as a fraction of the line's surge impedance, which is the characteristic impedance of the line.
In the given scenario, the surge impedance loading is less than the load. This means that the power being drawn by the load is greater than what the transmission line can handle based on its surge impedance. In such a situation, the power factor is said to be lagging.
Explanation:
- Surge Impedance Loading (SIL): Surge impedance loading is the maximum power that can be transferred through a transmission line without causing excessive voltage drop or distortion. It is a measure of the line's ability to carry power and is determined by its electrical characteristics.
- Power Factor: Power factor is a measure of how effectively electrical power is being used in a system. It is the ratio of real power (watts) to apparent power (volt-amperes). Power factor is typically expressed as a value between 0 and 1, where 1 represents perfect power factor (unity), and values less than 1 indicate a lagging power factor.
- Lagging Power Factor: A lagging power factor occurs when the load in an electrical system causes the current to lag behind the voltage waveform. This is typically the case in systems with inductive loads, such as motors and transformers. Inductive loads require reactive power, which causes the current to lag behind the voltage.
- Surge Impedance Loading < /> When the surge impedance loading is less than the load, it means that the power being drawn by the load exceeds the maximum power that the transmission line can handle based on its surge impedance. This indicates that the line is being operated at a higher capacity than it is designed for, leading to increased losses and potential voltage drop.
- Conclusion: In the given scenario, where the surge impedance loading is less than the load, the power factor is lagging. This means that the current being drawn by the load lags behind the voltage waveform, indicating the presence of inductive components in the load.
When considering the nature of power factor in electrical systems, it is important to understand the concept of surge impedance loading (SIL). SIL is a measure of how much power a transmission line can carry, and it is determined by the line's electrical characteristics, such as its resistance, inductance, and capacitance. The surge impedance loading is typically expressed as a fraction of the line's surge impedance, which is the characteristic impedance of the line.
In the given scenario, the surge impedance loading is less than the load. This means that the power being drawn by the load is greater than what the transmission line can handle based on its surge impedance. In such a situation, the power factor is said to be lagging.
Explanation:
- Surge Impedance Loading (SIL): Surge impedance loading is the maximum power that can be transferred through a transmission line without causing excessive voltage drop or distortion. It is a measure of the line's ability to carry power and is determined by its electrical characteristics.
- Power Factor: Power factor is a measure of how effectively electrical power is being used in a system. It is the ratio of real power (watts) to apparent power (volt-amperes). Power factor is typically expressed as a value between 0 and 1, where 1 represents perfect power factor (unity), and values less than 1 indicate a lagging power factor.
- Lagging Power Factor: A lagging power factor occurs when the load in an electrical system causes the current to lag behind the voltage waveform. This is typically the case in systems with inductive loads, such as motors and transformers. Inductive loads require reactive power, which causes the current to lag behind the voltage.
- Surge Impedance Loading < /> When the surge impedance loading is less than the load, it means that the power being drawn by the load exceeds the maximum power that the transmission line can handle based on its surge impedance. This indicates that the line is being operated at a higher capacity than it is designed for, leading to increased losses and potential voltage drop.
- Conclusion: In the given scenario, where the surge impedance loading is less than the load, the power factor is lagging. This means that the current being drawn by the load lags behind the voltage waveform, indicating the presence of inductive components in the load.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less ...
Surge Impedance Loading (SIL):
- It is the loading on the line whenever the load impedance is exactly matching to surge impedance of the transmission line.
- It is also known as characteristic impedance loading or ideal loading or ideal power transfer capability.
- So, at SIL the load impedance is equal to characteristic impedance (ZL = ZC).
Surge impedance loading 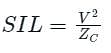
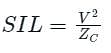
Where, ZC = Characteristic impedance = √(z/y)
Case 1: If loading is equal to SIL
- Load impedance is equal to characteristic impedance.
- The transmission line will act as neither sink nor source of reactive power.
- Receiving end voltage is equal to sending end voltage.
- Sending end current is equal to receiving end current.
- Both sending end and receiving end power factors are unity
Case 2: If loading is greater than SIL
- Load impedance is less than the characteristic equation.
- The transmission line will act as a sink of reactive power.
- Receiving end voltage is less than the sending end voltage
- Receiving current is more than sending end current.
- Receiving end power factor is unity but sending end power factor is lagging.
Case 3: If loading is less than SIL
- Load impedance is greater than the characteristic equation.
- The transmission line will act as a source of reactive power.
- Receiving end voltage is greater than the sending end voltage
- Receiving current is less than sending end current.
- Receiving end power factor is unity but sending end power factor is leading.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the nature of power factor if surge impedance loading is less than load?a)Unityb)Laggingc)Leadingd)ZeroCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























