UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Questions > The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε...
Start Learning for Free
The absorption at λmax 279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due to
- a)π−π∗ transition
- b)n−π∗ transition
- c)σ−σ∗ transition
- d)π−σ∗ transition
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum...
UV-Visible Spectroscopy:
- Molecular spectroscopy that involves the study of the interaction of Ultraviolet (UV)-Visible radiation with molecules.
- Ultraviolet light and visible light have just the right energy to cause an electronic Transition of electrons from one filled orbital to another of higher Energy unfilled orbital When a molecule absorbs light of an appropriate wavelength and an electron is promoted to a higher energy molecular orbital, the molecule is then in an excited state.
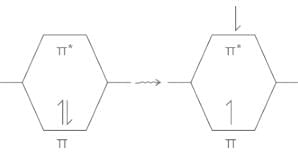
Electronic transitions:
- When molecule is getting excited by the absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the UV-visible region then its electrons are promoted from the ground state to the excited state or from the bonding orbital to the anti-bonding orbital.
Types of electronic transitions:
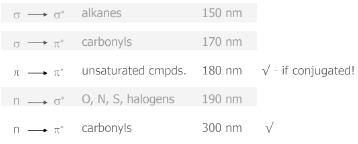
a) Transition: transition of an electron from bonding sigma orbital to anti-bonding sigma orbital , is represented by transition. For example, alkanes because in alkane all the atoms are held together with sigma bond.
b) Transition: Transitions from non-bonding molecular orbital to anti-bonding sigma orbital or anti-bonding pi orbital, are represented by transition respectively. These transition required less energy than transition. For example, alkyl halide, aldehydes, ketones etc.
c)Transition: This type of transition generally show in unsaturated molecules like alkenes, alkynes, aromatics, carbonyl compounds etc. This transition required less energy as compare to transition.
Absorption, intensity shift & UV spectrum:
a) Bathochromic shift: It is also known as Red shift, in this case absorption shift towards longer wavelength.
b) Hypsochromic shift: It is also known as Blue shift, in this case absorption shift towards shorter wavelength.
c) Hyperchromic shift: Intensity of absorption maximum increases.
d) Hypochromic shift: Intensity of absorption maximum decrease.
a) Transition: transition of an electron from bonding sigma orbital to anti-bonding sigma orbital , is represented by transition. For example, alkanes because in alkane all the atoms are held together with sigma bond.
b) Transition: Transitions from non-bonding molecular orbital to anti-bonding sigma orbital or anti-bonding pi orbital, are represented by transition respectively. These transition required less energy than transition. For example, alkyl halide, aldehydes, ketones etc.
c)Transition: This type of transition generally show in unsaturated molecules like alkenes, alkynes, aromatics, carbonyl compounds etc. This transition required less energy as compare to transition.

Absorption, intensity shift & UV spectrum:
a) Bathochromic shift: It is also known as Red shift, in this case absorption shift towards longer wavelength.
b) Hypsochromic shift: It is also known as Blue shift, in this case absorption shift towards shorter wavelength.
c) Hyperchromic shift: Intensity of absorption maximum increases.
d) Hypochromic shift: Intensity of absorption maximum decrease.
- The Wavelength of absorbed light provides the information on the energy gap which is related to the functional group.
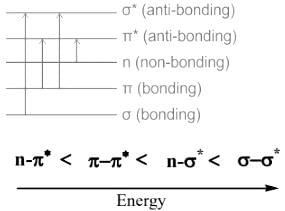
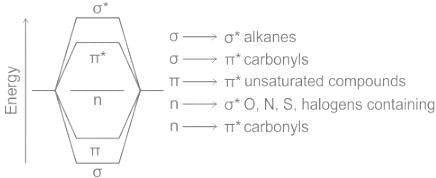
- The Possible Transitions of Organic Molecules in the UV-Spectroscopy is shown below:
- The UV spectra of organic compounds are generally collected from 200-700 nm.
- Electrons in the non-bonding orbital (n) are higher-energy than electrons in the bonding orbital.
- The transition from the non-bonding orbital (n) to the empty orbital requires less energy (ΔE) than the transition from the bonding orbital to the empty orbital (ΔE)
- The absorption maximum (λmax) at 275 nm corresponds to the n−π∗ transition.
- The absorption maximum (λmax) for the π−π∗ transition is at about 190 nm.
Hence, the absorption at λmax 279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due to n−π∗ transition.
Most Upvoted Answer
The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum...
A particular wavelength can be influenced by various factors, including the concentration of the absorbing substance, the path length of the light through the sample, and the presence of other substances that may interfere with the absorption. The absorption at a specific wavelength is typically measured using a spectrophotometer, which can provide information about the concentration of the absorbing substance in a sample. By comparing the absorption at different wavelengths, scientists can determine the unique absorption spectrum of a particular substance, which can be used for identification and quantification purposes.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Similar UGC NET Doubts
The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UGC NET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UGC NET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The absorption atλmax279 nm (ε = 15) in the UV spectrum of acetone is due toa)π−π∗ transitionb)n−π∗ transitionc)σ−σ∗ transitiond)π−σ∗ transitionCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UGC NET tests.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























