Cell Cycle & Mitosis | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is the Cell Cycle? |

|
| Phases of the Cell Cycle |

|
| Interphase |

|
| Intermediate Phase/ G0 Phase |

|
| Mitotic Phase/ M-Phase |

|
| Significance of Mitosis: |

|
It is a fundamental biological fact that all living organisms originate from a single cell. This raises the question of how a single cell can develop into complex and large organisms. The processes of growth and reproduction are is internal to cells and all living beings. Cells multiply by dividing into two, resulting in two daughter cells each time.
These newly formed cells possess the capacity to grow and divide themselves, leading to the creation of a new cell population originating from the original parent cell. Essentially, through repeated cycles of growth and division, a solitary cell can give rise to a structure comprised of millions of cells.
What is the Cell Cycle?
The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, synthesises the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells is termed cell cycle.
Phases of the Cell Cycle
A cell cycle consists of cell growth, DNA replication, and cell division. The events that occur during a cell cycle are genetically controlled. The duration of the cell cycle varies between organisms and cell types. The human cell cycle takes 24 hours on average, whereas a yeast cell finishes one cell cycle in 90 minutes.
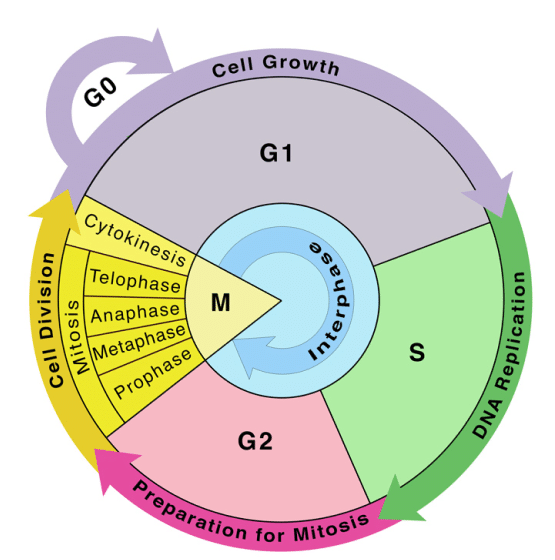 Phases of cell cycle
Phases of cell cycle
Interphase
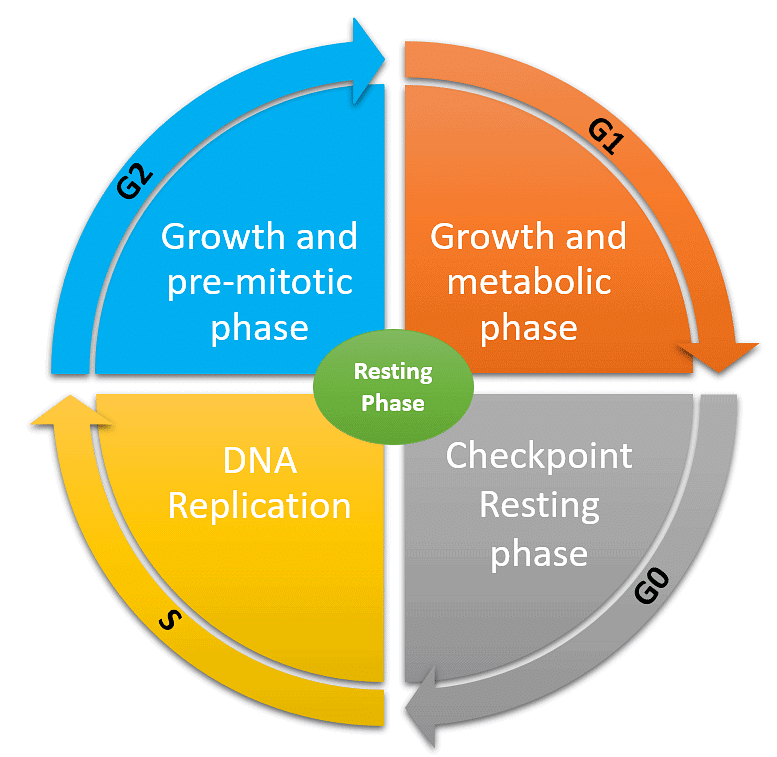
The interphase of the cell cycle is a crucial period of a cell's life when it is not actively dividing. It consists of three main phases:
- The interphase period is the time between two sequential M-phases of the cell division.
- The cell prepares to divide, grows, and DNA replication occurs.
- The interphase is divided into three stages: G1, S, and G2 phases.
 Phases of Cell Cycle
Phases of Cell Cycle
1. G1 Phase or Gap1
This is the time between the previous mitosis and the next cell cycle's DNA replication, or this phase is the interval between the M phase of the previous cycle and the S phase of the current cycle.- The cell is biologically active and gets bigger continuously during the G1 phase, but it does not copy its DNA.
- So as the cell prepares for the following stages, it's growing, duplicating its organelles.
2. Synthesis or S-Phase
DNA replication occurs during this phase, where the cell's DNA doubles in amount and the centriole duplicates.
- It is worth noting that the number of chromosomes remains constant.
- During the S phase of animal cells, replication of DNA starts in the nucleus, but the centriole multiplies in the cytoplasm.
3. G2 Phase or Gap2 Phase
This phase allows the cell to grow more along with the enlargement in the cell size, the cell also makes more proteins and organelles.
- Protein synthesis occurs in the Gap2 phase.
- The most important function of this phase is that it prepares the cell for mitosis. This phase helps the cell to prepare for the actual cell division in the M phase.
- Many cells in an adult human being do not divide, for example, heart cells divide only infrequently to replace injured and dead cells.
- These injured/ dead cells enter an inactive stage of the cell cycle known as G0 or the quiescent stage. For example, a Nerve cell that enters the quiescent stage and thus cannot divide.
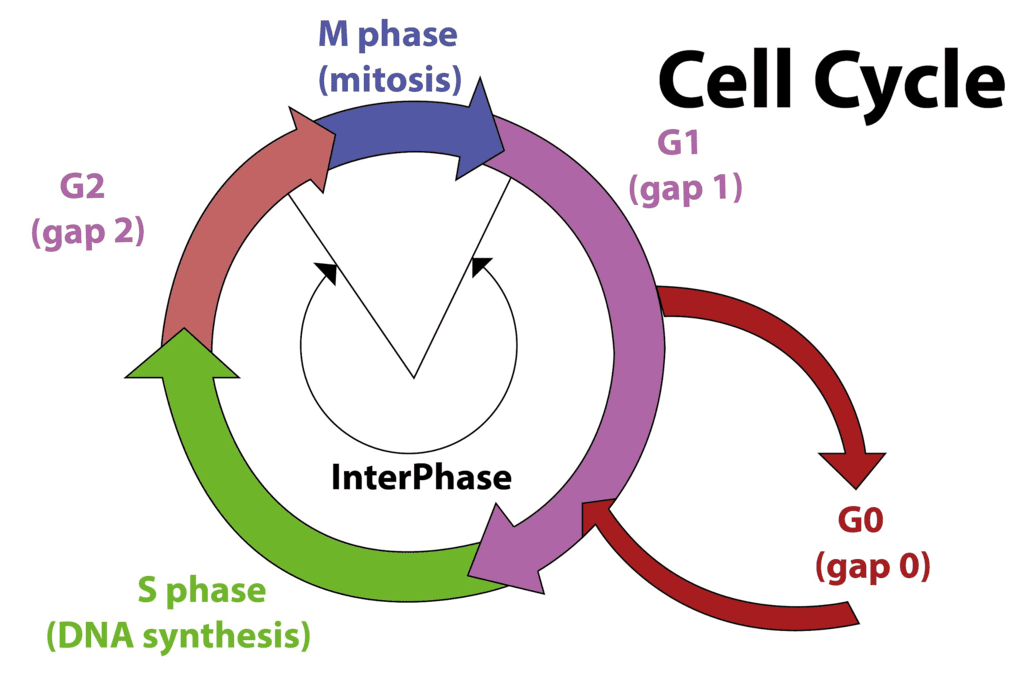
Intermediate Phase/ G0 Phase
The G0 phase refers to a period in the cell cycle where cells exit the active cell cycle and enter a state of quiescence or senescence. The G0 phase is a non-proliferative phase in which cells cease to divide but can still carry out their normal functions.
 G0 Phase
G0 Phase
There are two types of G0 phase:
1. Quiescent phase: This is a reversible and temporary phase that occurs when cells stop dividing but retain their ability to re-enter the cell cycle and begin dividing again in response to external signals. During the quiescent phase, cells remain metabolically active and carry out their normal functions, but they do not replicate their DNA or divide.
2. Senescent phase: This is a permanent and irreversible phase that occurs when cells stop dividing due to a variety of reasons, such as replicative exhaustion, DNA damage, or cellular stress. Senescent cells are characterised by changes in gene expression, morphology, and metabolic activity. They also secrete pro-inflammatory molecules that contribute to ageing and age-related diseases.
Mitotic Phase/ M-Phase
This is the stage at which actual cell division takes place.Mitosis (Mitotic Division)
Mitosis, the most intense phase of the cell cycle, sees a complete reorganization of nearly all cell components. It's termed equational division because the number of chromosomes remains the same in both parent and daughter cells.
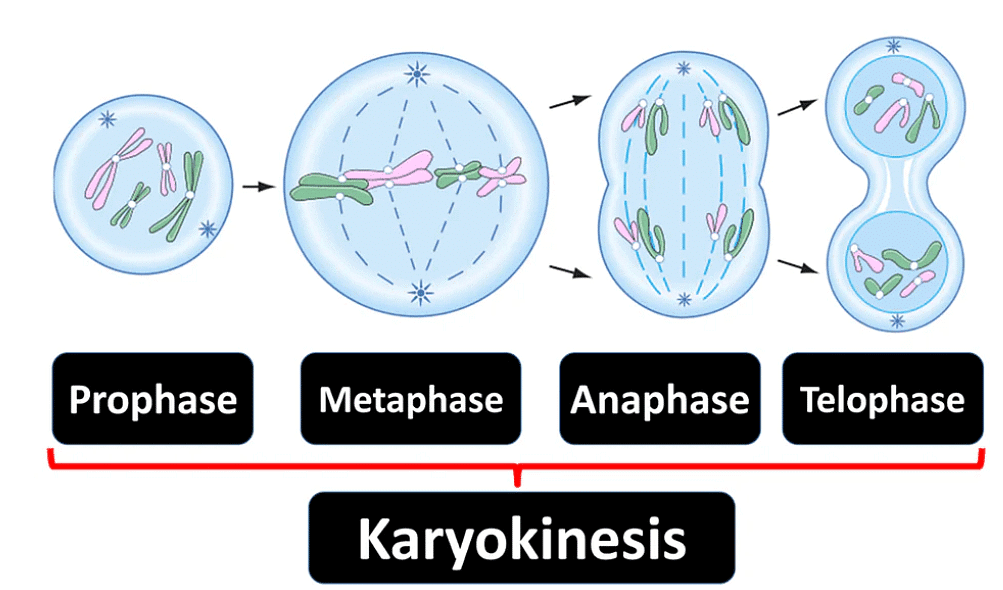
While mitosis is often broken down into four stages for convenience, it's crucial to understand that cell division is a continuous process without clear-cut boundaries between stages.
The four stages of nuclear division (karyokinesis) include:
Prophase
Prophase marks the start of the karyokinesis phase of mitosis, which comes after the S and G2 phases of interphase.
- In prophase, chromosomal material starts condensing, becoming more compact and untangled.
- The centrosome, which duplicated during interphase, begins to move toward opposite ends of the cell.
- Key events marking the completion of prophase:
(a) Chromosomal material condenses into compact mitotic chromosomes, each consisting of two chromatids attached at the centromere.
(b) Centrosomes move towards opposite poles, emitting microtubules called asters, which along with spindle fibers, form the mitotic apparatus. - Cells at the end of prophase, as seen under the microscope, lack golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, and the nuclear envelope.
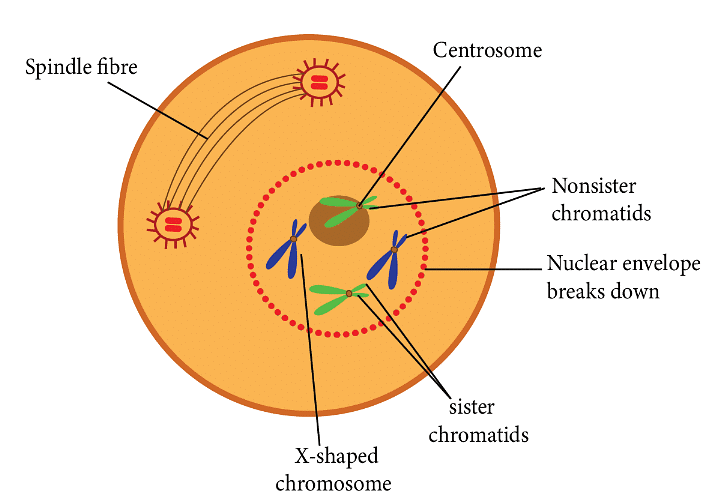 Prophase
Prophase
Metaphase
The nuclear envelope completely breaks down, initiating the second phase of mitosis, allowing chromosomes to disperse throughout the cell's cytoplasm. By this point, chromosome condensation is complete, making them easily visible under a microscope, ideal for studying their morphology.
- In metaphase, each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids held together by the centromere.
- Small disc-shaped structures called kinetochores on the centromeres serve as attachment sites for spindle fibers, which move the chromosomes to the cell's center.
- In metaphase, all chromosomes align at the equator, with one chromatid connected to spindle fibers from one pole and its sister chromatid connected to fibers from the opposite pole, forming the metaphase plate.
Key features of metaphase include:
- Spindle fibers attaching to kinetochores of chromosomes.
- Chromosomes aligning along the metaphase plate via spindle fibers to both poles.
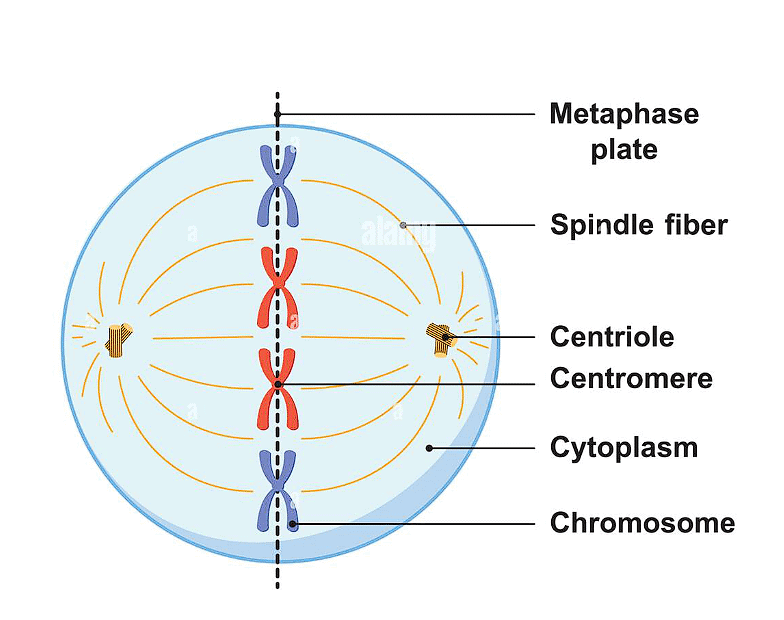 Metaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
- At the start of anaphase, each chromosome lined up at the metaphase plate splits at the same time.
- The two daughter chromatids, now called daughter chromosomes, begin to move towards opposite ends of the cell, which will become the new daughter nuclei.
- As the chromosomes shift away from the centre of the cell, the centromere of each chromosome points towards the pole, leading the way, while the arms of the chromosome follow behind.
- The main events that happen during anaphase include:
(ii) Chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell.
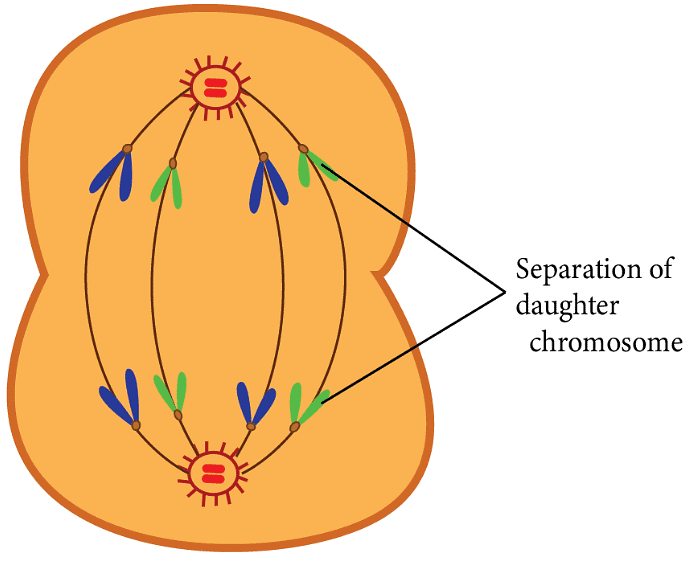 Anaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
In the initial phase of telophase, chromosomes that have reached their respective poles begin to decondense and lose their distinct shapes. Individual chromosomes become unrecognisable, and chromatin material gathers at each of the two poles.
Key events during telophase include:
(a) Chromosomes clustering at opposite spindle poles, losing their individual identities.
(b) Formation of a nuclear envelope around the chromosome clusters at each pole, resulting in the creation of two daughter nuclei.
(c) Reformation of nucleolus, Golgi complex, and endoplasmic reticulum.
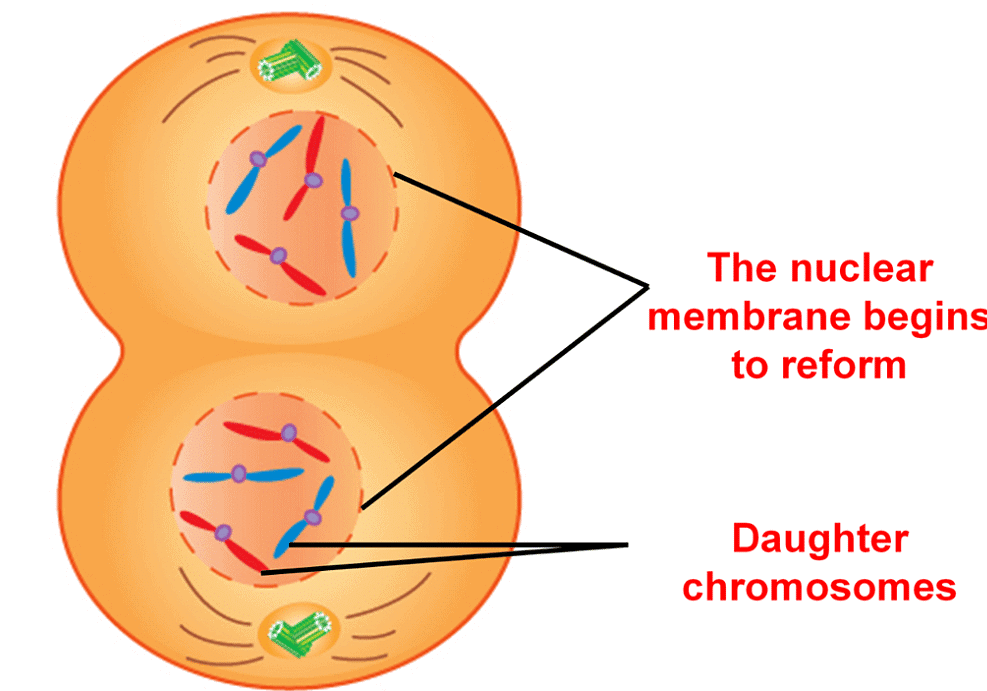 Telophase
Telophase
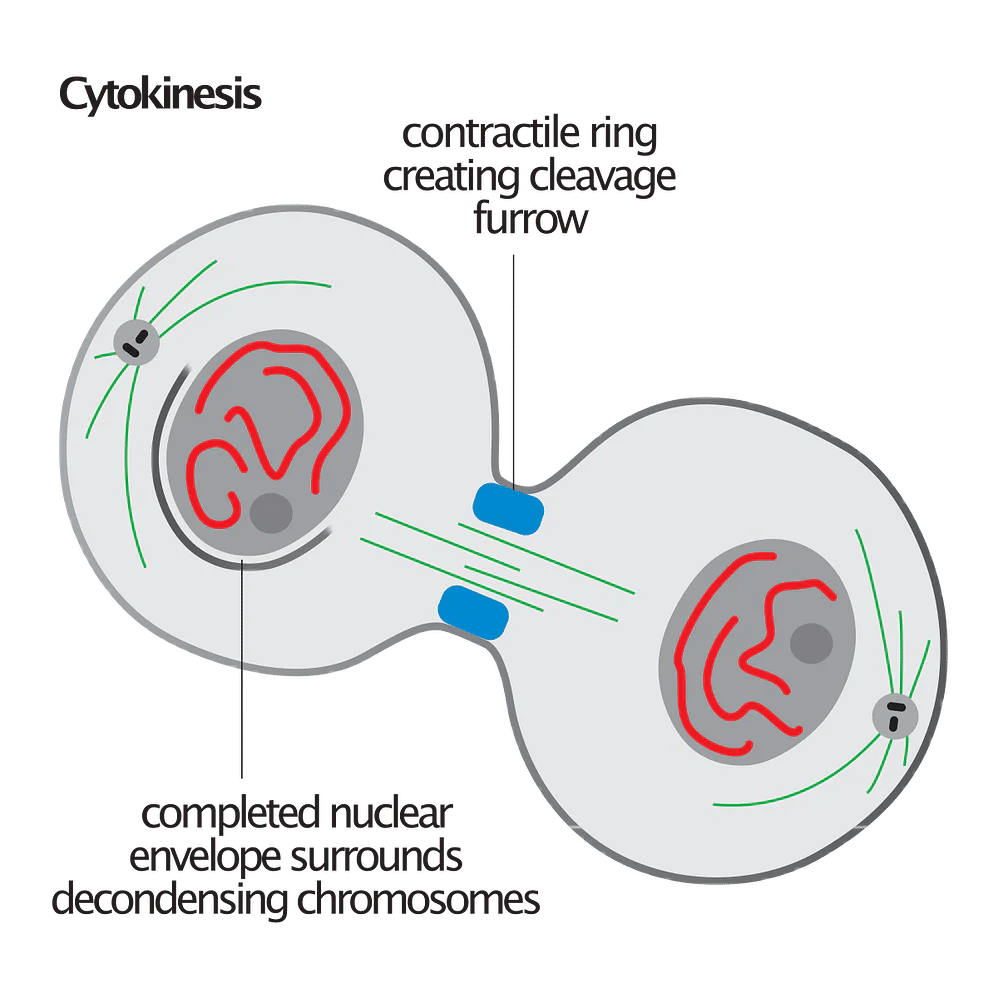
Cytokinesis:
- The separation of cytoplasm occurs after the formation of two nuclei.
- Cell organelles are shared by daughter cells.
- In some organisms, such as fungi, algae, and plant cells, cytokinesis is not shortly followed by karyokinesis.
- A multinucleate stage is known as a syncytium form, such as liquid endosperm in coconut, Rhizopus coenocytic hyphae, and so on.
Significance of Mitosis:
- Mitosis, or equational division, is usually limited to diploid cells.
- However, haploid cells divide by mitosis in certain lower plants and social insects.
- It is critical to comprehend the importance of this division in an organism's life.
- Mitosis typically produces diploid daughter cells with identical genetic material DNA.
- Mitosis is the process by which multicellular organisms grow.
- The nucleus-cytoplasm ratio is disrupted as a result of cell growth. As a result, cell division is required to revive the nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio.
- Mitosis makes an important contribution to cell repair. Cells in the upper epidermal layer, cells in the gut lining, and cells of the blood are constantly replaced.
- Mitotic divisions occur in the meristematic tissues like the apical and lateral cambium, resulting in plants growing continuously throughout their lives.
|
183 videos|524 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Cell Cycle & Mitosis - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the significance of mitosis in the cell cycle? |  |
| 2. What are the different phases of the cell cycle? |  |
| 3. What happens during interphase in the cell cycle? |  |
| 4. What is the G0 phase of the cell cycle? |  |
| 5. How does mitosis contribute to growth and development in multicellular organisms? |  |
















