NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Anatomy of Flowering Plants | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Find the statement that is NOT correct with regard to the structure of monocot stem. (NEET 2025)
(a) Vascular bundles are conjoint and closed.
(b) Phloem parenchyma is absent.
(c) Hypodermis is parenchymatous.
(d) Vascular bundles are scattered.
Ans: (c)
- The monocot stem has a sclerenchymatous hypodermis, a large number of scattered vascular bundles, each surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath, and a large, conspicuous parenchymatous ground tissue
- Vascular bundles are conjoint and closed.
- Peripheral vascular bundles are generally smaller than the centrally located ones.
- The phloem parenchyma is absent, and water-containing cavities are present within the vascular bundles.
2024
Q1: Bulliform cells are responsible for (NEET 2024)
(a) Inward curling of leaves in monocots.
(b) Protecting the plant from sall stress.
(c) Increased photosynthesis in monocots.
(d) Providing large spaces for storage of sugars.
Ans: (a)
Sol: Bulliform cells, which are specialized cells found in the leaves of many monocot plants such as grasses, play a crucial role in responding to environmental stress conditions like water scarcity. Their primary function is associated with the mechanism of leaf folding or rolling during drought or high temperature conditions. This adaptive feature helps in reducing the leaf surface exposed to the air, thereby minimizing water loss through transpiration.
Now, let’s evaluate each option in relation to the role of bulliform cells:
Option A: Inward curling of leaves in monocots.
This option is correct. Bulliform cells are large, thin-walled, and filled with water. When these cells lose water under dry conditions, they collapse, causing the leaf to fold or roll inward. This curling mechanism helps to reduce the exposure of the surface area of the leaf to the harsh environment, thus reducing water loss and protecting the plant during drought.
Option B: Protecting the plant from salt stress.
This option is not correct. While bulliform cells are involved in protecting the plant by reducing transpiration, their role specifically in protecting from salt stress isn't well-documented. Salt stress protection involves other physiological and biochemical responses in plants.
Option C: Increased photosynthesis in monocots.
This is also incorrect. Bulliform cells do not directly influence photosynthesis rates. Their function is mainly related to the mechanical folding of the leaf, which indirectly may influence photosynthetic efficiency under stress conditions but is not their primary role.
Option D: Providing large spaces for storage of sugars.
This option is incorrect. Bulliform cells are not involved in the storage of sugars. Their structure and function are geared towards managing water content for leaf folding mechanisms, rather than nutrient storage.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option A: Inward curling of leaves in monocots.
Q2: In the given figure, which component has thin outer walls and highly thickened inner walls? (NEET 2024)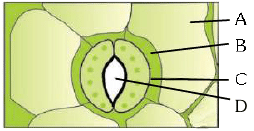 (a) C
(a) C
(b) D
(c) A
(d) B
Ans: (a)
Guard cells to stomata have thin outer wall and highly thickened inner walls.
Q3: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Parenchyma is living but collenchyma is dead tissue.
Statement II: Gymnosperms lack xylem vessels but presence of xylem vessels is the characteristic of angiosperms.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
(b) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(c) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
Ans: (c)
Statement I: Parenchyma is living but collenchyma is dead tissue.
This statement is False. Both parenchyma and collenchyma are living tissues; however, collenchyma has thickened cell walls that provide support.
Statement II: Gymnosperms lack xylem vessels but presence of xylem vessels is the characteristic of angiosperms.
This statement is True. Gymnosperms primarily have tracheids for water conduction, while angiosperms possess xylem vessels, which are more efficient for water transport.
The correct answer is (c) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
Q4: Arrange them in correct sequence starting from the periphery to the centre: (NEET 2024)
A. Endodermis
B. Pith
C. Epidermis
D. Pericycle
E. Cortex
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D, C, E, A, B
(b) A, C, E, B, D
(c) C, E, A, D, B
(d) C, E, D, B, A
Ans: (c)
In a monocot root, the internal tissue layers from the outside (periphery) to inside (center) are arranged in the following order:
- C. Epidermis – The outermost single layer of cells.
- E. Cortex – Located just beneath the epidermis, made of parenchyma.
- A. Endodermis – Innermost layer of cortex, regulates movement into the vascular cylinder.
- D. Pericycle – Thin layer of cells just inside the endodermis; gives rise to lateral roots.
- B. Pith – Central region, made up of parenchyma, prominent in monocot roots.
Thus, the correct sequence is: C (Epidermis) → E (Cortex) → A (Endodermis) → D (Pericycle) → B (Pith)
Hence, Option (c) is correct.
Q5: The given figure, with reference to the anatomy of plants, represents: (NEET 2024)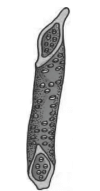 (a) Tracheid
(a) Tracheid
(b) Xylem fibre
(c) Xylem parenchyma
(d) Vessel
Ans: (d)
The figure represents a Vessel (d). Vessels are specialized structures in angiosperms for efficient water transport, distinct from tracheids found in gymnosperms.
Q6: Read the following statements and find out the correct set of statements: (NEET 2024)
A. Companion cells help in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
B. Gymnosperms lack vessels in their xylem
C. The xylem vessels are devoid of cytoplasm
D. Xylem fibres may be septate or aseptate
E. A mature sieve element in phloem possesses cytoplasm, vacuole and nucleus.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, D, E only
(b) A, B, D, E only
(c) A, B, C, D only
(d) C, D, E only
Ans: (c)
- A: True - Companion cells assist in maintaining the pressure gradient in sieve tubes.
- B: True - Gymnosperms do lack vessels in their xylem.
- C: True - Xylem vessels are devoid of cytoplasm at maturity.
- D: True - Xylem fibers may be septate or aseptate.
- E: False - A mature sieve element in phloem does not possess a nucleus.
Q7: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: In collenchyma, cell walls are thickened at corners due to deposition of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin.
Statement II: Sclerenchyma consists of lignified cell walls and possesses pits.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
(c) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(d) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
Ans: (a)
Statement I: In collenchyma, cell walls are thickened at corners due to deposition of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin.
This statement is True. Collenchyma provides flexible support due to its thickened corners.
Statement II: Sclerenchyma consists of lignified cell walls and possesses pits.
This statement is True. Sclerenchyma provides structural support with its lignified walls and pits for water movement.
The correct answer is (a) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
Q8: Which of the following simple tissues are commonly found in the fruit walls of nuts and pulp of pear? (NEET 2024)
(a) Sclereids
(b) Fibres
(c) Parenchyma
(d) Collenchyma
Ans: (a)
Sclereids are a type of sclerenchyma cells known for their thick, lignified walls that make plant parts hard and gritty. They are commonly found in the hard shells of nuts and the gritty texture of pear pulp. These cells provide mechanical support and protection.
Q9: Which of the following helps in maintenance of the pressure gradient in sieve tubes? (NEET 2024)
(a) Albuminous cells
(b) Sieve cells
(c) Phloem parenchyma
(d) Companion cells
Ans: (d)
Companion cells are closely associated with sieve tube elements in angiosperms. They assist in loading and unloading of sugars into the sieve tubes, helping in the maintenance of osmotic pressure and the pressure gradient essential for phloem transport (mass flow hypothesis).
They play a crucial role in the functioning and survival of sieve tube elements, which lack nuclei and rely on companion cells for many functions.
Q10: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: In a dicotyledonous leaf, the adaxial epidermis generally bears more stomata than the abaxial epidermis.
Statement II: In a dicotyledonous leaf, the adaxially placed palisade parenchyma is made up of elongated cells, which are arranged vertically and parallel to each other.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
Ans: (b)
Statement I: In dicot leaves, stomata are usually more numerous on the abaxial (lower) epidermis, not the adaxial (upper) one. However, in some plants adapted to dry conditions, the reverse may occur. But generally, this statement is incorrect.
Statement II: The palisade parenchyma cells are elongated and arranged vertically, allowing maximum light absorption for photosynthesis, and they are located adaxially (towards the upper side). This is correct.
Thus, only Statement II is correct.
2023
Q1: Given below are two statements : (NEET 2023)
Statement I : Endarch and exarch are the terms often used for describing the position of secondary xylem in the plant body.
Statement II : Exarch condition is the most common feature of the root system.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true
Ans: (d)
- Statement I : Endarch and exarch are the terms often used for describing the position of secondary xylem in the plant body.
- This statement is incorrect. Endarch and exarch are used to describe the developmental sequence of primary xylem, not secondary xylem. In endarch condition, the first formed xylem is towards the centre (protoxylem) and the last formed xylem is towards the periphery (metaxylem), which is typical of stems. In the exarch condition, the first formed xylem is towards the periphery and the last formed xylem is towards the centre, which is typical of roots.
- Statement II : Exarch condition is the most common feature of the root system.
- This statement is true. The exarch condition, where the first-formed xylem is towards the periphery and the last-formed xylem is towards the centre, is indeed the most common feature of the root system.
Q2: Identify the correct statements: (NEET 2023)
A. Lenticels are the lens-shaped openings permitting the exchange of gases.
B. Bark formed early in the season is called hard bark.
C. Bark is a technical term that refers to all tissues exterior to vascular cambium.
D. Bark refers to periderm and secondary phloem.
E. Phellogen is single-layered in thickness.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B and C only
(b) B, C and E only
(c) A and D only
(d) A, B and D only
Ans: (c)
A. True. Lenticels are indeed lens-shaped structures found in the bark of woody plants that facilitate gas exchange.
B. False. Bark formed early in the season is typically referred to as "soft bark," not hard bark.
C. True. Bark encompasses all tissues outside the vascular cambium, including periderm and secondary phloem.
D. True. Bark specifically refers to the periderm (outer bark) and the secondary phloem (inner bark).
E. False. Phellogen, or cork cambium, can be more than a single layer, depending on the plant species.
Q3: The transverse section of plant part showed polyarch, radial and exarch xylem, with endodermis and pericycle. The plant part is identified as: (NEET 2023)
(a) Monocot root
(b) Dicot root
(c) Dicot stem
(d) Monocot stem
Ans: (a)
(a) True. Monocot roots typically exhibit polyarch xylem arrangements and have a distinct endodermis and pericycle.
(b) False. Dicot roots usually have fewer than six xylem bundles and do not exhibit polyarch arrangements.
(c) False. Dicot stems have a different vascular arrangement and do not show polyarch xylem.
(d) False. Monocot stems do not typically have polyarch xylem; they have scattered vascular bundles.
Q4: Consider the following tissues in the stellar region of a stem showing secondary growth: (NEET 2023)
A. Primary xylem
B. Secondary xylem
C. Primary phloem
D. Secondary phloem
Arrange these in the correct sequence of their position from pith towards cortex:
(a) A, B, D, C
(b) B, A, C, D
(c) A, B, C, D
(d) B, A, D, C
Ans: (a)
(a) A, B, D, C: This is the correct sequence. Starting from the pith, you have primary xylem (A) closest to the center, followed by secondary xylem (B), then secondary phloem (D), and finally primary phloem (C) towards the outer layer. This arrangement reflects the typical structure of a dicot stem where secondary growth leads to the formation of secondary xylem and phloem.
(b) B, A, C, D: This sequence is incorrect. It suggests that secondary xylem (B) is closest to the pith, followed by primary xylem (A), which is not accurate as primary xylem is formed first during primary growth.
(c) A, B, C, D: This sequence is also incorrect. While it correctly places primary xylem (A) and secondary xylem (B) in order, it incorrectly positions primary phloem (C) before secondary phloem (D), which is not how they are arranged in a mature dicot stem.
(d) B, A, D, C: This sequence is incorrect as well. It incorrectly places secondary xylem (B) before primary xylem (A) and also misplaces the phloem types, suggesting a structure that does not exist in typical dicotyledonous stems.
Understanding the arrangement of these tissues is crucial for comprehending how dicotyledonous plants grow and develop, especially in terms of their vascular system and secondary growth capabilities.
2022
Q1: Read the following statements about the vascular bundles: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) In roots, the xylem and phloem in a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate manner along the different radii.
(b) Conjoint closed vascular bundles do not possess cambium.
(c) In open vascular bundles, cambium is present in between xylem and phloem
(d) The vascular bundles of dicotyledonous stem possess endarch protoxylem
(e) In the monocotyledonous root, usually there are more than six xylem bundles present
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (b), (c), (d) and (e) Only
(b) (a), (b), (c), (d) and (e)
(c) (a), (c), (d) and (e) Only
(d) (a), (b) and (d) Only
Ans: (b)
Statement a:
In roots, the xylem and phloem in a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate manner along the different radii.
Statement b:
Conjoint closed vascular:
- Xylem and phloem are jointly situated along the same radius of vascular bundles as in stems and leaves.
- The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the phloem located only on the outer side of the xylem.
- Cambium is absent.
Statement c:
- Cambium is present between the phloem and the xylem in open vascular bundles.
- They have the ability to form secondary xylem and phloem tissues due to the presence of cambium. Example: Secondary xylem and phloem tissues.
Statement d:
Endarch: the protoxylem lies towards the center (pith) and the metaxylem lies towards the periphery of the organ. Example: dicotyledonous stem
Statement e:
As compared to the dicot root which has fewer xylem bundles, there are usually more than six (polyarch) xylem bundles in the monocot root.
Q2: Initiation of lateral roots and vascular cambium during secondary growth takes place in cells of (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Pericycle
(b) Epiblema
(c) Cortex
(d) Endodermis
Ans: (a)
Initiation of lateral roots and vascular cambium during secondary growth takes place in pericycle cells of dicot roots. Epiblema, endodermis and cortex do not dedifferentiate.
2021
Q1: Match List I with List II (NEET 2021)
Select the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(a) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(b) (iii) (ii) (iv) (i)
(c) (ii) (iv) (i) (iii)
(d) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
Ans: (c)
(a) Meristematic tissues are those tissues which have cells with active cell division capacity.
(b) Simple tissues are those tissues which have all the cells similar in structure and function.
(c) Vascular tissues are complex permanent tissues hence they have different types of cells.
(d) Sclereids are sclerenchymatous cells which are dead with highly thickened walls and narrow lumen.
Q2: Select the correct pair. (NEET 2021)
(a) Cells of medullary rays that form part of a cambial ring - Interfascicular cambium
(b) Loose parenchyma cells rupturing the epidermis and forming a lens-shaped opening in the bark - Spongy parenchyma
(c) Large colourless empty cells in the epidermis of grass leaf - Subsidiary cells
(d) In dicot leaves, vascular bundles are surrounded tissue by large thick-walled cells - Conjunctive tissue
Ans: (a)
- When the cells of medullary rays differentiated, they give rise to the new cambium called interfascicular cambium.
- Loose parenchyma cells rupturing the epidermis and forming a lens-shaped opening in bark are called complementary cells.
- Large colorless empty cells in the epidermis of grass leaves are called bulliform cells.
- In dicot leave, vascular bundles are surrounded by large thick walled cells called bundle sheath cells.
2020
Q1: The transverse section of a plant shows the following anatomical features: (NEET 2020)
(i) a Large number of scattered vascular bundles surrounded by bundle sheath.
(ii) Large conspicuous parenchymatous ground tissue.
(iii) Vascular bundles conjoint and closed.
(iv) Phloem parenchyma absent.
Identify the category of plant and its part:
(a) Dicotyledonous stem
(b) Dicotyledonous root
(c) Monocotyledonous stem
(d) Monocotyledonous root
Ans: (c)
The monocot stem is characterised by conjoint, collateral, and closed vascular bundles, scattered in the ground tissue containing the parenchyma. Each vascular bundle is surrounded by sclerenchymatous bundle-sheath cells. Phloem parenchyma and medullary rays are absent in monocot stems.
2018
Q1: Stomata in grass leaf are (NEET 2018)
(a) Dumb-bell shaped
(b) Kidney-shaped
(c) Rectangular
(d) Barrel-shaped
Ans: (a)
Grass being a monocot, has Dumb-bell shaped stomata in their leaves.
Q2: Secondary xylem and phloem in dicot stem are produced by (NEET 2018)
(a) Apical meristems
(b) Vascular cambium
(c) Phellogen
(d) Axillary meristems
Ans: (b)
The cells of vascular cambium cut off towards pith, mature into secondary xylem and the cells cut off towards periphery mature into secondary phloem during secondary growth in dicot stem.
Q3: Casparian strips occur in (NEET 2018)
(a) Epidermis
(b) Pericycle
(c) Cortex
(d) Endodermis.
Ans: (d)
Endodermis have casparian strips on radial and inner tangential wall. It is rich in suberin.
Q4: Plants having little or no secondary growth are (NEET 2018)
(a) Grasses
(b) Deciduous angiosperms
(c) Conifers
(d) Cycads.
Ans: (a)
Grasses are monocots and monocots usually do not have secondary growth.
Palm like monocots have anomalous secondary growth
2017
Q1: The vascular cambium normally gives rise to (NEET 2017)
(a) Primary phloem
(b) Secondary xylem
(c) Periderm
(d) Phelloderm.
Ans: (b)
Cells of vascular cambium divide periclinally both on the outer and inner sides to form secondary permanent tissues, i.e., secondary xylem and secondary phloem.
2016
Q1: Cortex is the region found between (NEET 2016)
(a) Epidermis and stele
(b) Pericycle and endodermis
(c) Endodermis and pith
(d) Endodermis and vascular bundle.
Ans: (a)
In botanical terms, the cortex of a plant is the region found between the epidermis and the stele. Therefore, the correct answer is:
Option (a) : Epidermis and stele.
To clarify:
- Epidermis: This is the outermost layer of cells in the plant stem and root. It serves as a protective barrier against the external environment.
- Stele: This is the central part of the root or stem, containing the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), pith, and often a pericycle. The stele is located inside the endodermis.
- The cortex lies between these two layers, functioning mainly in storage and transport of nutrients and water. It is composed primarily of parenchyma cells and is a significant part of the root and stem where it often stores starch.
The other options refer to different parts of the plant anatomy:
- Option C: "Endodermis and pith" - The pith is located in the center of the stem, surrounded by the vascular tissue, which is inside the endodermis. The cortex is not between these two.
- Option D: "Endodermis and vascular bundle" - The endodermis is a single layer of cells forming a boundary between the cortex and the stele; it doesn't define the boundaries of the cortex.
- Option B: "Pericycle and endodermis" - The pericycle is a layer of cells found just inside the endodermis, and it is part of the stele. This option does not correctly describe the position of the cortex.
Thus, Option A is the most accurate in describing the location of the cortex in a plant.
Q2: Specialized epidermal cells surrounding the guard cells are called (NEET 2016)
(a) Bulliform cells
(b) Lenticels
(c) Complementary cells
(d) Subsidiary cells.
Ans: (d)
Specialized epidermal cells surrounding the guard cells are known as Subsidiary or accessory cell.
2015
Q1: Vascular bundles in monocotyledons are considered closed because: (NEET 2015)
(a) Cambium is absent
(b) There are no vessels with perforations
(c) Xylem is surrounded all around by phloem
(d) A bundle sheath surrounds each bundle
Ans: (a)
Vascular bundles in monocotyledons are considered as closed because cambium is absent in the vascular system and thus they lack secondary growth in the thickness.
2014
Q1: You are given a fairly old piece of dicot stem and a dicot root. Which of the following anatomical structures will you use to distinguish between the two? (NEET 2014)
(a) Secondary xylem
(b) Secondary phloem
(c) Protoxylem
(d) Cortical cells
Ans: (c)
The anatomically fairly old dicotyledonous root is distinguished from the dicotyledonous stem by position of protoxylem. In dicot root the protoxylem is located near the periphery of the vascular cylinder while in dicot stem the protoxylem is located near the centre of vascular bundle i.e., the xylem is endarch.
|
169 videos|531 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Biology Class 11
| 1. What are the main parts of a flowering plant? |  |
| 2. What is the function of flowers in flowering plants? |  |
| 3. How do flowering plants reproduce? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the anatomy of flowering plants? |  |
| 5. What are some common types of flowering plants studied in NEET? |  |

















