Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 he...
Start Learning for Free
Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light?
Most Upvoted Answer
Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light?
Balancing the Equation: C2H6 + O2 -> H2O + CO2 + heat and light
Introduction
The given equation represents the combustion of ethane (C2H6) in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), heat, and light. Balancing the equation ensures that the number of atoms on both sides of the equation is equal, indicating the conservation of mass.
Balancing the Equation
To balance the equation, we need to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides. Let's break it down step by step:
Carbon (C)
The left side of the equation has 2 carbon atoms from the ethane molecule (C2H6). To balance it, we need 1 carbon atom on the right side. Therefore, we add a coefficient of 2 in front of CO2:
C2H6 + O2 -> 2CO2 + H2O + heat and light
Hydrogen (H)
On the left side, there are 6 hydrogen atoms from the ethane molecule (C2H6). To balance it, we need 3 hydrogen atoms on the right side. Therefore, we add a coefficient of 3 in front of H2O:
C2H6 + O2 -> 2CO2 + 3H2O + heat and light
Oxygen (O)
On the left side, there are 2 oxygen atoms from the ethane molecule (C2H6), and 2 oxygen atoms from the oxygen molecule (O2). To balance it, we need 4 oxygen atoms on the right side. Therefore, we add a coefficient of 2 in front of O2:
C2H6 + 2O2 -> 2CO2 + 3H2O + heat and light
Explanation
The balanced equation now represents the combustion of ethane (C2H6) with oxygen (O2) to form carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), heat, and light. This reaction is highly exothermic, meaning it releases energy in the form of heat and light.
During the combustion process, ethane (C2H6) reacts with oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The heat and light energy are released due to the breaking and formation of chemical bonds. The reaction is considered a combustion reaction as it involves the rapid oxidation of a hydrocarbon fuel (ethane) in the presence of oxygen.
The balanced equation shows that for every 1 molecule of ethane, 2 molecules of carbon dioxide and 3 molecules of water are formed. The coefficients indicate the ratio of reactants and products in the reaction.
In summary, balancing the equation ensures the conservation of mass and provides a clear representation of the reactants and products involved in the combustion of ethane.
Community Answer
Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light?
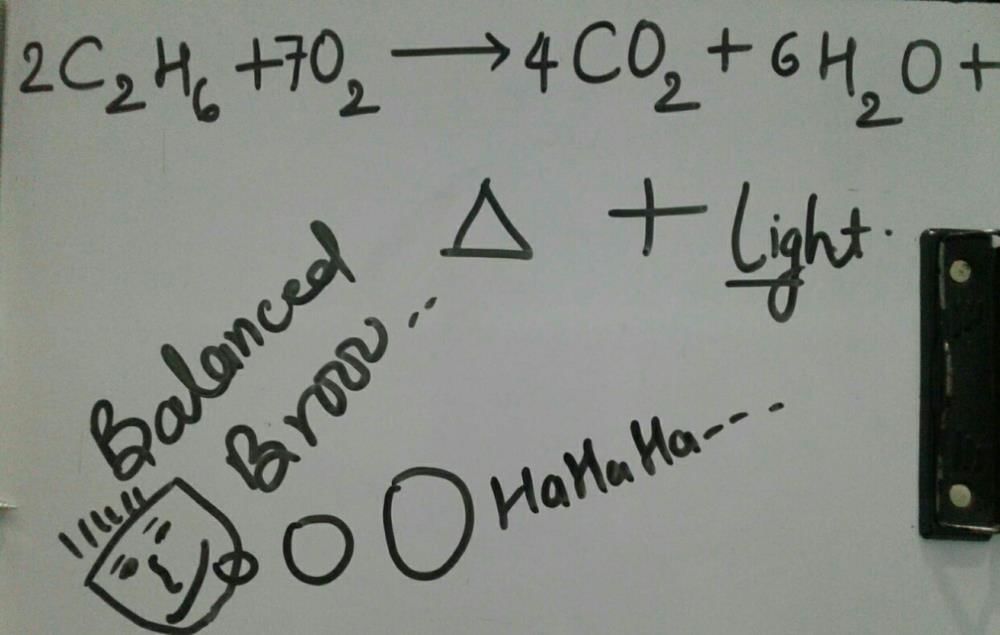

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light?
Question Description
Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light?.
Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light?.
Solutions for Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light?, a detailed solution for Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? has been provided alongside types of Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Balance the equation C2H6 O2. -> H2O CO2 heat and light? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























