UPSC Exam > UPSC Questions > The color of the sun appears reddish during s...
Start Learning for Free
The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.
Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?
- a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphere
- b)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the day
- c)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particles
- d)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the day
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the follow...
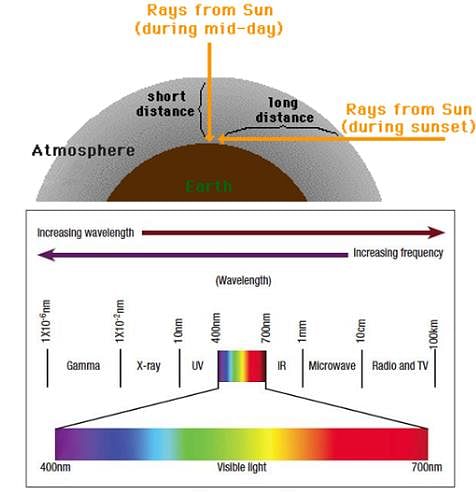
- As sunlight travels through the earth’s atmosphere, it gets scattered (changes its direction) by the atmospheric particles. Light of shorter wavelengths is scattered much more than light of longer wavelengths. (The amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. This is known as Rayleigh scattering). At sunset or sunrise, the sun’s rays have to pass through a larger distance in the atmosphere. Most of the blue and other shorter wavelengths are removed by scattering. The least scattered light reaching our eyes, therefore, the sun looks reddish. This explains the reddish appearance of the sun and full moon near the horizon.
- This is also the reason that the sky appears blue during the day, as blue has a shorter wavelength than red and is scattered much more strongly. In fact, violet gets scattered even more than blue, having a shorter wavelength. But since our eyes are more sensitive to blue than violet, we see the sky blue.
- Hence option (c) is the correct answer.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the follow...
Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particles:
The phenomenon of the sun appearing reddish during sunset is primarily due to the scattering of light rays by atmospheric particles. When the sun is low on the horizon during sunset, the sunlight has to pass through a thicker layer of Earth's atmosphere. This causes the shorter wavelengths of light, such as blue and green, to be scattered out of the direct line of sight, leaving mostly the longer wavelengths like red and orange to reach our eyes.
Explanation:
- As sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere, it interacts with air molecules and particles such as dust and water droplets.
- The shorter wavelengths of light (blue and green) are scattered more easily by these particles due to their shorter wavelengths.
- This scattering phenomenon is known as Rayleigh scattering, which is more pronounced for shorter wavelengths of light.
- During sunset, when the sun is closer to the horizon, the sunlight has to travel through a longer path in the atmosphere, leading to more scattering of shorter wavelengths.
- As a result, the longer wavelengths (red and orange) dominate the light reaching our eyes, giving the sun a reddish appearance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reddish color of the sun during sunset is mainly a result of the scattering of shorter wavelengths of light by atmospheric particles, allowing longer wavelengths to be more prominent in the light that reaches our eyes.
The phenomenon of the sun appearing reddish during sunset is primarily due to the scattering of light rays by atmospheric particles. When the sun is low on the horizon during sunset, the sunlight has to pass through a thicker layer of Earth's atmosphere. This causes the shorter wavelengths of light, such as blue and green, to be scattered out of the direct line of sight, leaving mostly the longer wavelengths like red and orange to reach our eyes.
Explanation:
- As sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere, it interacts with air molecules and particles such as dust and water droplets.
- The shorter wavelengths of light (blue and green) are scattered more easily by these particles due to their shorter wavelengths.
- This scattering phenomenon is known as Rayleigh scattering, which is more pronounced for shorter wavelengths of light.
- During sunset, when the sun is closer to the horizon, the sunlight has to travel through a longer path in the atmosphere, leading to more scattering of shorter wavelengths.
- As a result, the longer wavelengths (red and orange) dominate the light reaching our eyes, giving the sun a reddish appearance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reddish color of the sun during sunset is mainly a result of the scattering of shorter wavelengths of light by atmospheric particles, allowing longer wavelengths to be more prominent in the light that reaches our eyes.
Attention UPSC Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed UPSC study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in UPSC.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2024 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2024 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UPSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The color of the sun appears reddish during sunset.Which of the following is the reason behind this phenomenon?a)Absorption of light rays by the atmosphereb)Human eyes are not sensitive to other colors during that part of the dayc)Scattering of light rays by atmospheric particlesd)The sun emits different wavelengths of light during different times of the dayCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UPSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















