Causes of Decline: The Mughal Empire | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
The Mughal Empire, once a dominant force in South Asia, began to decline due to a combination of internal weaknesses and external pressures. Understanding these factors is crucial to grasp the historical context of India's transition to regional powers and eventually, British colonial rule.
The Mughal Empire, established in the early 16th century, was renowned for its cultural richness, architectural marvels, and effective governance. However, several key factors contributed to its decline:
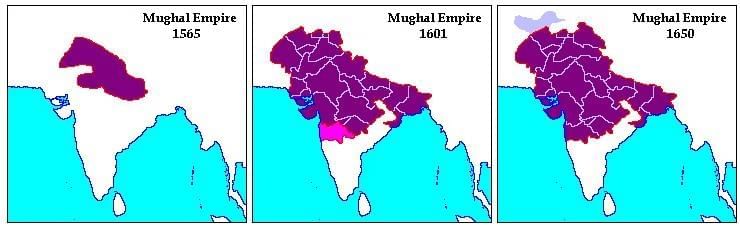
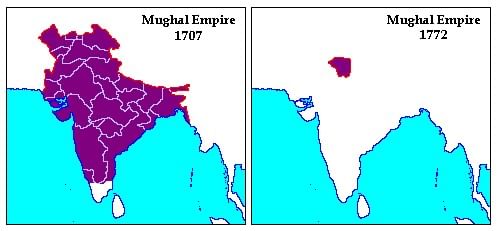 Decline of Mughal Empire
Decline of Mughal Empire
However, several key factors contributed to its decline:
- Weak Successors: After the death of Aurangzeb in 1707, the empire was led by a series of weak successors who were unable to maintain control over the vast territory.
- Internal Strife: The later Mughal period was marked by internal conflicts, including power struggles among nobles and regional governors (subahdars) who sought greater autonomy.
- Economic Decline: The empire faced economic difficulties due to declining trade, heavy taxation, and the costs of frequent military campaigns.
- External Invasions: Invasions by external forces, such as the Persian invasion led by Nadir Shah in 1739, further weakened the empire.
- Rise of Regional Powers: As central authority weakened, regional powers such as the Marathas, Sikhs, and later the British East India Company, began to assert control over various parts of the subcontinent.
- Colonial Expansion: The British East India Company, initially a trading entity, gradually expanded its control over Indian territory, capitalizing on the Mughal decline and regional instability.
By the mid-18th century, the Mughal Empire had fragmented, paving the way for the rise of British colonial rule in India. The factors leading to its decline are crucial in understanding the historical transition from a prominent empire to colonial domination.
Factors Behind the Decline of the Mughal Empire
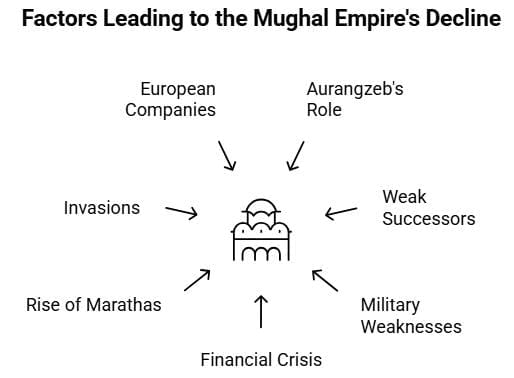
Aurangzeb's Role
- Aurangzeb expanded the Mughal Empire to its greatest size, but this vast expansion made it difficult to govern effectively.
- After his reign, Aurangzeb's successors were weak and struggled to manage the enormous territory, exacerbated by poor communication.
- Aurangzeb's religious policies alienated many groups, leading to revolts from the Sikhs, Jats, and Bundelas.
- His harsh treatment of the Rajputs and aggressive campaigns against the Deccani states and Marathas drained the Empire's resources.
Weak Successors and Nobles
- The Mughal Empire required strong leadership, but Aurangzeb's successors were more interested in luxury than governance.
- This neglect led to uprisings and allowed regional powers, particularly the Marathas, to strengthen their influence.
- Foreign invasions further weakened the Empire and depleted its resources.
- Nobles, mirroring their rulers, either lived extravagantly or established independent states.
- They became embroiled in succession disputes, forming factions that hindered unity during foreign invasions.
Military Weaknesses
- The Mughal army was organised on a feudal basis, with soldiers loyal to their mansabdars rather than the Emperor.
- This loyalty issue worsened in the later period of the Empire.
- The military was disorganised, lacked discipline, and failed to keep pace with European advancements in weaponry.
- Military leaders frequently changed allegiances, and financial difficulties led to soldiers going unpaid.
- A fragmented military with minimal loyalty was ineffective in defending the Empire.
 Mansabdari System
Mansabdari System
Financial Crisis
- Aurangzeb's campaigns in the Deccan drained the treasury and disrupted trade.
- Continuous warfare devastated crops, resulting in a demoralised peasantry who abandoned farming.
- This decline worsened revenue collection as local powers gained independence.
- The condition of the Empire continued to deteriorate under the later Mughal rulers.
Rise of the Marathas
- The Marathas played a crucial role in the downfall of the Mughal Empire.
- The Peshwas envisioned a Hindu Empire, believing it could only be achieved after the Mughal Empire's decline.
- The Marathas' ambitions were facilitated by the Mughal Empire's inability to unite Hindus and Muslims.
- Some Indian chiefs perceived Mughal rulers as foreign oppressors and adversaries of Hinduism.
Invasions of Nadir Shah and Ahmed Shah Abdali
- The invasions by Nadir Shah and Ahmed Shah Abdali revealed the military weaknesses of the Mughal Empire.
- These invasions also resulted in the plundering of the Empire's financial resources.
European Companies
- The progressive West posed a challenge to the medieval nature of the Mughal Empire.
- In the competition among civilizations, European powers gained an upper hand over Indian states.
|
110 videos|652 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Causes of Decline: The Mughal Empire - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What were the main political factors that led to the decline of the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 2. How did economic issues contribute to the fall of the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 3. What role did religious intolerance play in the decline of the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 4. How did the invasions and conflicts with neighboring states affect the Mughal Empire? |  |
| 5. In what ways did the European colonization impact the Mughal Empire's decline? |  |

















