Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter Notes | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Breathing |

|
| Respiration |

|
| Human Respiratory System |

|
| Mechanism of Breathing |

|
| Respiratory Volumes and Capacities |

|
| Exchange of Gases |

|
| Transport of Gases |

|
| Regulation of Respiration |

|
Breathing
Breathing is the fundamental physiological process by which organisms exchange gases with their environment. It primarily involves the intake of oxygen-rich air and the expulsion of carbon dioxide-rich air. This exchange takes place in the respiratory system, specifically in the lungs.
Respiration
Respiration is a broader biochemical process occurring within cells, involving the breakdown of organic molecules (such as glucose) to release energy. This process requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct. While breathing facilitates the exchange of gases necessary for respiration, respiration itself occurs at the cellular level and is essential for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of cells.
Some Examples of Respiratory Organs
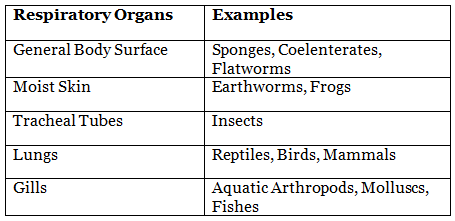
Respiratory Organs
In unicellular organisms, gas exchange occurs directly through the cell membrane by diffusion. However, in multicellular organisms, specialized respiratory organs facilitate the exchange of gases. These include lungs in mammals, gills in fish, and tracheal systems in insects.
Human Respiratory System
The human respiratory system is divided into the upper and lower respiratory tracts, each comprising several organs with distinct functions.
The Upper Respiratory Tract:
The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx. These structures are involved in the initial processes of breathing such as air filtration, humidification, and vocalization.
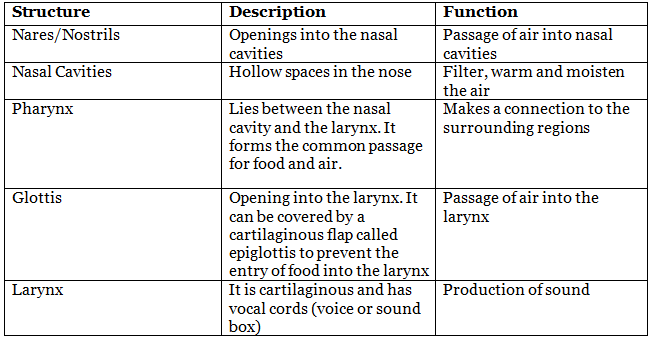
The Lower Respiratory Tract
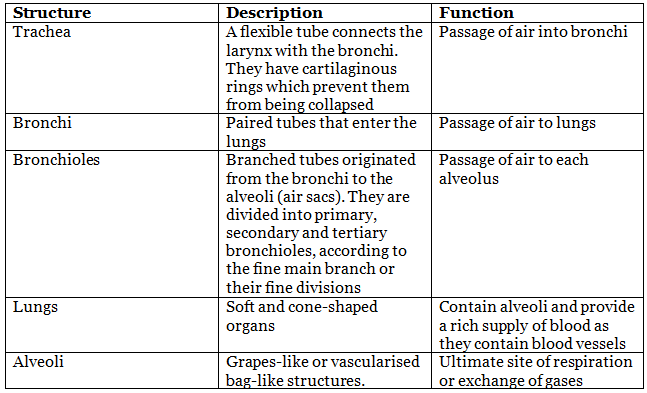
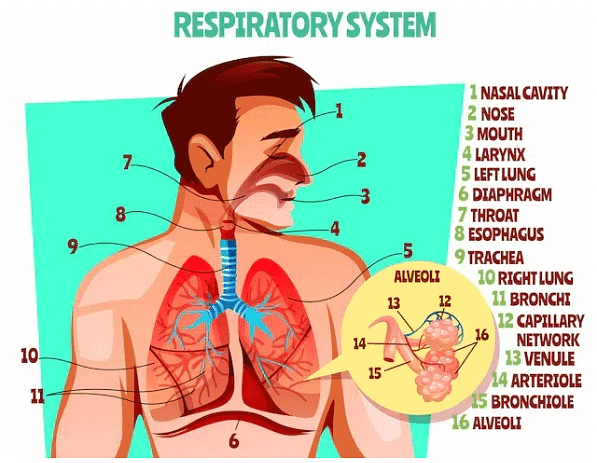
Humans have two lungs, each enveloped by a double-layered membrane called the pleura. Between these pleural layers is pleural fluid, which reduces friction on the lung surfaces during breathing movements. The outer pleural membrane is close to the thoracic lining, while the inner pleural membrane lies adjacent to the lungs' surface.
Steps Involved in Respiration
- Breathing or pulmonary ventilation, in which oxygen from the atmosphere is drawn in and CO2-rich air from the alveoli is expelled.
- Diffusion of gases (O2 and CO2) occurs at the alveolar membrane.
- Transportation of gases by the blood.
- Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and body tissues.
- Utilisation of O2 by cells and release of CO2 during cellular respiration.
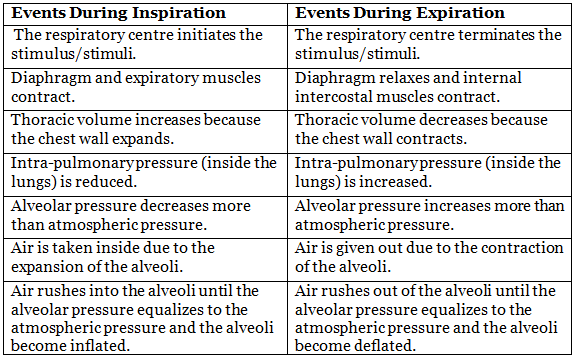
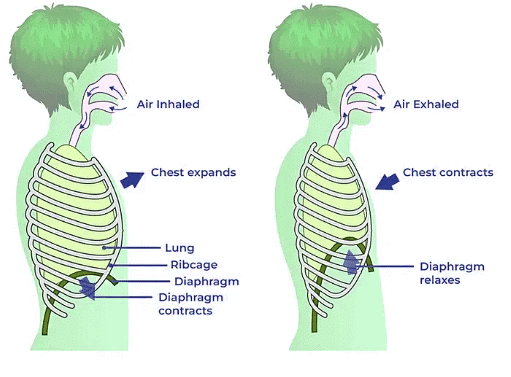
Mechanism of Breathing
Breathing involves two main processes: inhalation (inspiration) and exhalation (expiration). During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, and the ribcage expands, creating negative pressure in the chest cavity that draws air into the lungs. Exhalation occurs when the diaphragm relaxes and the ribcage returns to its resting position, decreasing chest cavity volume and expelling air from the lungs.
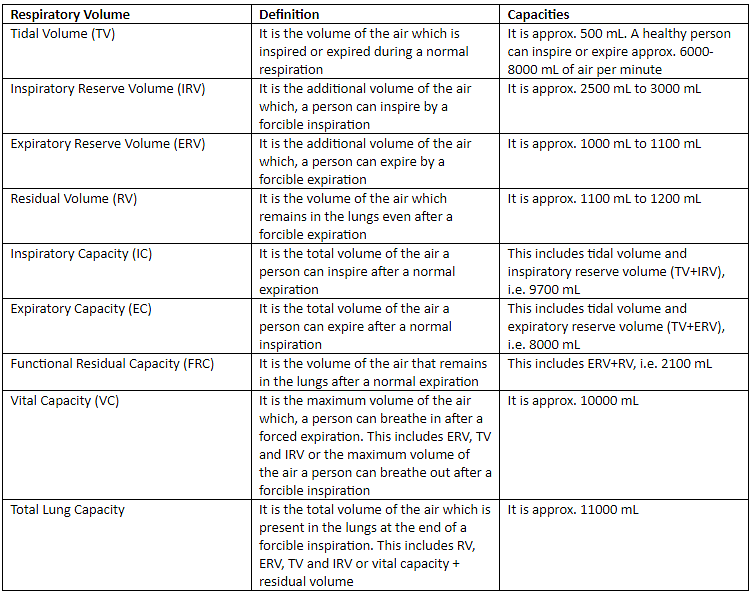
Respiratory Volumes and Capacities
Respiratory volumes and capacities are measurements used to evaluate lung function. These include tidal volume (the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing), inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, and vital capacity (the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation).
Exchange of Gases
The exchange of gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide, occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Oxygen from inhaled air diffuses across the alveolar membrane into the bloodstream, where it binds to haemoglobin in red blood cells for transport to tissues. Meanwhile, carbon dioxide produced by cellular metabolism diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Transport of Gases
Blood acts as the medium for transporting gases between the lungs and tissues. Oxygen is primarily transported by binding to haemoglobin in red blood cells, while carbon dioxide is transported in several forms: dissolved in plasma, bound to haemoglobin, or as bicarbonate ions.
Transport of Oxygen
About 97 per cent of oxygen is transported by red blood cells, bound to haemoglobin, and the remaining 3 per cent is dissolved in plasma.
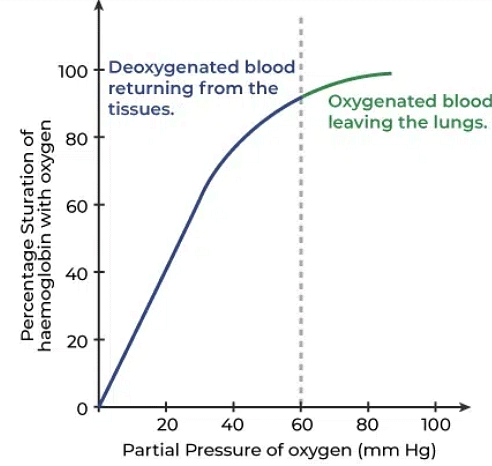
- Oxygen binds reversibly with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin.
- Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2), hydrogen ion concentration, and temperature affect this binding.
- A sigmoid-shaped curve, known as the oxygen dissociation curve, results when haemoglobin saturation with oxygen is plotted against partial pressure of oxygen (pO2).
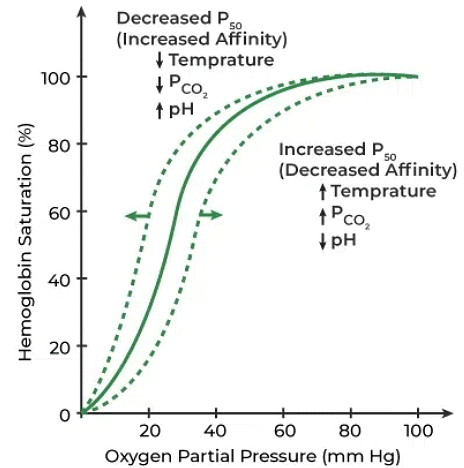
- Factors favourable for oxyhaemoglobin formation: In the alveoli, pO2 is high, pCO2 is low, H+ concentration is low, and temperature is lower.
- Factors favourable for oxyhaemoglobin dissociation: In tissues, pO2 is low, pCO2 is high, H+ concentration is high, and temperature is higher.
- This ensures oxygen is loaded onto haemoglobin at the lungs and released in the tissues.
Transport of Carbon Dioxide
Approximately 20–25 per cent of carbon dioxide is transported by red blood cells by binding to haemoglobin, forming carbaminohaemoglobin. Around 70 per cent is transported as bicarbonate ions (HCO3–), and 8–9 per cent is dissolved in plasma.
- Formation of carbaminohaemoglobin depends on the partial pressure of CO2 (pCO2).
- Factors favouring CO2 binding: High pCO2 and low pO2 in tissues.
- Factors favouring CO2 dissociation: Low pCO2 and high pO2 in alveoli.
- CO2 bound to haemoglobin in tissues is released in the alveoli.
- Red blood cells contain a high concentration of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase; only small amounts are present in plasma.
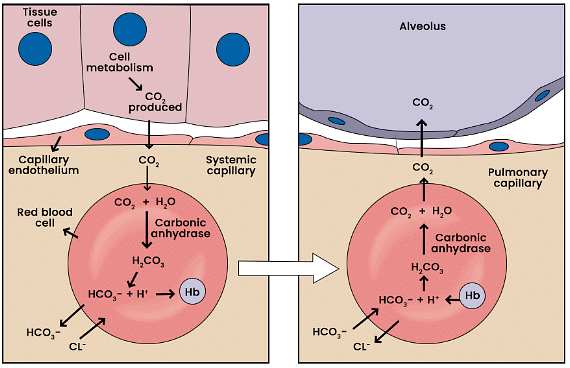
- In tissues with high pCO2 due to metabolism, CO2 diffuses into blood (RBCs and plasma) and reacts to form HCO3– and H+ ions.
- In the alveoli, low pCO2 reverses the reaction, converting bicarbonate ions back to CO2 and water (H2O).
- CO2 is thus formed from bicarbonates in tissues and transported to the alveoli where it is released for exhalation.
Regulation of Respiration
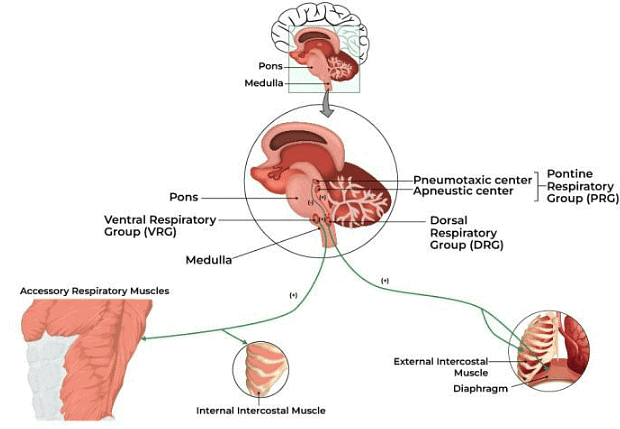
Respiration is regulated by neural and chemical mechanisms. Respiratory centres in the brainstem, particularly the medulla oblongata and pons, monitor blood levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH, adjusting the breathing rate and depth accordingly. Chemoreceptors sensitive to changes in blood chemistry provide constant feedback to regulate respiration effectively.
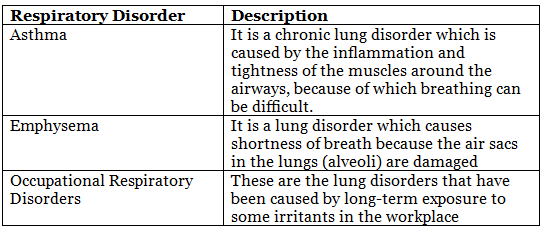
Disorders of the Respiratory System
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter Notes - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the main function of the human respiratory system? |  |
| 2. How does the mechanism of breathing work in the human body? |  |
| 3. What are the different respiratory volumes and capacities and their significance? |  |
| 4. How are gases exchanged in the lungs during respiration? |  |
| 5. What factors regulate respiration in the human body? |  |















