Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What is the primary function of the alveoli in the lungs?
(A) To produce oxygen
(B) To absorb water
(C) To exchange gases
(D) To filter blood
Solution: (C) To exchange gases
The alveoli are responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and the blood in the lungs.
2. Which of the following processes is involved in autotrophic nutrition?
(A) Absorption of complex food materials
(B) Breakdown of glucose in the cytoplasm
(C) Synthesis of carbohydrates from CO2 and water
(D) Breakdown of proteins into amino acids
Solution: (C) Synthesis of carbohydrates from CO2 and water
Autotrophic nutrition involves the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates using sunlight.
3. What is the role of guard cells in plants?
(A) To regulate the opening and closing of stomata
(B) To absorb water from the soil
(C) To perform photosynthesis
(D) To store food
Solution: (A) To regulate the opening and closing of stomata
Guard cells control the opening and closing of stomatal pores, regulating gas exchange and water loss in plants.
4. Which of the following is a waste product of aerobic respiration?
(A) Oxygen
(B) Glucose
(C) Carbon dioxide and water
(D) Lactic acid
Solution: (C) Carbon dioxide and water
Aerobic respiration breaks down glucose with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and a large amount of energy in the form of ATP.
5. What is the main function of the human heart?
(A) To produce oxygen
(B) To pump blood throughout the body
(C) To digest food
(D) To filter waste
Solution: (B) To pump blood throughout the body
The heart's primary function is to pump oxygenated blood to various organs and tissues, and deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Short Question/Answer (Q&A)
1. What is the role of enzymes in the digestion process?
Solution: Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up the breakdown of complex food molecules into simpler substances, allowing the body to absorb nutrients effectively.
2. How does the respiratory system in human beings help in gas exchange?
Solution: The respiratory system facilitates gas exchange by taking in oxygen through the lungs and expelling carbon dioxide from the body. Oxygen enters the blood in the alveoli, and carbon dioxide is removed during exhalation.
3. Explain the importance of chlorophyll in photosynthesis.
Solution: Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight, which is essential for the process of photosynthesis. It helps convert light energy into chemical energy, which plants use to make their food from carbon dioxide and water.
4. What is the function of the kidneys in human beings?
Solution: The kidneys filter waste products, such as urea and excess salts, from the blood to form urine, which is then excreted from the body. They also regulate water and electrolyte balance.
5. Describe the process of transpiration in plants.
Solution: Transpiration is the process where water is lost as vapor from the aerial parts of plants, primarily through the stomata. It helps in the movement of water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and also aids in temperature regulation.
Activity-Based Questions
1. After conducting the starch test on a variegated leaf, what conclusions can you draw about the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Solution: The starch test shows that only the green areas of the leaf, where chlorophyll is present, are able to produce starch through photosynthesis. This confirms that chlorophyll is essential for the process of photosynthesis.
2. Explain the results of the experiment involving potassium hydroxide and its effect on photosynthesis in plants.
Solution: The plant in the bell jar with potassium hydroxide showed less starch production compared to the plant without potassium hydroxide, as potassium hydroxide absorbs carbon dioxide, preventing photosynthesis from occurring. This experiment demonstrates the importance of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis.
Research-Based Question
Q1. Investigate the role of hemoglobin in human blood. Why is it essential for respiration and how does its deficiency affect the body?
Solution: Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that binds to oxygen in the lungs and transports it to tissues throughout the body. It also carries carbon dioxide back to the lungs for removal. A deficiency in hemoglobin leads to anemia, causing fatigue, weakness, and insufficient oxygen supply to the body's cells.
Think & Explain
Question: Imagine you are a plant. How would you get the energy you need to survive, and what processes would take place inside you to provide the energy required for growth and reproduction?
Ans: As a plant, I get the energy I need to survive through a process called photosynthesis. Here's how it works:
Absorbing Sunlight: I take in sunlight through my leaves, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll helps me absorb light energy from the sun.
Making Food: With the help of chlorophyll, I convert carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil into glucose (a type of sugar) using the energy from the sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis. The chemical reaction looks like this:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose) + 6O₂
Storing and Using Energy: The glucose I produce is used as a source of energy. Some of it is used immediately for growth, reproduction, and carrying out basic life functions. Any extra glucose is stored in my roots, stems, or fruits for future use.
Respiration: I also carry out respiration, a process where I break down the glucose to release energy. During respiration, oxygen is used to break down glucose, and the energy released is used for various life processes like growth, repair, and reproduction. The process is as follows:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + energy (ATP)
This energy helps me perform vital functions such as growing taller, producing flowers and fruits, and maintaining my overall health.
Crossword Puzzle
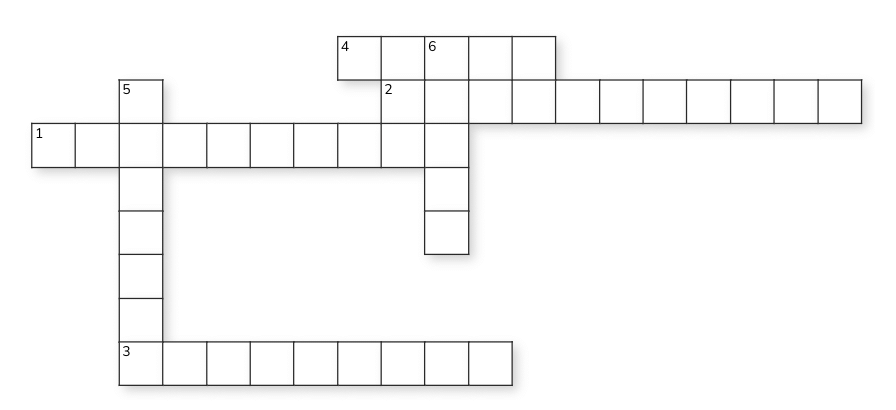

Solution:
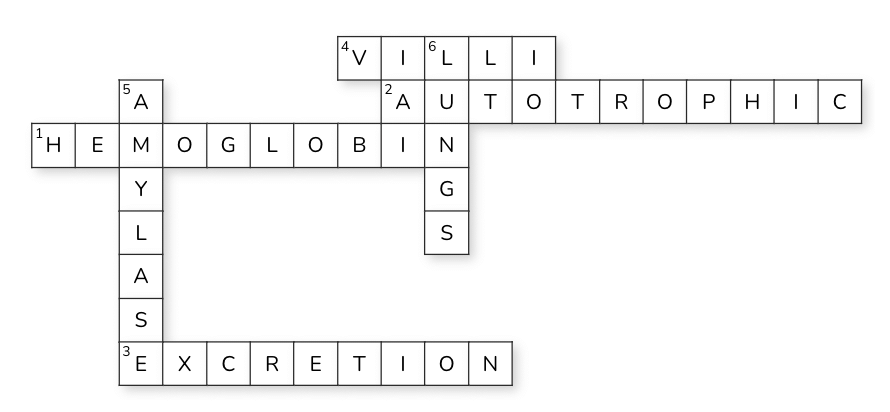
Can have diagram based labelling question too !!!!

















