Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > What compound is produced when cyclohexene is...
Start Learning for Free
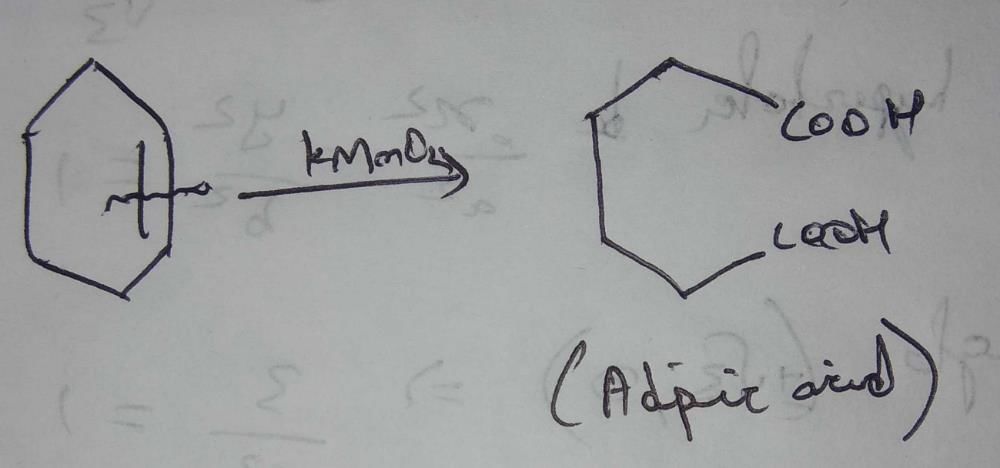
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?
- a)adipic acid
- b)succinic acid
- c)hexanoic acid
- d)cyclohexanecarboxylic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrate...
Conc KMnO4 will cause oxidation and ring opening forming adipic acid.
Most Upvoted Answer
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrate...
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrate...
Cyclohexene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H10. When it is treated with concentrated potassium permanganate (KMnO4), a chemical reaction called oxidative cleavage occurs. This reaction breaks the double bond in cyclohexene and forms two carboxylic acid groups on each side of the double bond.
Here is a detailed explanation of the reaction and the compound produced:
Oxidative Cleavage Reaction:
The reaction between cyclohexene and concentrated KMnO4 is an example of oxidative cleavage. In this reaction, the double bond in cyclohexene is cleaved, and two new carbon-carbon single bonds are formed. The oxygen atoms from KMnO4 are added to the carbons previously involved in the double bond, resulting in the formation of carboxylic acid groups.
Steps of the Reaction:
1. The double bond in cyclohexene attacks one of the oxygen atoms in KMnO4, resulting in the formation of a cyclic intermediate.
2. The cyclic intermediate is then hydrolyzed by water, leading to the formation of two carboxylic acid groups.
3. The potassium permanganate is reduced in the process and changes color from purple to brown.
Compound Produced:
The compound produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4 is adipic acid (option A). Adipic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the molecular formula C6H10O4. It has two carboxylic acid groups (-COOH) attached to a hexane chain. Adipic acid is used in the production of nylon, polyurethane, and other polymers.
Overall Reaction Equation:
The overall reaction equation for the reaction between cyclohexene and concentrated KMnO4 can be represented as follows:
C6H10 + 2KMnO4 + 3H2O → C6H10O4 + 2MnO2 + 2KOH
In this equation, the cyclohexene is oxidized to adipic acid, and KMnO4 is reduced to MnO2.
Here is a detailed explanation of the reaction and the compound produced:
Oxidative Cleavage Reaction:
The reaction between cyclohexene and concentrated KMnO4 is an example of oxidative cleavage. In this reaction, the double bond in cyclohexene is cleaved, and two new carbon-carbon single bonds are formed. The oxygen atoms from KMnO4 are added to the carbons previously involved in the double bond, resulting in the formation of carboxylic acid groups.
Steps of the Reaction:
1. The double bond in cyclohexene attacks one of the oxygen atoms in KMnO4, resulting in the formation of a cyclic intermediate.
2. The cyclic intermediate is then hydrolyzed by water, leading to the formation of two carboxylic acid groups.
3. The potassium permanganate is reduced in the process and changes color from purple to brown.
Compound Produced:
The compound produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4 is adipic acid (option A). Adipic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the molecular formula C6H10O4. It has two carboxylic acid groups (-COOH) attached to a hexane chain. Adipic acid is used in the production of nylon, polyurethane, and other polymers.
Overall Reaction Equation:
The overall reaction equation for the reaction between cyclohexene and concentrated KMnO4 can be represented as follows:
C6H10 + 2KMnO4 + 3H2O → C6H10O4 + 2MnO2 + 2KOH
In this equation, the cyclohexene is oxidized to adipic acid, and KMnO4 is reduced to MnO2.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What compound is produced when cyclohexene is treated with concentrated KMnO4?a)adipic acidb)succinic acidc)hexanoic acidd)cyclohexanecarboxylic acidCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















