How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 7
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Do Organisms Create Exact Copies of Themselves? |

|
| Modes of Reproduction Used by Single Organisms |

|
| 1. Asexual Reproduction |

|
| 2. Sexual Reproduction |

|
Introduction
"Have you ever wondered why organisms reproduce, even though it isn’t needed for day-to-day survival like breathing or eating? To understand why, imagine a world where no organisms reproduced—there would be no new plants, animals, or even humans. The world would be very different, right? That’s why reproduction is so important!"
When organisms reproduce, they create new individuals that look a lot like them. It’s like how you might resemble your parents.
- Reproduction is significant because it allows for the existence of large numbers of organisms belonging to a single species.
- If there was only one non-reproducing member of a particular kind, it is unlikely that we would have noticed its existence.
- Organisms belonging to the same species are often identified by their similarity in appearance.
- Reproducing organisms create new individuals that closely resemble themselves.
Do Organisms Create Exact Copies of Themselves?
- Organisms look similar because they share similar body designs, indicating a common source for these designs.
- Reproduction is the process through which these similar designs are created.
- The cell's nucleus contains chromosomes, carrying information for inheriting features, present in the form of DNA molecules.
DNA(Deoxyribonuleic acid) in the nucleus is the source of information for protein synthesis, and changes in this information lead to altered body designs.
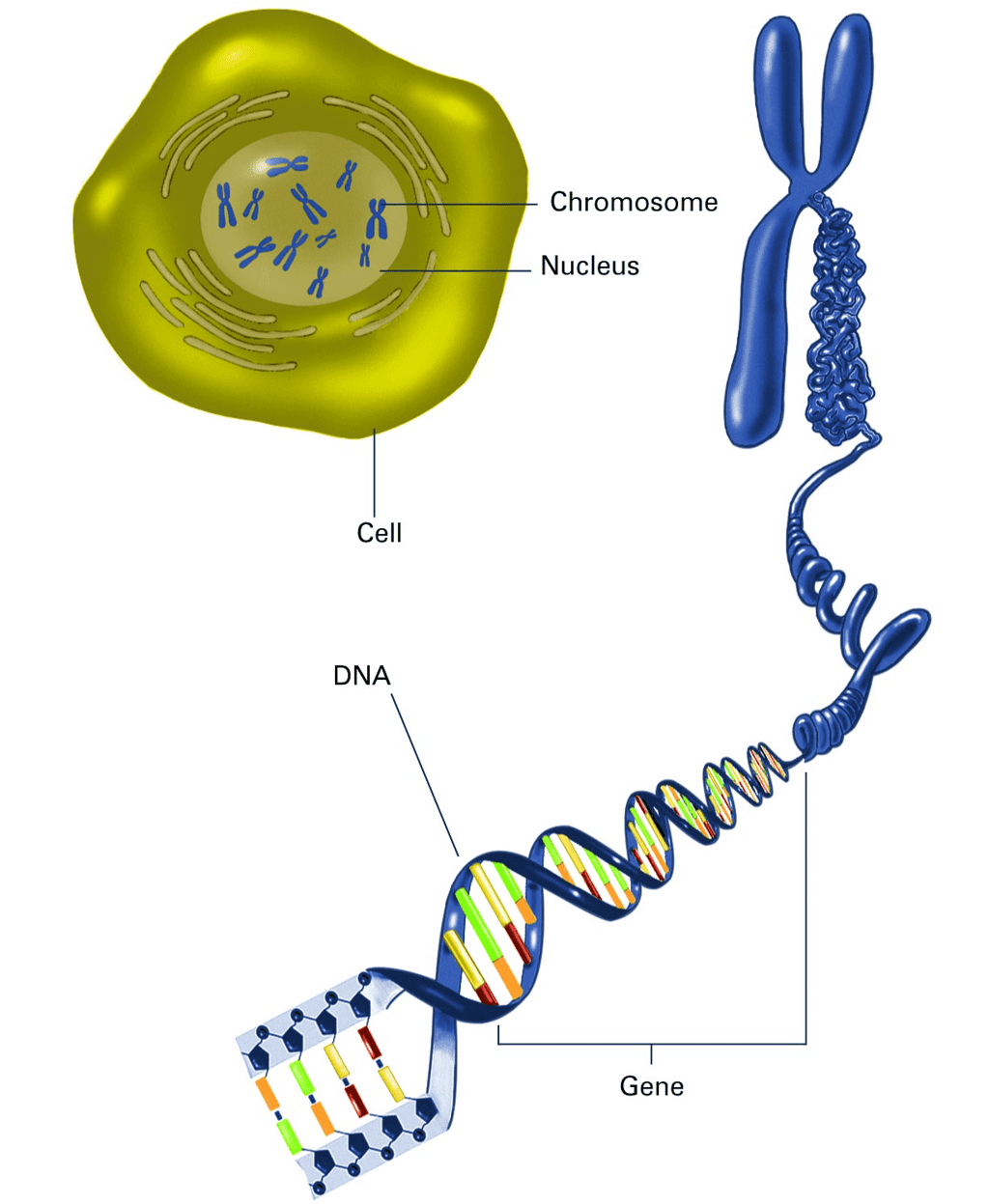 DNA
DNAA fundamental event in reproduction involves the creation of a DNA copy.
DNA copying results in the formation of an additional cellular apparatus, leading to the separation of DNA copies into two cells through cell division.
As DNA copying is a biochemical process, variations may occur each time, making the process not entirely reliable.
If the new DNA copy is not viable, the cell will not survive, and surviving cells may be similar but not identical, subtly differing from each other.
The Importance of Variation
- Reproduction's consistent DNA copying is crucial to preserve an organism's body design, allowing it to occupy a specific space or niche in the ecosystem.
- Reproduction is closely tied to maintaining the stability of a species population.
- Variations become significant as they help organisms adapt to new environmental conditions, ensuring survival.
- In situations with environmental changes, organisms with variations stand a better chance of adapting to new niches, maintaining the species over time.
- For example, if bacteria in temperate waters face a temperature rise due to global warming, variants resistant to heat may survive and prevent the extinction of the entire bacterial species.
- The survival of a species over time relies on the importance of variations.
Modes of Reproduction Used by Single Organisms
Reproduction can be defined as a process that involves the production of an offspring by a particular individual or individuals with the aim of propagating their species. Generally, reproduction happens during the reproductive phase of an organism. The mode of reproduction may vary in organisms. They can be broadly categorised as: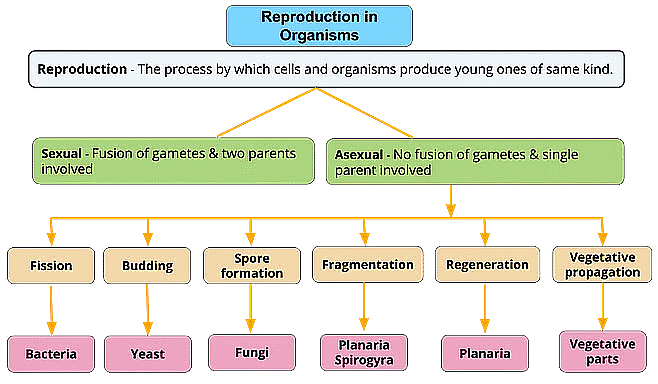
1. Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which the new offspring arise from a single parent. The offsprings are identical to each other, both physically as well as genetically. They are the exact copies of their parent cell. Hence, they are ‘clones’. This mode of reproduction in both unicellular and multicellular organisms.
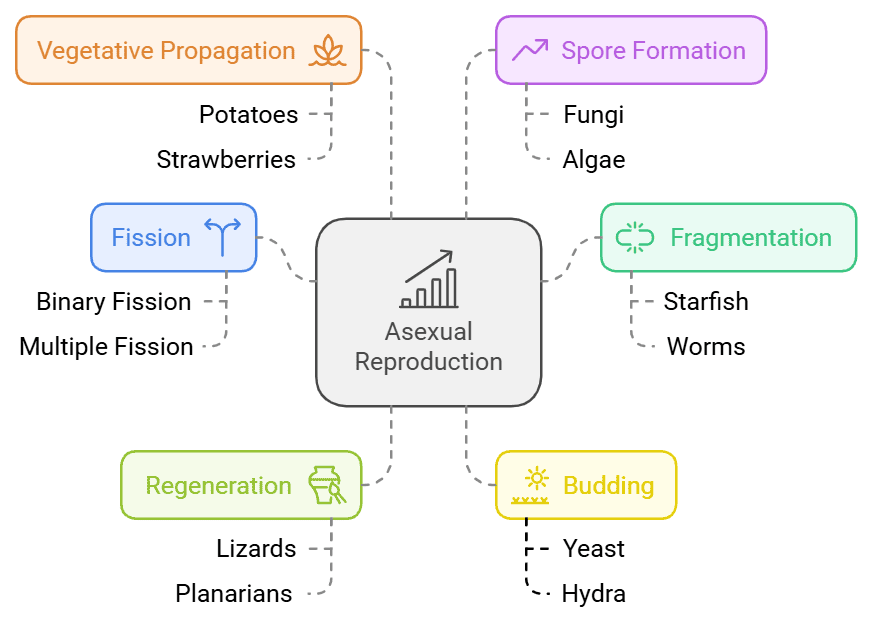
Types of Asexual Mode of Reproduction:
(a) Fission
Fission reproduction refers to a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism splits into two or more parts, and each part develops into a separate individual. The parent cell divides into daughter cells.
Single-celled organisms, like bacteria and amoebas, reproduce by dividing into new cells. Here’s how it works:
Simple Division: Many bacteria and protozoa just split into two equal parts. It’s like cutting a cookie in half.
Amoeba: Amoebas can divide in any direction, not just straight down the middle.
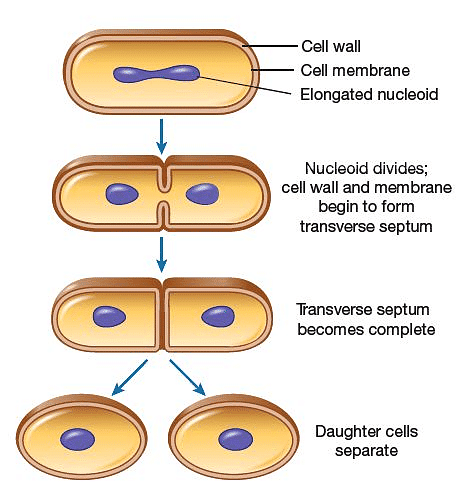 IBinary Fission in Amoeba
IBinary Fission in Amoeba
- Organized Division: Some single-celled organisms, like Leishmania (which has a tail-like structure), divide in a specific direction related to this tail.
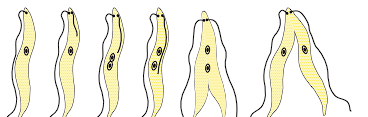 Binary Fission in Leishmania
Binary Fission in Leishmania
Multiple Division: Other organisms, like the malaria parasite Plasmodium, don’t just make two new cells; they split into many new cells all at once.
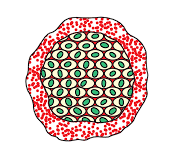 Multiple Fission In Plasmodium
Multiple Fission In Plasmodium
Let's Revise: In which organisms does binary fission take place?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Single-celled organisms, like bacteria and amoebas, reproduce by dividing into new equal cells.
(b) Fragmentation
Fragmentation is a type of asexual reproduction where an organism breaks into fragments, and each fragment develops into a new individual. Example: Spirogyra.
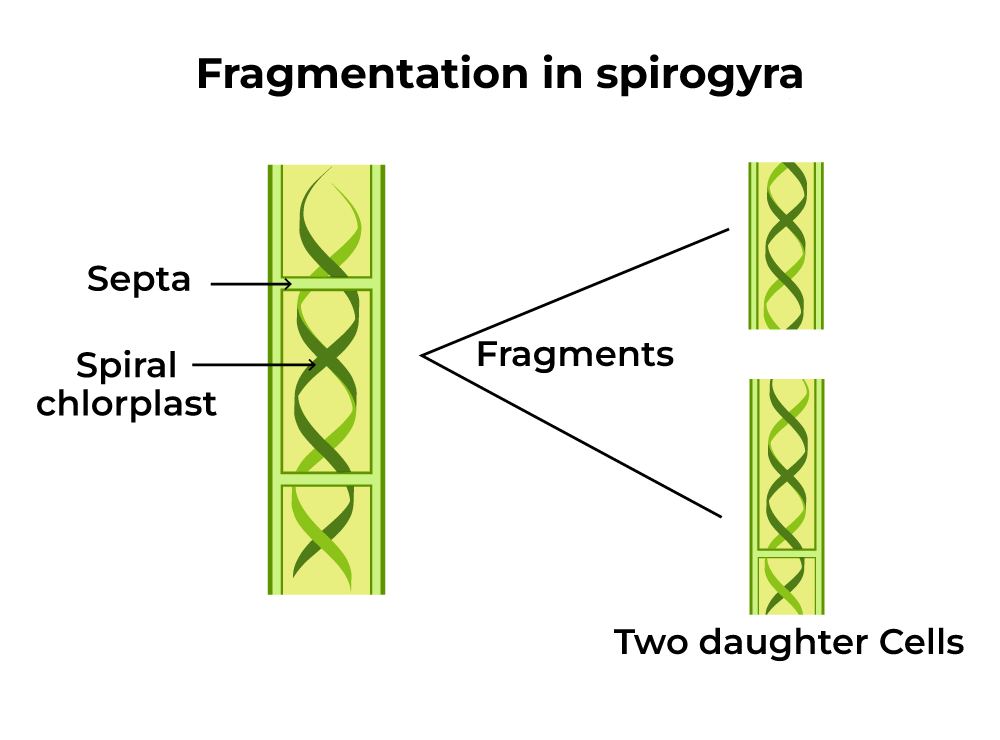
- Simple Reproduction: In simple multi-cellular organisms like Spirogyra, reproduction can happen by breaking into smaller pieces. Each piece grows into a new organism.
- Complex Bodies: More complex organisms, like animals and plants, have specialized cells organized into tissues and organs.
- Specialized Cells: Because these complex organisms have many different cell types, they can't just divide into smaller pieces to reproduce.
- Reproductive Cells: Instead, they use special cells designed for reproduction. These cells can grow and make all the different types of cells needed for the organism.
- Organism Growth: These specialized reproductive cells help create new organisms by producing and organizing all the different cell types required.
Let's Revise: Why can’t complex organisms reproduce by fragmentation?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Because they have specialized cells organised into tissues and organs that can't regenerate from simple fragments.
(c) Regeneration
- When an organism is cut or broken into multiple pieces, and each of those pieces has the ability to develop into a complete and functional organism, it is referred to as regeneration.
- Examples: Animals like Hydra and Planaria can be split into pieces, and each piece can become a new organism.
- Regeneration happens with the help of special cells. These cells quickly make many new cells. From this group of new cells, some change into different types of cells and tissues. This process of changing and organizing cells is called development.
Note: Not the Same as Reproduction: Regeneration is not the same as regular reproduction because most organisms don’t need to be cut to reproduce.
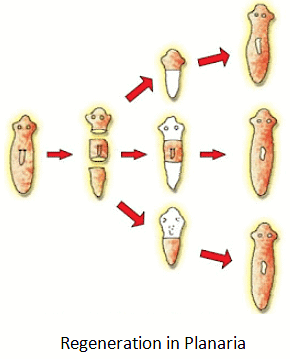
Q: How does regeneration in Hydra differ from typical reproduction?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Regeneration involves regrowing a complete organism from a fragment, not a standard reproductive process.
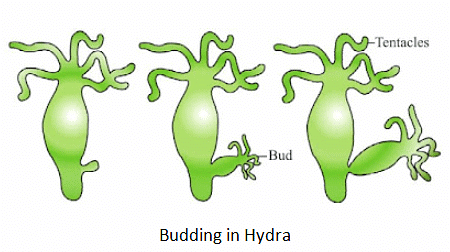
(d) Budding
- In some organisms, a bud forms as a small outgrowth on the parent body. This bud undergoes development and gradually matures into a miniature individual.
- Once matured, the bud detaches from the parent body and continues to grow and develop independently, eventually becoming a fully functional new individual.
- This process is known as budding and is a form of asexual reproduction observed in various organisms.
Example: Hydra
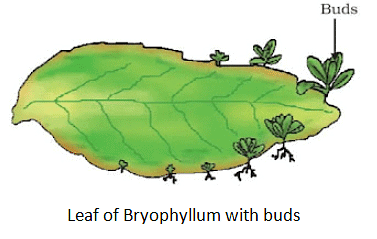
(e) Vegetative Propagation
This is the mode of reproduction by which plants reproduce asexually. In this mode, new plants are developed from a plant’s vegetative parts like stem, leaf, and root.
- Special Methods: Methods like layering and grafting help grow plants such as sugarcane, roses, and grapes.
- Faster Growth: Plants grown this way can produce flowers and fruits quicker than those grown from seeds.
- Seedless Plants: This method helps grow plants like bananas and roses that don’t produce seeds.
- Similar Traits: New plants are very similar to the parent plant and have the same characteristics.
Note: Leaf buds: This is a method in which the buds in the notches of leaves develop into new plants. This can be seen in bryophyllum.
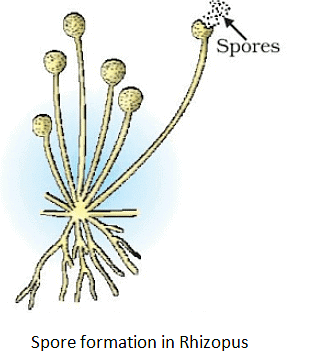
(f) Spore Formation
- Spores are small bulb-like structures that are covered by thick walls. Under favourable conditions, they germinate and produce new organisms.
- The thread-like structures on the bread are called hyphae and they belong to the bread mold Rhizopus. Hyphae are not reproductive parts.
- The tiny structures resembling blobs on a stick are called sporangia and they are involved in reproduction.
- Sporangia contain cells, called spores, which can develop into new individual Rhizopus organisms.
Example: Rhizopus
2. Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction refers to the process of reproduction in which the fusion of male and female gametes occurs, leading to the formation of genetically diverse offspring with unique combinations of traits.
Why the Sexual Mode of Reproduction?
- Sexual reproduction involves a male and a female to produce offspring, contributing to greater variations within a species due to the different patterns of variations in the individuals.
- This method combines DNA from two distinct individuals, creating unique combinations and variations, mixing the gene pool and promoting species survival through genetic recombination.
- Offspring from sexual reproduction have twice the amount of DNA as the previous generation, but germ cells or gametes with half the chromosomes solve this issue.
- Germ cells, specialized for sexual reproduction, vary in complexity among organisms. In simpler organisms, germ cells are similar, while in more complex ones, they differentiate into female (storing food) and male (small and motile) gametes, contributing to the differences in male and female bodies and reproductive systems.
(a) Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual reproduction in plants involves the fusion of male and female gametes, found in the stamen and pistil of flowers.
- The stamen, or male reproductive part, consists of a filament and an anther enclosing pollen grains containing male gametes.
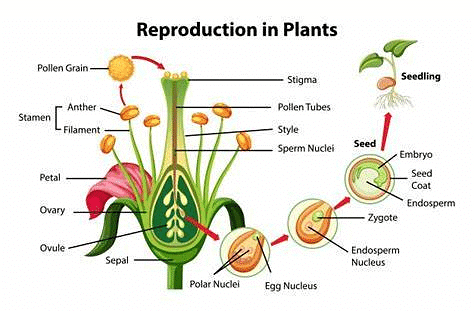
- The pistil, or female reproductive part, comprises the stigma, style, and ovary, with the ovary containing an ovule housing the egg cell.
- Flowers are classified as unisexual (incomplete flowers, having either stamens or pistils) or bisexual (containing both stamens and pistils).
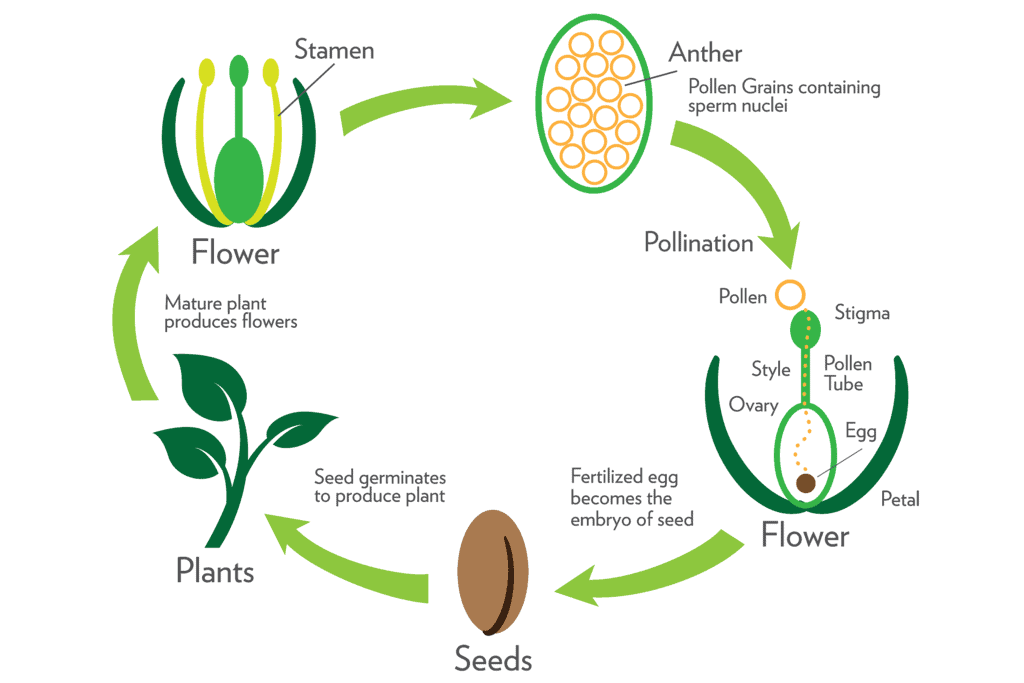
- The process begins with pollination, where pollen grains transfer from the stamen's anther to the pistil's stigma, facilitated by agents like wind, birds, or animals.
- Pollination can be self-pollination (within the same flower) or cross-pollination (between flowers of the same species).
- Fertilization follows, involving the fusion of male and female germ-cells, forming a zygote that develops into an embryo inside the ovule.
- The ovule matures into a seed within the fruit as the flower's other parts shed.
- Germination occurs when the seed, containing the embryo, develops into a seedling under suitable conditions, relying on stored nutrients in cotyledons and protected by a seed coat.
(b) Reproduction in Human Beings
- Human reproduction is sexual, and the reproductive phase is when an individual is ready to have offspring, marked by changes starting from birth.
- Adolescence is a crucial phase for sexual maturation, leading to the development of specialized germ cells during puberty.
- Puberty brings noticeable changes like facial and body hair growth, voice deepening, sweat and sebaceous glands activation, and penis enlargement in boys.
- Girls experience pubic hair growth, breast enlargement, oily skin causing pimples, and the onset of menstruation during puberty.
- Both boys and girls become conscious of their changing appearances.
- Special organs like the penis in males and the uterus in females are essential for the actual transfer of germ cells in sexual reproduction.
Male Reproductive System
- The male reproductive system consists of organs that produce and transport the male germ-cell or gamete, male hormone testosterone and the organs which facilitate the discharge of male germ-cells into the female reproductive system for fertilization.
- The male gamete is the sperm which is a tiny body containing the genetic material and they have a long tail for motility to help them reach the female germ-cell for fertilization.
- The system consists of some external organs like penis, scrotum, testes and internal organs like urethra, prostate and seminal vesicles.
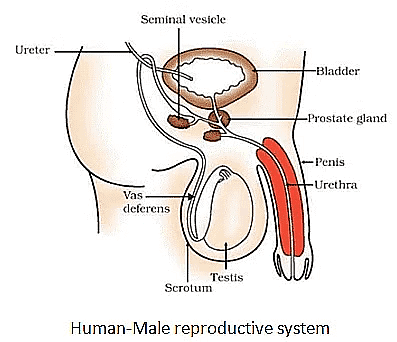
(i) Testes
- A pair of testes are located inside the scrotum which is present outside the abdominal cavity.
- Scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production of sperm.
- Male germ cells i.e. sperms are formed here.
- Testes release the male sex hormone (testosterone).
The function of testes:
- Regulate the production of sperm.
- Bring changes at puberty.
(ii) Vas deferens
- It passes sperm from the testes up to the urethra.
(iii) Urethra
- It is a common passage for both sperm and urine. Its outer covering is called the penis.
(iv) Associated glands
- Seminal vesicles and prostate gland add their secretion to the sperms. This fluid provides nourishment to sperms and makes their transport easy.
- Sperm along with the secretion of glands form semen.
Let's Revise: How does the scrotum contribute to sperm production in the male reproductive system?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The scrotum maintains a lower temperature necessary for the production of viable sperm in the testes.
Female Reproductive System
- The female reproductive system consists of organs responsible for producing female germ cells, facilitating gamete fertilization, and supporting embryo development into a new individual.
- Ovaries are the organs producing female gametes, known as eggs.The ovaries also generate hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, which trigger the development of secondary sexual characteristics in girls during puberty.
- Components of this system include a pair of ovaries, oviducts, uterus, and the vagina, which opens externally through the urethra.
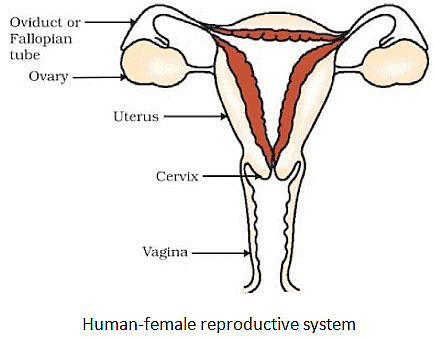
(i) Ovary
- A pair of ovaries are located on both sides of the abdomen.
- Female germ cells i.e. eggs are produced here.
- At the time of birth of a girl, thousands of immature eggs are present in the ovary.
- At the onset of puberty, some of these eggs start maturing.
- One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
(ii) Oviduct or Fallopian tube
- Receives the egg produced by the ovary and transfers it to the uterus.
- Fertilisation i.e. fusion of gametes takes place here.
(iii) Uterus
- It is a bag-like structure where the development of the baby takes place.
- The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
Fertilisation of Egg
1. When the egg is fertilised
- The fertilized egg called a zygote is planted in the uterus and develops into an embryo.
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called the placenta. It provides a large surface area for the exchange of glucose, oxygen and waste material.
- The period from fertilization up to the birth of the baby is called the gestation period. It is about 9 months.
2. When the egg is not fertilised
- The uterus prepares itself every month to receive fertilized eggs.
- The lining of the uterus becomes thick and spongy, required to support the embryo.
- When fertilisation had not taken place, this lining is not needed any longer.
- This lining breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus.
- This cycle takes around 28 days every month and is called menstruation.
Let's Revise
Q: What is the role of the placenta in human reproduction?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The placenta facilitates the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste between the mother and the developing embryo.
Q: Why does menstruation occur in the absence of fertilisation?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Menstruation occurs when the unfertilized egg and the thickened uterine lining are shed as they are not needed for pregnancy.
Reproductive Health
Reproductive health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction i.e. physical, emotional, social and behavioural.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- Many diseases can be sexually transmitted such as:
(i) Bacterial: Gonorrhoea and syphilis
(ii) Viral: Warts and HIV-AIDS - The use of condoms prevents these infections to some extent.
Contraception: It is the avoidance of pregnancy, which can be achieved by preventing the fertilisation of ovum.
Methods of contraception
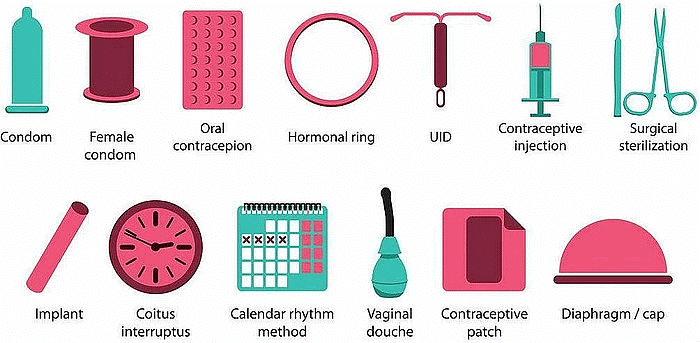
(i) Physical barrier
- To prevent the union of egg and sperm.
- Use of condoms, cervical caps and diaphragm.
(ii) Chemical methods
- Use of oral pills
- These change the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released.
- May have side effects.
(iii) Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD)
- Copper-T or loop is placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
(iv) Surgical methods
- In males, the vas deferens are blocked to prevent sperm transfer called vasectomy.
- In females, the fallopian tube is blocked to prevent egg transfer called tubectomy.
Female Foeticide
- The practice of killing a female child inside the womb is called female foeticide.
- For a healthy society, a balanced sex ratio is needed which can be achieved by educating people to avoid malpractices like female foeticide and prenatal sex determination.
- Prenatal sex determination is a legal offence in our country to maintain a balanced sex ratio.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 7
| 1. What is asexual reproduction and how does it differ from sexual reproduction? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of organisms that reproduce asexually? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction? |  |
| 4. Why is sexual reproduction considered beneficial for the survival of species? |  |
| 5. How do environmental factors influence the mode of reproduction in organisms? |  |
















