Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxida...
Start Learning for Free
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z?
Most Upvoted Answer
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular ...
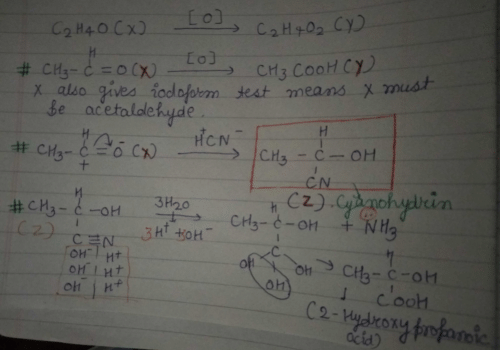
Community Answer
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular ...
Molecular Formula of X
----------------------
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O.
Oxidation of X to Y
--------------------
When X undergoes oxidation, it gives Y with a molecular formula of C2H4O2.
Iodofom Test
-------------
X gives a positive result for the iodofom test.
Reaction of X with HCN to form Z
--------------------------------
When X reacts with HCN, it gives Z.
Hydrolysis of Z to form 2-Hydroxypropanoic Acid
-----------------------------------------------
Z, upon hydrolysis, forms 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
Explanation of Z
-----------------
Z is formed when compound X reacts with HCN. The reaction between X and HCN is a nucleophilic addition reaction. In this reaction, the cyanide ion (CN-) acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom of X. The resulting intermediate undergoes hydrolysis to form Z.
Z is identified as 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. This compound is also known as lactic acid. It is a carboxylic acid with a hydroxyl group attached to the second carbon atom. The hydrolysis of Z involves breaking the bond between the carbon and the cyanide group, resulting in the formation of a carboxyl group (COOH) and a hydroxyl group (OH) on the second carbon atom.
The formation of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (Z) from X through the reaction with HCN and subsequent hydrolysis is a common method to synthesize lactic acid. Lactic acid is widely used in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. It is also an important intermediate in the production of biodegradable polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA).
In summary, X with the molecular formula C2H4O, upon oxidation, gives Y with the molecular formula C2H4O2. X also gives a positive result for the iodofom test. When X reacts with HCN, it forms Z, which is identified as 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid) upon hydrolysis.
----------------------
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O.
Oxidation of X to Y
--------------------
When X undergoes oxidation, it gives Y with a molecular formula of C2H4O2.
Iodofom Test
-------------
X gives a positive result for the iodofom test.
Reaction of X with HCN to form Z
--------------------------------
When X reacts with HCN, it gives Z.
Hydrolysis of Z to form 2-Hydroxypropanoic Acid
-----------------------------------------------
Z, upon hydrolysis, forms 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.
Explanation of Z
-----------------
Z is formed when compound X reacts with HCN. The reaction between X and HCN is a nucleophilic addition reaction. In this reaction, the cyanide ion (CN-) acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom of X. The resulting intermediate undergoes hydrolysis to form Z.
Z is identified as 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. This compound is also known as lactic acid. It is a carboxylic acid with a hydroxyl group attached to the second carbon atom. The hydrolysis of Z involves breaking the bond between the carbon and the cyanide group, resulting in the formation of a carboxyl group (COOH) and a hydroxyl group (OH) on the second carbon atom.
The formation of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (Z) from X through the reaction with HCN and subsequent hydrolysis is a common method to synthesize lactic acid. Lactic acid is widely used in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. It is also an important intermediate in the production of biodegradable polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA).
In summary, X with the molecular formula C2H4O, upon oxidation, gives Y with the molecular formula C2H4O2. X also gives a positive result for the iodofom test. When X reacts with HCN, it forms Z, which is identified as 2-hydroxypropanoic acid (lactic acid) upon hydrolysis.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z?
Question Description
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z?.
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z?.
Solutions for The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z?, a detailed solution for The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? has been provided alongside types of The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The molecular formula of X is C2H4O. On oxidation X gives Y molecular formula C2H4O2. X also give Iodofom test. On RXN with HCN X gives Z . Z on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. What is Z? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















