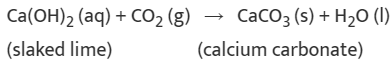Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 1
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Chemical Reaction? |

|
| Chemical Equations |

|
| Types of Chemical Reactions |

|
| Have You Observed the Effects of Oxidation Reaction in Everyday Life? |

|
In our daily lives, physical changes involve alterations in appearance or state without creating new substances, like melting ice. On the other hand, chemical changes result in the formation of entirely new substances, such as cooking food or rusting iron. Recognizing these changes helps us understand when a chemical reaction occurs.
What is a Chemical Reaction?
A chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances, the Reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the Products.
Chemical Equations
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using the symbols and formulas of the substances involved.
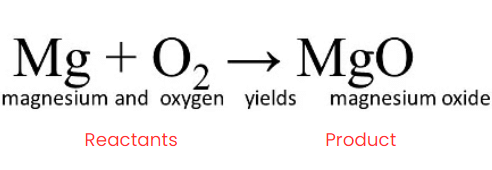
The substances that undergo chemical change in the reaction, Magnesium and Oxygen, are the Reactants. When magnesium burns in air, it combines with oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
Chemical equations can be made more concise and useful if we use chemical formulae instead of words. Example: The chemical formula for water is H2O, which indicates that it is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
1. Writing a Chemical Equation
Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and chemical formulae of the reactants and products is known as a chemical equation.
- For solids, the symbol is “(s)”.
- For liquids, it is “(l)”.
- For gases, it is “(g)”.
- For aqueous solutions, it is “(aq)”.
- For gas produced in the reaction, it is represented by “(↑)”.
- For precipitate formed in the reaction, it is represented by “(↓)”.
The reactants are on the left (LHS) of the arrow, while the products are on the right (RHS). A plus sign (+) links the different reactants and products together.
A balanced account of a chemical transaction is a complete chemical equation, which symbolically depicts the reactants, products, and their physical states.
2. Balanced Chemical Equations
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that in a chemical reaction, atoms can't be created or destroyed. This means that the total number of atoms for each element in the starting materials (reactants) must be the same as in the end products, keeping the overall mass the same.
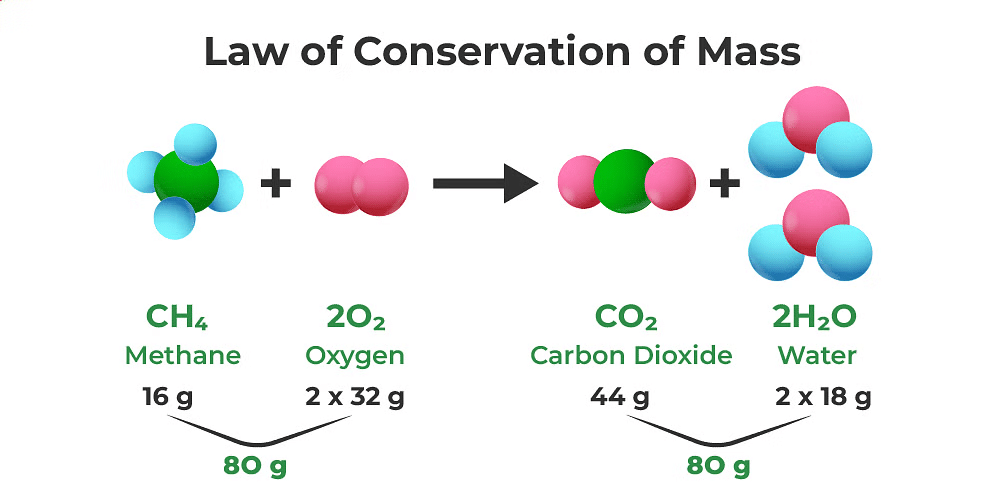
(ii) Balanced chemical equation
A chemical equation is considered balanced when the number of atoms for each element on the reactant side is identical to the product side.
Steps for Balancing Chemical Equations
- To balance chemical equations, coefficients (numeric values preceding chemical symbols or formulas) are utilized. These coefficients represent the number of atoms or molecules involved. Adjust the coefficients as needed to make sure that the number of each type of atom is the same on both sides of the equation.
- For instance, in the equation Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2, balancing involves adding coefficients to achieve equilibrium: Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2. This balancing process often involves trial and error adjustments to ensure the equality of atoms on both sides.
Here are the steps to write a balanced chemical equation: Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Step 1: Write the number of atoms of elements present in reactants and in products in a table as shown here.
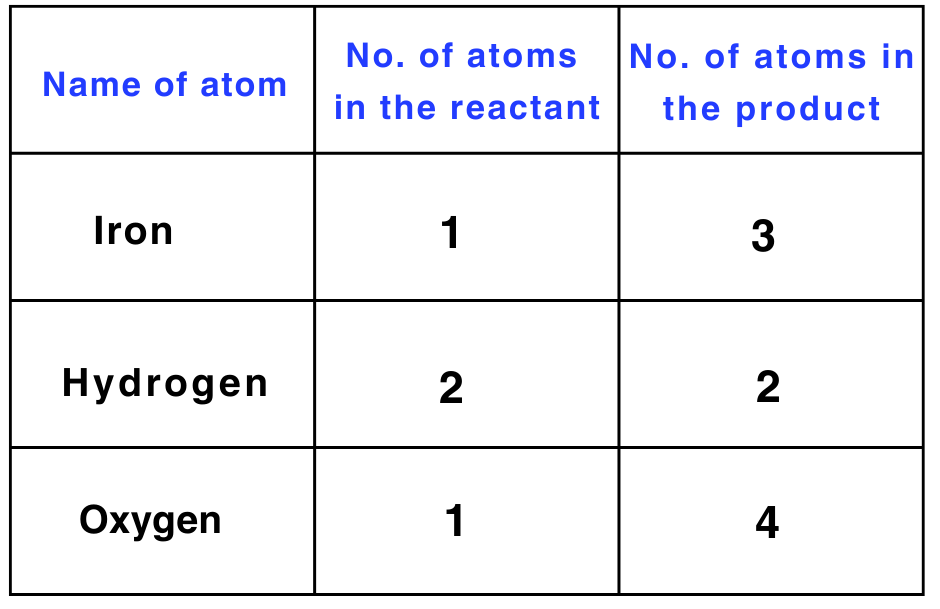
Step 2: Balance the atom which is maximum in number on either side of a chemical equation.
Start by balancing the number of oxygen atoms, which has the maximum count on the right-hand side (RHS).
To balance oxygen, multiply the number of oxygen atoms on the left-hand side (LHS) by 4.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Step 3: Balancing oxygen created an imbalance in the number of hydrogen atoms. There are now eight hydrogen atoms on the LHS and two on the RHS.
To balance hydrogen, multiply the number of hydrogen atoms on the RHS by 4.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
Step 4: There is only one iron atom on the LHS and three on the RHS.
To balance iron, multiply the number of iron atoms on the LHS by 3.
3 × Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
The equation is now balanced, and the same number of atoms of each element is present on both sides.
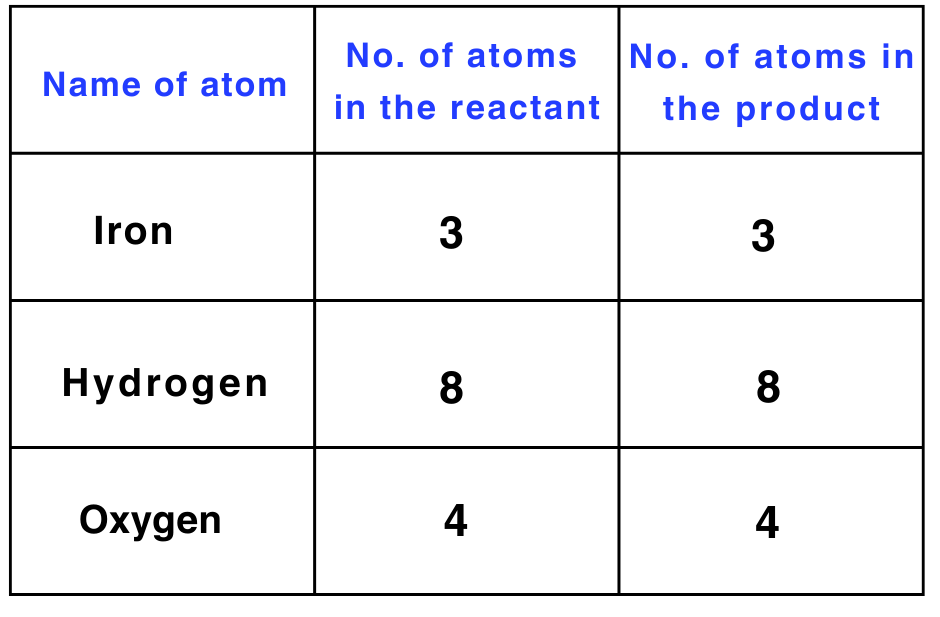
After balancing, the above equation can be written as follows:
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
- To make a chemical equation more informative, it is important to include the physical state of the substances involved.
- The symbol (g) is used to represent a gaseous state, (l) for liquid state, (s) for solid state, and (aq) for an aqueous solution.
- The conditions under which the reaction takes place are also important to include in the chemical equation.
- These conditions can be written above and/or below the arrow in the chemical equation.
- Including this information can help provide a clearer understanding of the chemical reaction taking place. Example :
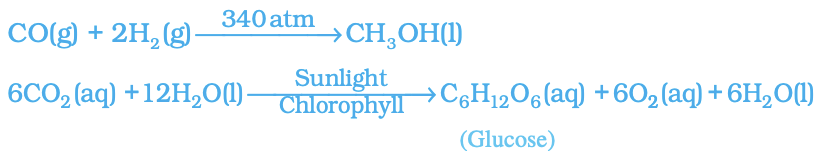
- In this equation, (g) indicates that carbon dioxide is a gas, (l) indicates that water is a liquid, and (aq) indicates that glucose is dissolved in water. Sunlight and chlorophyll are specifically mentioned as the sources of energy used in the reaction. This highlights the importance of these specific components in the photosynthesis process.
Types of Chemical Reactions
Considering various factors, chemical reactions are classified into several categories.
1. Combination Reaction
It occurs when two or more reactants combine to form a single product. or we say, such a reaction in which a single product is formed from two or more reactants is known as a combination reaction.
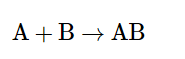
This is the equation of a combination reaction.
Example:
(i) Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) releasing a large amount of heat.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + Heat
(ii) A solution of slaked lime produced by the reaction is used for white-washing walls. Calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide in the air to form calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate is formed after two to three days of white washing and gives a shiny finish to the walls. It is interesting to note that the chemical formula for marble is also CaCO3.
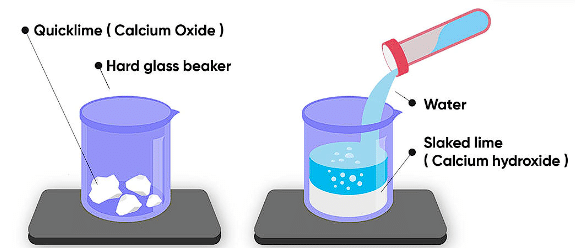
Note: Reactions that release heat when products are formed are known as exothermic chemical reactions.
Other Examples of Exothermic Reactions
(a) Burning of Coal: When carbon is burnt in oxygen (air), carbon dioxide is formed. In this reaction, carbon is combined with oxygen.
C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
(b) Formation of H2 and O2
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
(c) Burning of natural gas
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
Note: Do you know that respiration is an exothermic process?
We need energy to live, and we get it from the food we eat. When we digest food, it's broken down into simpler forms. For instance, rice, potatoes, and bread have carbohydrates, which are turned into glucose. This glucose then mixes with oxygen in our cells to produce energy.
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (aq) → 6CO2 (aq) + 6H2O (l) + energy
Let's Revise: Give an example of a combination reaction used in white-washing walls.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Calcium oxide reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, which later reacts with carbon dioxide to form calcium carbonate used in white-washing.
2. Decomposition Reaction
A single reactant breaks down when exposed to heat, light, or electricity, resulting in the formation of two or more products.
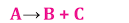
There are three types of decomposition reactions:
(a) Thermal decomposition
A decomposition reaction carried out by heating is called thermal decomposition
Example 1: Heating of Ferrous Sulphate

Ferrous sulphate crystals (FeSO4. 7H2O) lose water when heated and the green colour of ferrous sulphate crystals fades. It then decomposes to ferric oxide (Fe203), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3). Ferric oxide is a solid, while S02 and SO3 are gases.
Example 2: Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate
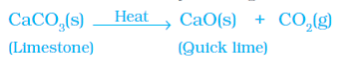
Heating calcium carbonate breaks it down into calcium oxide (lime) and carbon dioxide. This reaction is important in industries, with calcium oxide being used in cement production.
Example 3: Heating of Lead Nitrate Powder
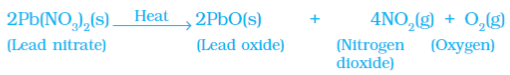
(b) Photolytic decomposition
where light is needed for the reaction. An example is the photolytic decomposition of H2O2.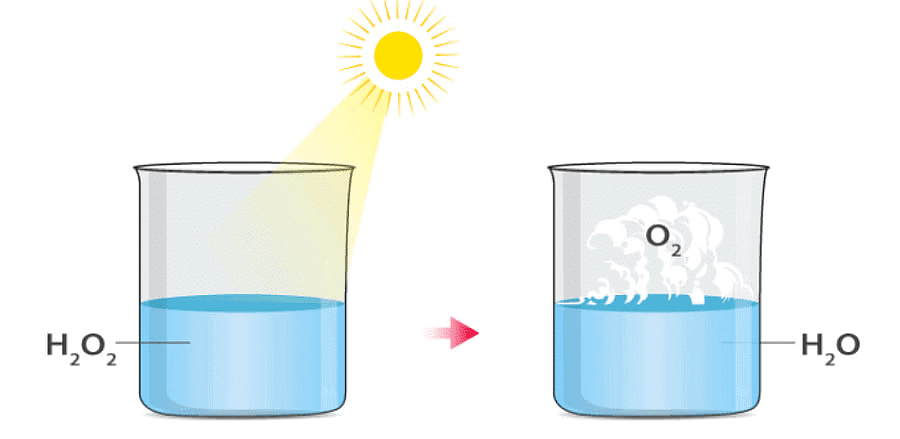 Photolytic Decomposition
Photolytic Decomposition
Example: Photolytic Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen Peroxide undergoes photolytic decomposition when exposed to sunlight, breaking down into water and oxygen gases:
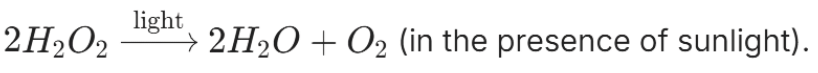
This process is an example of photolytic decomposition, which is crucial in certain chemical reactions and can be influenced by light intensity.
Example: Effect of sunlight on Silver Chloride

White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight. This occurs due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine when exposed to light.
Silver bromide also behaves in the same way. The above reactions are used in black and white photography.
The above reactions are used in black and white photography.
(c) Electrolytic decomposition
where electricity is necessary for the reaction. An example is the electrolytic decomposition of H2O. Electrolysis of water is the decomposition into oxygen and hydrogen gas due to an electric current passed through the water.
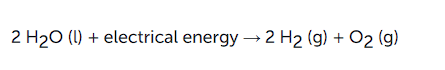
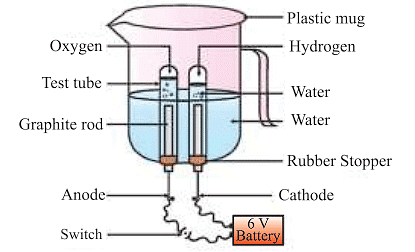
Note: What form of energy is causing these decomposition reactions?
Decomposition reactions need energy to break down the substances involved. This energy can come from heat, light, or electricity. These types of reactions, where energy is taken in rather than given off, are called endothermic reactions.
Let's Revise
Q: What happens when ferrous sulphate is heated?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: It loses water and decomposes into ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide, and sulphur trioxide.
Q: Are decomposition reactions endothermic or exothermic? Why?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: They are endothermic because they require energy input to break compounds.
3. Displacement Reaction
A displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound. Both metals and non-metals take part in displacement reactions.
Some Important Reactions are:
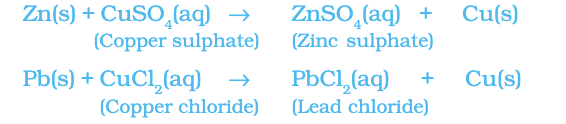
Reaction of iron nails with copper sulphate solution.
Fe (s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu (s)
The iron nail becomes brownish in colour and the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades. In this reaction, iron has displaced or removed another element, copper from the copper sulphate solution.
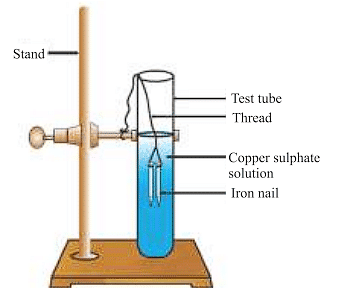
Other examples of displacement reactions are:
Zinc and lead are more reactive elements than copper. They displace copper from its compounds.
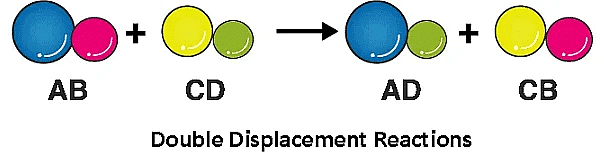
4. Double Displacement Reaction
A double displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction where two compounds react, and the positive ions (cation) and the negative ions (anion) of the two reactants switch places, forming two new compounds or products.
Example: When the solution of barium chloride reacts with the solution of sodium sulphate, white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride.
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + NaCl (aq)
Note: Double Displacement Reaction, in which precipitate is formed, is also known as precipitation reaction. Neutralisation reactions are also examples of double displacement reactions
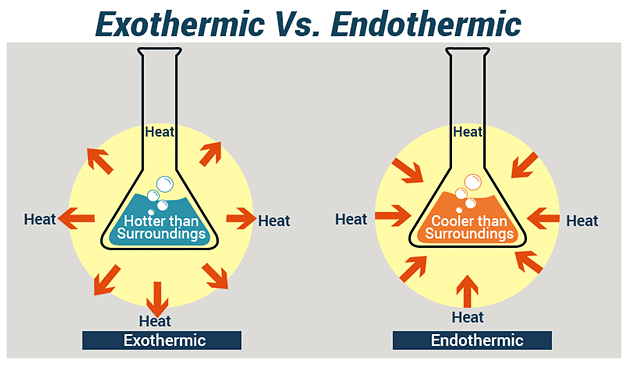
5. Endothermic and Exothermic Reaction
(i) Exothermic Reaction: An exothermic reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which energy is released from the reaction system into the surroundings, usually in the form of heat .
Example: Formation of Carbon dioxide
The chemical reaction can be depicted as:
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Heat
(ii) Endothermic Reaction: An endothermic reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which energy is absorbed from the surroundings in the form of heat, light, or electricity.
Example: Photosynthesis
Plants absorb heat energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Reaction as: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
6. Oxidation and Reduction
A redox reaction happens when there is a change in the oxidation states of the substances involved. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state of a substance or its atoms, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state of a substance or its atoms.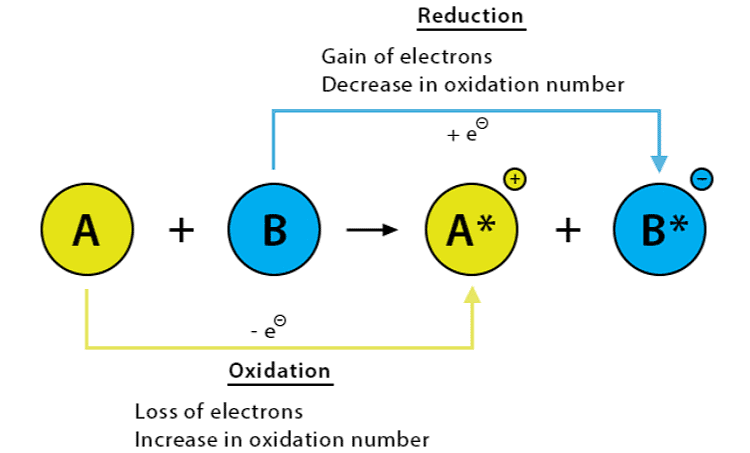
(i) Oxidation is the process in which an atom, ion, or molecule loses one or more electrons. During oxidation, the oxidation state of the atom or molecule increases, since it becomes more positive or less negative.
Some examples of oxidation include the reaction of iron with oxygen to form rust and the reaction of glucose with oxygen in cellular respiration.
(ii) Reduction is the opposite process of oxidation, in which an atom, ion, or molecule gains one or more electrons.
Some examples of reduction include the reaction of silver ions with electrons to form silver metal, and the reaction of hydrogen ions with electrons to form hydrogen gas.
Oxidation of Copper to Copper Oxide
The surface of copper powder becomes coated with black copper(ll) oxide because oxygen is added to copper and copper oxide is formed. If hydrogen gas is passed over this heated material (CuO), the black coating on the surface turns brown as the reverse reaction takes place, and copper is obtained. During this reaction, the copper(ll) oxide loses oxygen and is reduced. The hydrogen gets oxygen and is oxidized.
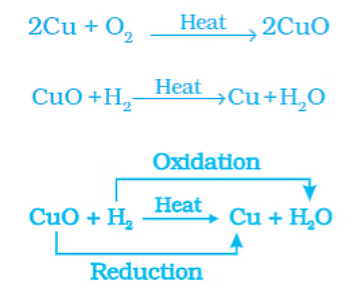
Examples:
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
- Oxidation and reduction always occur together in a chemical reaction and are often referred to as redox reactions.
- In a redox reaction, one substance is oxidized while another substance is reduced. The substance that is oxidized is called the reducing agent.
- It causes the reduction of another substance by donating electrons. The substance that is reduced is called the oxidizing agent. It causes the oxidation of another substance by accepting electrons.
- Example: In the reaction between zinc metal and hydrochloric acid, zinc is oxidized to form zinc ions, while hydrogen ions are reduced to form hydrogen gas:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) - In this reaction, zinc is the reducing agent and HCl acts as the oxidizing agent..
Have You Observed the Effects of Oxidation Reaction in Everyday Life?
1. Corrosion
- Numerous metals, prone to chemical activity, easily react with moisture, oxygen, and acids. Iron, for example, starts as shiny but eventually rusts, forming a reddish-brown powder due to oxidation.
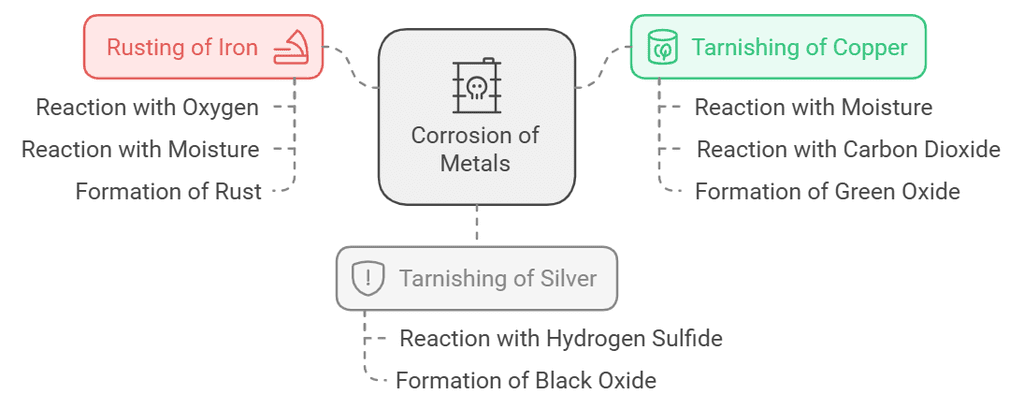
- Metals, like iron, face corrosion as their oxides don't firmly attach, causing flaking, structural weakening, and breakdown. The process of metal deterioration due to environmental substances is called corrosion.
- Copper and silver items tarnish when exposed to air and water. Copper develops a green oxide layer, while silver acquires a black oxide covering. These oxide formations act as barriers, limiting further exposure and reducing corrosion.
- Rusting:
4Fe(s) + 3O2(from air) + xH2O(moisture) → 2Fe2O3.xH2O(rust)
Corrosion of copper:
Cu(s) + H2O(moisture) + CO2(from air) → CuCO3.Cu(OH)2(green)Corrosion of silver:
Ag(s) + H2S (from air) → Ag2S(black) + H2(g) Rusting
Rusting
2. Rancidity
- The taste and odour of food materials containing fat and oil change when they are left exposed to air for a long time. This is called rancidity. It is caused by the oxidation of fats and oils present in food materials.
- Prevention:
(i) Seal food in air-tight containers.
(ii) Employ nitrogen packaging.
(iii) Store in refrigeration.
(iv) Add antioxidants or preservatives.
Let's Revise
Q: What roles do zinc and hydrochloric acid play in the redox reaction Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Zinc is the reducing agent (oxidized to Zn²⁺), and hydrochloric acid is the oxidizing agent (H⁺ reduced to H₂).
Q: What is the primary cause of rancidity in food containing fats and oils?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Oxidation of fats and oils when exposed to air.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 1
| 1. What is a chemical reaction and how can it be identified? |  |
| 2. How do you write and balance a chemical equation? |  |
| 3. What are the main types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. Can you provide everyday examples of oxidation reactions? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to study chemical reactions and equations in chemistry? |  |