Evolution Chapter Notes | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Theories: Origin of Life |

|
| Theories of Evolution |

|
| Evidence for Evolution |

|
| Evolution of Humans |

|
Evolutionary biology is the study of the evolutionary processes that produced the diversity of life on Earth. Earth came into existence sometime between 4 and 5 billion years ago. Life evolved on planet Earth about 3.5 billion years ago. Since then, approximately 15 million different species of organisms have evolved. But only about two million have been identified so far. In this article, we will discuss how the life of these, at first originated on earth and how such a vast variety of organisms evolved through variation and natural selection.
Theories: Origin of Life
The origin of life is considered a unique event in the history of the universe. Several theories have been put forth to explain the origin of life.
1. Big Bang Theory: The universe is vast. Huge clusters of galaxies comprise the universe. The Big Bang theory attempts to explain to us the origin of the universe and the creation of life. Developed in 1927, it is considered the most credible scientific explanation of how the universe was created. It suggests that through a process of expansion and explosion, hydrogen gas was created which led to the formation of stars, and their death (supernova) led to the creation of life.
2. Panspermia Theory: The panspermia hypothesis states that the seeds of life exist all over the universe and can be propagated through space from one location to another. For millennia, this idea has been a topic of philosophical debate. However, due to the lack of any validation, it remained merely speculative until a few decades ago.
3. Theory of Spontaneous Generation: The theory of spontaneous generation believed that life originated spontaneously from non-living decaying and rotting matter like straw and mud. This theory was disproved by Louis Pasteur. Louis Pasteur demonstrated that life comes from pre-existing life. He showed that in pre-sterilized flasks, life did not come from killed yeast while in another flask open to air, new living organisms arose from ‘killed yeast’.
4. Chemosynthetic Theory of Life: It was proposed by A.I. Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England. They proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules, e.g. RNA, protein, etc., and that the formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, i.e., the formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents. The conditions on earth were – high temperature, volcanic storms, and reducing atmosphere containing CH4, NH3, etc.
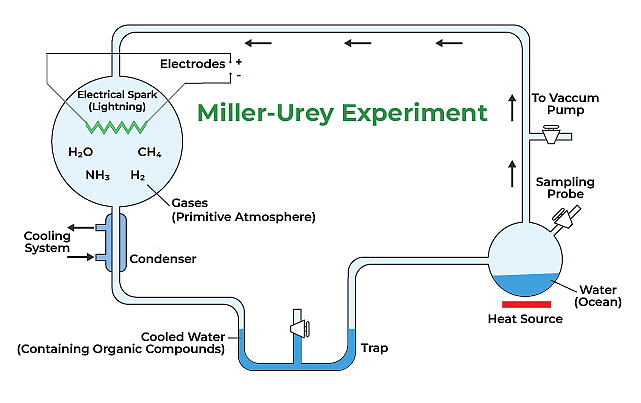
The chemosynthetic theory was supported by S.L. Miller, who in 1953 replicated similar conditions in a laboratory setting. By creating an environment with electric discharges and specific gases like Methane, Hydrogen, Ammonia, and Water vapor, he observed the formation of amino acids. Miller's experiment illustrated how simple molecules could evolve into the complex molecules necessary for life through natural processes.
Theories of Evolution
The theory of evolution by natural selection was proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace.
Key Concepts of Darwinian Theory of Evolution:
- Branching descent: It describes the development of new species from a common ancestor with geographic adaptations leading to reproductive isolation and the emergence of new species.
- Natural selection: This process involves populations adapting and changing over time due to naturally occurring variations. Individuals with traits better suited to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Natural selection is the process where organisms better equipped for survival pass on their traits.
- Survival of the fittest: Organisms best suited to their environment are more likely to reproduce.
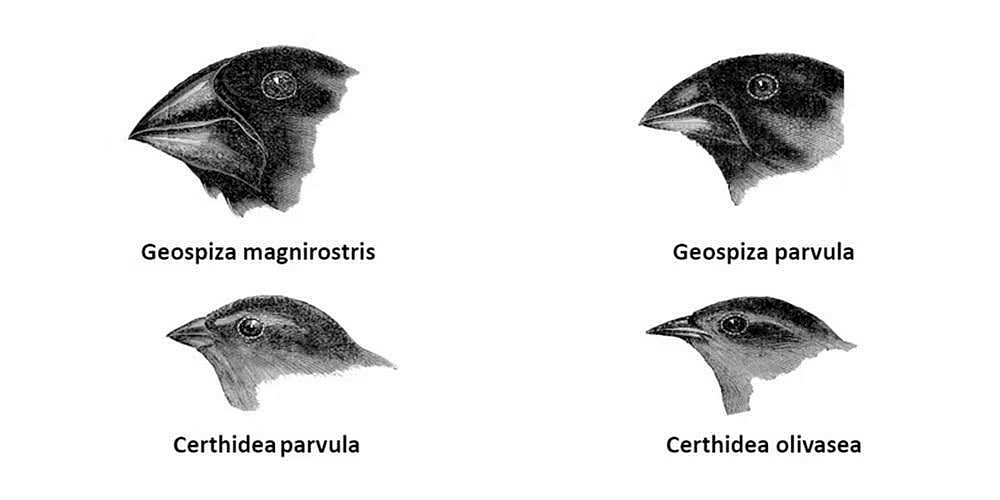
Adaptive radiation: It involves a rapid increase in species number with a shared ancestor, showcasing significant ecological and morphological diversity due to natural selection.
Darwin's finches on the Galapagos Islands exemplify adaptive radiation—a multitude of finch species evolving from a single ancestor species that accidentally arrived on the island. These finches developed diverse beak shapes and feeding habits to adapt to various environments.
Branching Descent: This process involves the development of a new species from a common ancestor. As new species evolve, they adapt to different environments, leading to reproductive isolation and ultimately the emergence of a new species.-
Natural Selection: This is the mechanism through which populations of organisms adapt and change. Individuals within a population exhibit natural variation, with some possessing traits better suited to their environment. Over time, those individuals with advantageous traits reproduce more, leading to changes in the population's characteristics and the emergence of new forms.-
Inheritance of Acquired Characters: Darwin discussed variation without knowing its sources. With advancements in genetics, the sources of variation were identified, leading to modifications in Darwin's original theory of Natural Selection. This updated theory, known as Neo-Darwinism or the Modern Synthetic Theory,
Evidence for Evolution
1. Palaeontological Evidence:
Fossils in rock sediments show the history of life on Earth. Different-aged rock sediments preserve fossils of organisms that likely perished during the formation of those sediments. Some fossils resemble modern life forms and represent extinct organisms like Dinosaurs. By studying fossils in various sediment layers, scientists can determine the geological periods in which these organisms lived. This evidence suggests that new life forms emerged at different times throughout Earth's history
2. Embryological Evidence: Common features in embryos suggest shared ancestry among vertebrates. Ernst Haeckel introduced this concept based on shared embryonic features among vertebrates. For instance, during the embryonic stage, all vertebrates, including humans, develop vestigial gill slits behind their heads. While these slits are functional only in fish, they are present in the embryos of all vertebrates, indicating a common ancestry
3. Morphological Evidence: Common structures and functions in different species support evolutionary relationships. Organisms from different species and groups exhibit common features, supporting the theory of evolution. This evidence includes: -
(a) Divergent evolution: Species stemming from a shared ancestor develop similar anatomical structures (homologous structures) with differing functions. For example, mammals like whales, bats, cheetahs, and humans share similarities in the bone patterns of their forelimbs. - (b) Convergent evolution: This process leads to the development of analogous structures with similar functions or forms, despite not being present in the groups' last common ancestor.
- Divergent evolution: Species from a common ancestral origin evolve similar anatomical parts (homologous structures) with different functions. For instance, mammals like whales, bats, cheetahs, and humans share similarities in the bone patterns of their forelimbs.
- Convergent evolution: This process leads to the development of analogous structures with similar forms or functions among species that do not share a recent common ancestor. For example, sharks and dolphins have similar body shapes despite being distantly related sharks being fish and dolphins being mammals.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle: This principle explains how gene frequencies remain constant over generations when certain conditions are met. It mathematically illustrates the stability of allelic frequencies within a gene pool.The evolution of species through processes like natural selection and branching descent, alongside the understanding of genetic variation and the principles governing gene frequencies, form the basis of modern evolutionary theory.
Factors affecting the Hardy-Weinberg principle:
- Mutation
- Genetic drift
- Natural selection
- Genetic recombination
- Gene flow
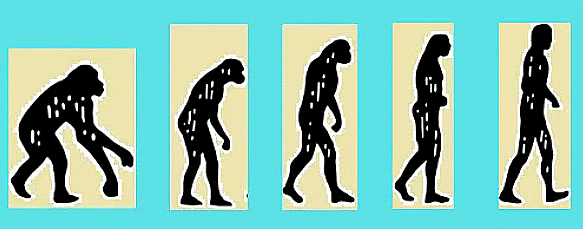
Evolution of Humans
1. Dryopithecus: Considered the earliest known ancestor of humans, Dryopithecus was found in various regions across Africa, Asia, and Europe. The evolutionary journey of humans traces back to this species. Following Dryopithecus came Australopithecus.-
2. Australopithecus: These hominins stood at about 1.2 meters tall and displayed the ability to walk upright. They predominantly inhabited the African continent. Notably, Australopithecus featured large jaws and teeth resembling those of modern humans.-
3. Homo habilis: Standing at a height of around five feet, Homo habilis demonstrated tool-making capabilities and is thought to have had rudimentary speech abilities.-
4. Homo erectus: This species represented a more advanced stage of human evolution. They were bipedal, possessed a larger brain relative to their predecessors, and notably showcased significant advancements, such as the use of fire and a carnivorous diet.-
5. Neanderthals: While Homo sapiens are the sole surviving species of hominins today, in the past, other species like Neanderthals, Denisovans, and Homo floresiensis coexisted with anatomically modern humans. Neanderthals are now considered by scientists to be a subspecies of humans rather than a distinct species.-
6. Homo sapiens: Modern humans, Homo sapiens, are characterized by their cognitive abilities, tool usage, omnivorous diet, and artistic expressions.
|
75 videos|387 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Evolution Chapter Notes - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the main theories of the origin of life? |  |
| 2. What is the theory of evolution and how does it explain the diversity of life on Earth? |  |
| 3. What evidence supports the theory of evolution? |  |
| 4. How have humans evolved over time according to the theory of evolution? |  |
| 5. How does the theory of evolution impact our understanding of life and the natural world? |  |