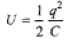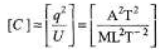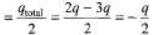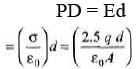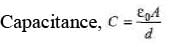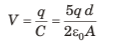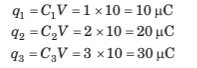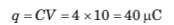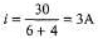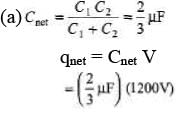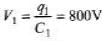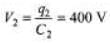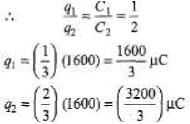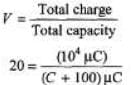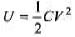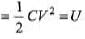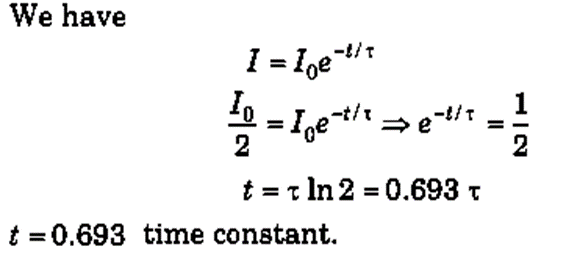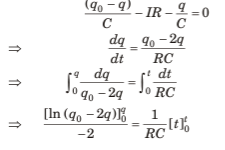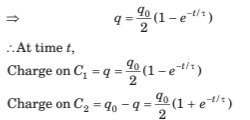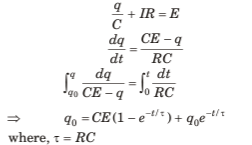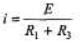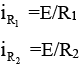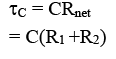DC Pandey Solutions: Capacitors | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 22.1
Q.1. Find the dimensions of capacitance.
Sol.
= [M-1L-2T4A2]
Q.2. No charge will flow when two conductors having the same charge are connected to each other. Is this statement true or false?
Sol. False . Charge does not flow if their potentials are same. It does not depend on amount of charge present.
Q.3. Two metallic plates are kept parallel to one another and charges are given to them as shown in the figure. Find the charge on all four faces.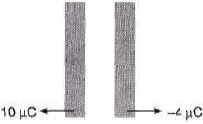
Sol. Consider the charge distribution shown in figure.

Electric field at point P
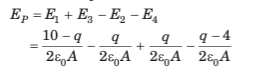
But P lies inside conductor
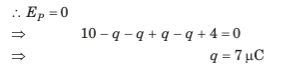
Hence, the charge distribution is shown in figure.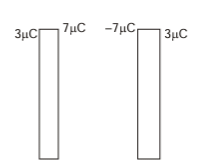
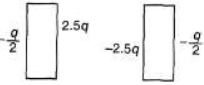
Q.4. Charges 2q and -3g are given to two identical metal plates of area of cross-section A. The distance between the plates is d. Find the capacitance and potential difference between the plates.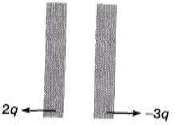
Sol. Charge on outermost surfaces.
Hence charge on different faces are as shown below.
Electric field and hence potential difference between the two plates is due to ±2.5 q
Introductory Exercise 22.2
Q.1. Find the charge stored in all the capacitors.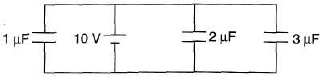
Sol:All three capacitors are in parallel wit h the battery. Potential Difference across each of them is 10V. So, apply q = CV for all of them.
Q.2. Find the charge stored in the capacitor.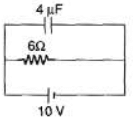
Sol. Capacitor and resistor both are in parallel with the battery. PD across the capacitor is 10V. Now apply q = CV.
Q.3. Find the charge stored in the capacitor.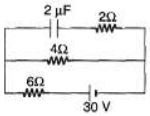
Sol. In steady state current flows in lower loop of the circuit.
Now, potential difference across capacitor = potential difference across 4Ω resistance.
= iR
= (3)(4)=12V
q = CV = (2μF) (12 V)
= 24μC
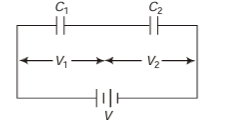
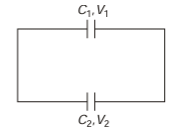
Q.4. A 2μF capacitor and a 2μF capacitor are connected in series across a 1200 V supply line.
(a) Find the charge on each capacitor and the voltage across them.
(b) The charged capacitors are disconnected from the line and from each other and reconnected with terminals of like sign together. Find the final charge on each and the voltage across them.
Sol.
= 800μC
(b) In series, q remains same
q1 = q2 = 800 μC
and
Now total charge will become 1600 μC. This will now distribute in direct ratio of capacity
Q.5. A 100 μF capacitor is charged to 100 V. After the charging, the battery is disconnected. The capacitor is then connected in parallel to another capacitor. The final voltage is 20 V. Calculate the capacity of the second capacitor.
Sol. Charge, q = CV = 104μC
In parallel common potential is given by
Solving this equation we get
C = 400μF
Introductory Exercise 22.3
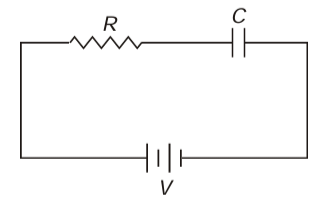
Q.1. An uncharged capacitor C is connected to a battery through a resistance R. Show that by the time the capacitor gets fully charged, the energy dissipated in R is the same as the energy stored in C.
Sol. Charge supplied by the battery,
q= CV
Energy supplied by the battery,
E = qV =CV2
Energy stored in the capacitor,
∴ Energy dissipated across R in the form of heat = E - U
Q.2. How many time constants will elapse before the current in a charging RC circuit drops to half of its initial value?
Sol.
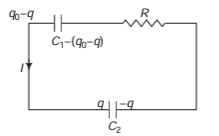
Q.3. A capacitor of capacitance C is given a charge q0. At time t = 0 it is connected to an uncharged capacitor of equal capacitance through a resistance R. Find the charge on the first capacitor and the second capacitor as a function of time f. Also plot the corresponding q-t graphs.
Sol. Let capacitor C1 is initially charged and C2is uncharged.
At any instant, let charge on C2 be q, charge on C1 at that instant = q0 - q
By Kirchhoff’s voltage law,
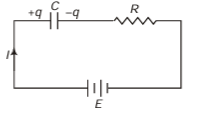
Q.4. A capacitor of capacitance C is given a charge q0. At time f = 0, it is connected to a battery of emf E through a resistance R. Find the charge on the capacitor at time t.
Sol. Let q be the charge on capacitor at any instant t
By Kirchhoff’s voltage law
Q.5. Determine the current through the battery in the circuit shown in figure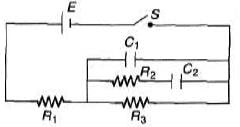
(a) immediately after the switch S is closed
(b) after a long time.
Sol.
(a) Immediately after the switch is closed whole current passes through C1
i = E/R1
(b) Long after switch is closed no current will pass through C1 and C2.
Q.6. For the circuit shown in the figure find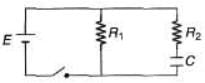
(a) the initial current through each resistor
(b) steady-state current through each resistor
(c) final energy stored in the capacitor
(d) the time constant of the circuit when the switch is opened.
Sol.
(a) At t = 0 equivalent resistance of capacitor is zero. R1 and R2 are in parallel across the battery PD across each is E.
(b) In steady state no current flow through capacitor wire. PD across R1 is E.
(c) In steady state potential difference across capacitor is E.
∴
(d) When switch is opened, capacitor is discharged through resistors R1 and R2
|
98 videos|332 docs|102 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Capacitors - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the principle behind capacitors and how do they store energy? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the equivalent capacitance in series and parallel combinations? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of capacitors and their applications? |  |
| 4. How does the dielectric material affect the performance of a capacitor? |  |
| 5. What are the common applications of capacitors in electronic circuits? |  |