UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > History Optional for UPSC > Ancient Ports
Ancient Ports | History Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Bhagatrav
Bharuch District, Gujarat:- Historical Significance: Bharuch district is an important site from the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Harappan Period: During this time, Bharuch was a significant port.
- Decline of Settlement: Evidence suggests that the decline of the Harappan settlement in this area was due to flooding.
Bhrigukachha
Bharuch Port:- Bharuch district, Gujarat.
- Port at the mouth of the Narmada River.
- Ancient center of trade and shipbuilding.
- Trade route to the west utilized monsoon winds.
- Goods from the Far East used this port for land-sea trade routes.
- Known to Greeks, Romans, and other western civilizations.
- Arab traders entered Gujarat via Bharuch.
- British and Dutch established business centers here.
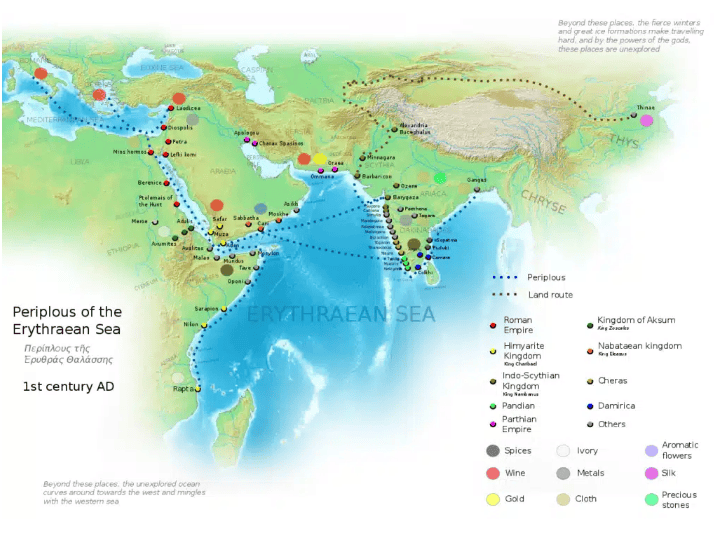
Muziris
- Ancient port located in Cranganore, Kerala, during the Chera kingdom in the Sangam Age.
- Known for trade with regions like Arabia, Rome, and Greece.
- Mentioned in Sangam literature and by Greek and Roman writers such as Pliny and the Periplus.
Exports from Muziris included:
- Spices
- Semi-precious stones
- Pearls
- Diamonds
- Sapphires
- Ivory
- Tortoise shells
Imports to Muziris included:
- Roman gold coins
- Figured linens
- Copper
- Tin
- Lead
- Coral
- Raw glass
- Wine
The Muziris Heritage Project was initiated by the Kerala government to preserve and promote the heritage of this ancient port.
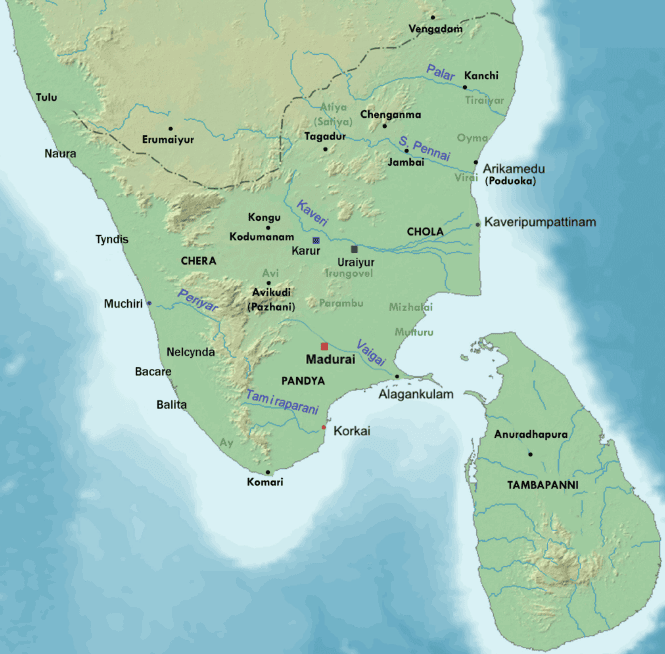
Puhar/ Pumpuhar/ Kaveripattinam (Lost Port)
Nagapattinam District, Tamil Nadu:- Sea port of the Cholas during the Sangam age.
- Centre of foreign trade.
- Capital of the early Chola kings.
- Located near the Kaveri River.
- Mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea and Silapathikaram.
- Medieval Chola coins found, indicating its continued importance as a port in later times.
- Ancient pottery discovered.
Arikamedu/ poduka
- Near Puducherry: Known as Poduka to the Romans.
- Famous port during the Sangam Age under Early Chola: Bead making facility and trading with Romans.
- Roman artifacts: Amphorae bearing the mark of Roman pottery, Roman lamps, glassware, and gems.
- Roman golden coins: Evidence that India received a lot of gold in return for her exports.
Tamralipti
Tamluk, located near the mouth of the Ganges in the Midnapur district of West Bengal, was a significant emporium of trade during ancient times.- Tamluk was connected to Taxila by both land and river, and it had maritime links with Southeast Asia.
- Antiquities from the Chalcolithic period and the Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW) phase have been found in the area, indicating its historical significance.
- The discovery of Roulette ware and red polished ware of Roman type suggests trade contact with the Roman Empire.
- Evidence of urban character is supported by findings of terracotta figurines, coins, and beads or semi-precious stones.
Lothal
In Ahmedabad District, Gujarat:Pre-Harappan Period: It was a small village.
- Became a center for harbor activities, cotton and rice cultivation, and bead-making industries.
- The city was divided into a citadel and a lower town.
- Buildings were constructed using fire-dried bricks, lime, and sand mortar. Evidence shows a sophisticated drainage system.
Important Archaeological Findings:
- Dockyard
- Seals from the Persian Gulf
- Shell ornaments maker’s shop
- Bead maker’s shop
- Metal worker’s shop
- Fire altars
- Terracotta figurine of a house
- Warehouse
- Merchant house
- Impression of cloth on seals
- Twelve bathrooms in the citadel area
- Ivory Scale: The smallest known decimal divisions in the Indus civilization.
- Connected to other cities via river routes.
Later Harappan culture:
Continued to be inhabited,
- Much smaller population
- Devoid of urban influences.
- Trade and resources of the city were almost gone,
- The people retained several Harappan ways in writing, pottery and utensils.
Sopara (Surparaka)
Thane District, Maharashtra:
- Known to ancient scholars like Ptolemy and the author of the Periplus.
- Functioned as a seaport and a hub of international trade.
- Renowned for artisanal production of swords, shoes, and other leather goods that were highly sought after in the western world.
- Site of a significant rock edict left by Ashoka.
- Remnants of a stupa have also been discovered here.
Masulipatnam (Machilipatnam)
- Overview of a historical town in the Krishna district of Andhra Pradesh, highlighting its significance during ancient times.
Historical Significance
- The town existed during the Satavahana period, which indicates its importance in ancient Indian history.
- It is mentioned by ancient historians and geographers such as Ptolemy and in The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, suggesting its significance in trade and commerce.
Trade and Commerce
- The town was known for trading muslin, a fine cotton fabric, which was highly valued by the ancient Greeks.
- It served as a settlement for European traders, including the English and Dutch, indicating its continued importance in trade during later periods.
Mamallapuram
Mahabalipuram in Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu is famous for its historical monuments. It was developed by Pallava kings Narsimhavarman Mamalla and Rajasimhavarman in the 7th century AD. The site includes cave temples, monolithic rathas, sculpted reliefs, and structural temples. Mahabalipuram is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.Some of the most famous monuments in Mahabalipuram are:
- Descent of the Ganges: This is a giant open-air rock relief that depicts the descent of the Ganges River.
- Pancha Rathas (Five Chariots): These are nine monolithic temples carved from a single large piece of granite stone. They are named after the five Pandava brothers from the Mahabharata.
- Shore Temple: This is a structural temple located along the Bay of Bengal, with its entrance facing west, away from the sea.
The Pallavas used the port at Mahabalipuram to launch trade and diplomatic missions to Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia.
Korkai
- The Pandyas were one of the three ancient Tamil dynasties, known for their pearl fishing and trade.
- They ruled over the southern part of India, including modern-day Tamil Nadu.
- The Pandyas had a rich cultural heritage, with contributions to literature, art, and architecture.
- They were also known for their maritime activities, trading with distant lands.
Archaeological Findings in Tirunelveli:
- Excavations in the Tirunelveli district, near the mouth of the Vaigai River, have revealed evidence of an early Pandya port.
- This port was famous for its pearls, as mentioned in ancient Sangam literature and Greek accounts.
Pearl Fishing Centre:
- The site is identified as an important pearl fishing center during ancient times, supported by excavation evidence and references in texts like the Arthashastra.
Pottery and Inscriptions:
- Archaeologists found black-red ware and locally made rouletted ware with Brahmi inscriptions dating from around 200 BCE to 200 CE.
The document Ancient Ports | History Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course History Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
367 videos|995 docs
|
FAQs on Ancient Ports - History Optional for UPSC
| 1. What were the significant ancient ports in India and their contributions to trade? |  |
Ans. Significant ancient ports in India included Lothal, Sopara, and Kaveripattinam. Lothal, part of the Indus Valley Civilization, was known for its dockyard that facilitated maritime trade with Mesopotamia. Sopara was an important trade center for exporting pearls and textiles. Kaveripattinam served as a crucial port for the Chola dynasty, enhancing trade in the South Indian region.
| 2. How did ancient ports influence cultural exchange in India? |  |
Ans. Ancient ports acted as melting pots for various cultures, facilitating the exchange of ideas, art, and religion. They attracted traders from different regions, leading to the spread of Buddhism and Hinduism to Southeast Asia. The interaction between local communities and foreign traders resulted in a rich blend of cultural practices, languages, and traditions.
| 3. What role did geography play in the establishment of ancient ports in India? |  |
Ans. Geography played a critical role in the establishment of ancient ports. Proximity to rivers and coastlines allowed for easy access to maritime routes. Natural harbors provided safe docking areas, while river systems enabled inland trade. For instance, the location of Lothal near the Gulf of Khambhat made it an ideal spot for maritime commerce.
| 4. What were the trade goods commonly exchanged through ancient Indian ports? |  |
Ans. Ancient Indian ports facilitated the exchange of various trade goods, including spices, textiles, gemstones, and metals. Cotton and silk textiles were highly sought after, along with spices like black pepper and cardamom. Additionally, goods such as ivory and pottery were traded, reflecting the diverse economic activities of ancient India.
| 5. How did the decline of ancient ports affect trade in India? |  |
Ans. The decline of ancient ports, due to factors such as changing trade routes, invasions, and natural disasters, significantly impacted trade in India. It led to a reduction in maritime commerce and the loss of economic prosperity in port cities. As trade shifted to newer routes, especially during the medieval period, many ancient ports became less significant, resulting in the decline of local economies.
Related Searches















