Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > An impulse is applied to a moving object with...
Start Learning for Free
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is
- a)120o
- b)0o
- c)60o
- d)240o
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of...
The product of average force and the time it is exerted is called the impulse of force. From Newton's second law
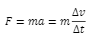
The impulse of force can be extracted and found to be equal to the change in momentum of an object provided the mass is constant:
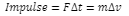
The change in momentum is in the same direction as the applied impulse.
Thus, angle between themis 0degree.
View all questions of this test
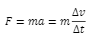
The impulse of force can be extracted and found to be equal to the change in momentum of an object provided the mass is constant:
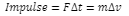
The change in momentum is in the same direction as the applied impulse.
Thus, angle between themis 0degree.
Most Upvoted Answer
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of...
The impulse-momentum theorem and the angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector
The impulse-momentum theorem states that the change in momentum of an object is equal to the impulse applied to it. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
Δp = J
Where Δp represents the change in momentum and J represents the impulse.
Understanding the given scenario
In the given scenario, an impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector. This means that the force is not in the same direction as the velocity vector. Let's analyze the situation step by step to determine the angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector.
The change in momentum vector
The change in momentum vector can be calculated by subtracting the initial momentum vector from the final momentum vector.
Δp = pf - pi
Since the object is already moving, it has an initial momentum vector pi. The impulse is applied, resulting in a change in momentum Δp. The object's final momentum vector pf can be calculated by adding the initial momentum vector and the change in momentum vector.
The impulse vector
The impulse vector can be calculated using the equation:
J = F * Δt
Where F represents the force applied and Δt represents the time interval over which the force is applied.
In this scenario, the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector. Therefore, the impulse vector can be broken down into two components: one along the direction of the velocity vector and one perpendicular to it.
The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector
Since the impulse vector has two components, one along the direction of the velocity vector and one perpendicular to it, the change in momentum vector can also be broken down into two components along the same directions.
The component of the change in momentum vector along the direction of the velocity vector is responsible for changing the speed of the object, while the component perpendicular to the velocity vector is responsible for changing the direction of the object's velocity.
In this scenario, the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector. Since the impulse vector and the force vector are in the same direction, the component of the impulse vector along the direction of the velocity vector will be equal to the component of the force vector along the direction of the velocity vector.
Since the angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is the same as the angle between the force vector and the velocity vector, which is 0°, the correct answer is option B) 0°.
The impulse-momentum theorem states that the change in momentum of an object is equal to the impulse applied to it. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
Δp = J
Where Δp represents the change in momentum and J represents the impulse.
Understanding the given scenario
In the given scenario, an impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector. This means that the force is not in the same direction as the velocity vector. Let's analyze the situation step by step to determine the angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector.
The change in momentum vector
The change in momentum vector can be calculated by subtracting the initial momentum vector from the final momentum vector.
Δp = pf - pi
Since the object is already moving, it has an initial momentum vector pi. The impulse is applied, resulting in a change in momentum Δp. The object's final momentum vector pf can be calculated by adding the initial momentum vector and the change in momentum vector.
The impulse vector
The impulse vector can be calculated using the equation:
J = F * Δt
Where F represents the force applied and Δt represents the time interval over which the force is applied.
In this scenario, the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector. Therefore, the impulse vector can be broken down into two components: one along the direction of the velocity vector and one perpendicular to it.
The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector
Since the impulse vector has two components, one along the direction of the velocity vector and one perpendicular to it, the change in momentum vector can also be broken down into two components along the same directions.
The component of the change in momentum vector along the direction of the velocity vector is responsible for changing the speed of the object, while the component perpendicular to the velocity vector is responsible for changing the direction of the object's velocity.
In this scenario, the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector. Since the impulse vector and the force vector are in the same direction, the component of the impulse vector along the direction of the velocity vector will be equal to the component of the force vector along the direction of the velocity vector.
Since the angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is the same as the angle between the force vector and the velocity vector, which is 0°, the correct answer is option B) 0°.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of...
The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector can be determined by understanding the definitions of impulse and momentum, as well as their relationship to each other.
1. Impulse:
- Impulse is the product of force and time. It represents the change in momentum of an object.
- Mathematically, impulse (J) is given by the equation J = F * Δt, where F is the force applied and Δt is the time interval over which the force is applied.
2. Momentum:
- Momentum is the product of an object's mass and its velocity. It represents the quantity of motion possessed by the object.
- Mathematically, momentum (p) is given by the equation p = m * v, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
3. Relationship between impulse and momentum:
- The impulse experienced by an object is equal to the change in its momentum.
- Mathematically, this can be expressed as J = Δp, where J is the impulse and Δp is the change in momentum.
To determine the angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector, we need to consider the given information that the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector.
4. Impulse vector:
- The impulse vector can be represented as J = F * Δt, where F is the force vector and Δt is the time interval vector.
- Since the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector, the impulse vector will also be at the same angle with the velocity vector.
5. Change in momentum vector:
- The change in momentum vector can be represented as Δp = m * Δv, where m is the mass vector and Δv is the change in velocity vector.
- As the object is already moving, the change in velocity vector will be in the same direction as the velocity vector.
- Therefore, the change in momentum vector will also be in the same direction as the velocity vector.
6. Angle between impulse vector and change in momentum vector:
- Since both the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector are in the same direction as the velocity vector, their angle will be 0°.
- This means that the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector are parallel to each other.
Hence, the correct answer is option B) 0°.
1. Impulse:
- Impulse is the product of force and time. It represents the change in momentum of an object.
- Mathematically, impulse (J) is given by the equation J = F * Δt, where F is the force applied and Δt is the time interval over which the force is applied.
2. Momentum:
- Momentum is the product of an object's mass and its velocity. It represents the quantity of motion possessed by the object.
- Mathematically, momentum (p) is given by the equation p = m * v, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
3. Relationship between impulse and momentum:
- The impulse experienced by an object is equal to the change in its momentum.
- Mathematically, this can be expressed as J = Δp, where J is the impulse and Δp is the change in momentum.
To determine the angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector, we need to consider the given information that the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector.
4. Impulse vector:
- The impulse vector can be represented as J = F * Δt, where F is the force vector and Δt is the time interval vector.
- Since the force is applied at an angle of 120° with the velocity vector, the impulse vector will also be at the same angle with the velocity vector.
5. Change in momentum vector:
- The change in momentum vector can be represented as Δp = m * Δv, where m is the mass vector and Δv is the change in velocity vector.
- As the object is already moving, the change in velocity vector will be in the same direction as the velocity vector.
- Therefore, the change in momentum vector will also be in the same direction as the velocity vector.
6. Angle between impulse vector and change in momentum vector:
- Since both the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector are in the same direction as the velocity vector, their angle will be 0°.
- This means that the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector are parallel to each other.
Hence, the correct answer is option B) 0°.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An impulse is applied to a moving object with the force at an angle of 120o with the velocity vector. The angle between the impulse vector and the change in momentum vector is a)120ob)0oc)60od)240oCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























