Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 10
Introduction
We have already explored how lenses bend light in previous chapters. Now, let's apply these concepts to understand the human eye, which also has a lens. The lens in our eye helps us see by focusing light. This chapter will explain the role of the eye's lens and how spectacles, using different lenses, can correct vision problems.

How Our Eyes Work Like a Camera Lens?
- The image shows how our eyes work like a camera.
- When we observe an object, light rays from that object enter our eyes. Similar to a camera lens, our eyes have a lens that focuses these light rays.
- The eye lens creates an inverted real image on the retina. The retina is a thin layer with many light-sensitive cells that activate when illuminated, producing electrical signals sent to the brain through the optic nerve. The brain then interprets these signals, allowing us to see objects accurately.
- The ability of the eye lens to change its focal length is known as accommodation, enabling us to see clearly at various distances.
- Behind the cornea lies the iris, a dark muscle that controls the size of the pupil, managing the amount of light entering the eye.
The Human Eye
The human eye is a remarkable natural optical instrument that enables us to perceive the world around us. It functions similarly to a camera, employing a complex system of lenses and a screen to capture and process image.Structure of The Human Eye
- Eyeball Shape: The eyeball is roughly spherical, with a diameter of about 2.3 cm.
- Retina: The human eye is like a camera. Its lens system forms an image on a light-sensitive screen called the retina.
- Cornea: Light enters the eye through a thin membrane called the cornea. It forms the transparent bulge on the front surface of the eyeball. Most of the refraction for the light rays entering the eye occurs at the outer surface of the cornea.
 Human Eye
Human Eye - Crystalline Lens: The crystalline lens provides the finer adjustment of the focal length required to focus objects at different distances on the retina.
- Iris: We find a structure called the iris behind the cornea. Iris is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil.
- Pupil: The pupil regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye.
- The eye lens (convex lens) forms an inverted real image of the object on the retina.
- Light Sensitive cells: The retina is a delicate membrane with an enormous number of light-sensitive cells. The light-sensitive cells get activated upon illumination and generate electrical signals. These signals are sent to the brain via the optic nerves. The brain interprets these signals and, finally, processes the information so that we perceive objects as they are.
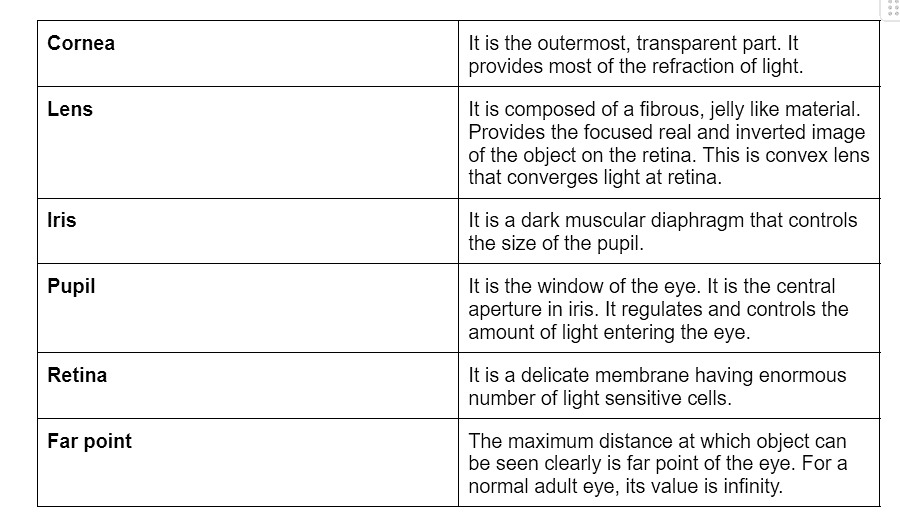 Components of the Human Eye
Components of the Human Eye
Power of Accommodation
- The eye lens is made of a soft, jelly-like material, and its shape can change due to the ciliary muscles.
- When these muscles are relaxed, the lens becomes thinner, which increases its focal length to allow us to see distant objects clearly.
- When focusing on nearby objects, the ciliary muscles contract, making the lens thicker, which decreases its focal length for clear vision.
Power of Accommodation: The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length is called accommodation. Focal length can be changed with the help of ciliary muscles.
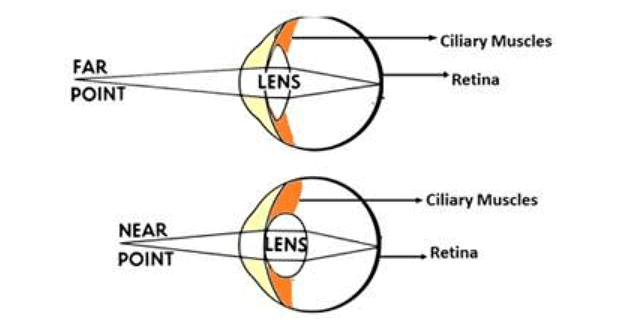 Power of Accomodation
Power of Accomodation
Near point or Least distance of distinct vision:
- The minimum distance at which objects can be seen most distinctively without strain.
- For a normal adult eye, its value is 25 cm.
- Range of human vision – 25 cm to infinity.
The far point of the eye:
- The farthest point up to which the eye can see objects clearly is called the far point of the eye.
- It is infinity for a normal eye.
Cataract:
- Sometimes, the crystalline lens of people in old age becomes milky and cloudy. This condition is called cataract. This causes a partial or complete loss of vision.
- Vision can be restored through a cataract surgery.
Defects of Vision and Their Correction
At times, the eye can experience a gradual decline in its ability to adjust, leading to difficulty in seeing objects clearly and comfortably. This blurriness is caused by refractive issues in the eye.
The three common refractive problems are:
1. Myopia (near-sightedness)
2. Hypermetropia (far-sightedness)
3. Presbyopia.
Spherical lenses are employed to correct these vision defects, and we will explore each of them and their corrections.
1. Myopia (Near sightedness)
- A myopic person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects clearly.
- The image is formed in front of the retina.
Causes of Myopia
- Excessive curvature of the eye lens.
- Elongation of eyeball
Correction of Myopia
- It is done by using the concave lens of appropriate power.

2. Hypermetropia (Far sightedness)
- Affected person can see far objects clearly but cannot see nearby objects clearly.
- The person's near point is located farther away than the usual near point of 25 cm.
- The image is formed behind the retina.
- A person with this condition needs to hold reading material well beyond 25 cm from their eyes for comfortable reading.
- This is due to the fact that light rays from a nearby object are focused at a point behind the retina.
Causes of Hypermetropia
a) The focal length of the eye lens becomes too long.
b) The eyeball has become too small.
Correction of Hypermetropia
- The use of a suitable power convex lens can correct the defect.
 Hypermetropia
Hypermetropia
3. Presbyopia (Old age Hypermetropia)
- As people age, the eye's ability to adjust its focus generally diminishes.
- For most individuals, the near point gradually moves farther away, making it challenging to clearly and comfortably see objects up close without the use of corrective glasses. This condition is known as Presbyopia.
- It is a defect of vision that causes an old person to be unable to see the nearby objects clearly due to loss of power in the accomodation of the eye.
- The near-point of the old person having presbyopia gradually recedes and becomes much more than 25 cm away.

Causes of Presbyopia
- Gradual weakening of ciliary muscles.
- Diminishing flexibility of eye lens.
Correction of Presbyopia
- Use of convex lens of suitable power.
Sometimes a person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia.
Such people require bifocal lens for correction.
Bifocal Lens: The upper part contains a concave lens, which aids in distant vision, while the lower part has a convex lens, which assists with near vision.
Refraction of Light Through a Prism
- Imagine a triangular glass prism with two triangular bases and three rectangular lateral surfaces.
- The angles between these surfaces are called the angles of the prism.
- When a ray of light enters the prism from the air at the first surface (AB), it bends toward the normal.
- As the ray exits through the second surface (AC) and passes from glass to air, it bends away from the normal.
- Due to the unique shape of the prism, the emergent ray deviates at an angle from the original incident ray, known as the angle of deviation, which is denoted as ∠D in this scenario.

- Prism: It is a pyramidal piece of glass with two triangular bases and three rectangular lateral surfaces.
- Angle of Prism: The angle between two adjoining lateral surfaces. Refraction through a glass prism.
- Angle of deviation (d): It is the angle between incident ray and emergent ray.
Dispersion of White Light by a Glass Prism
- When a ray of white light is incident on a glass prism, it splits the incident white light into a band of colours. The various colours seen are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red (VIBGYOR).
- The band of the coloured components of a light beam is called its spectrum.
- The splitting of light into its component colours is called dispersion.
Why do we get these colours? (Cause of Dispersion of Light)
- Different colors of light bend at varying angles relative to the incident ray as they pass through a prism.
- As a result, each color's rays emerge along separate paths, making them distinct.
- This separation of colors forms the band of distinct hues that we observe in a spectrum.
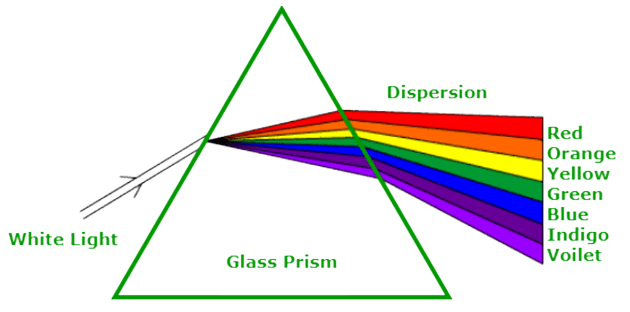 Dispersion of Light
Dispersion of Light
V I B G Y O R
- The angle of deviation ∝ 1/wavelength
- Red is the least deviated colour as it has the largest/longest wavelength.
- Violet is the most deviated colour as it has the smallest wavelength in the visible spectrum.
Recombination of White Light
Issac Newton was the first person to proved that sunlight is made up of seven colours :
(i) He passed sunlight through a glass prism to form a band of seven colours.
(ii) He tried to split the colours further by putting another prism ahead of the prism forming spectrum, but he failed to obtain more colours.
(iii) He formed a spectrum from sunlight and placed an identical but inverted prism in front of the prism, forming the spectrum. All the seven colours combined by the inverted prism and emerged as white light.
Rainbow Formation
- A rainbow is a natural spectrum that appears in the sky following a rain shower.
- It forms when sunlight is dispersed by tiny water droplets in the atmosphere.
- A rainbow always appears in the direction opposite the Sun.
- The water droplets act as small prisms, refracting and dispersing the incoming sunlight, reflecting it inside the droplet, and then refracting it again as it exits.
- This process of light dispersion and internal reflection results in the various colors visible to the observer.
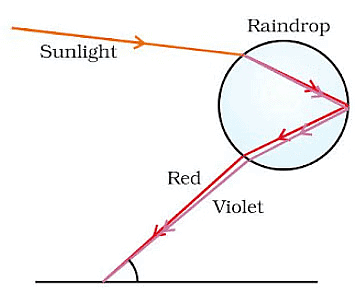 Rainbow Formation
Rainbow Formation
Atmospheric Refraction
The refraction of light by different layers of the atmosphere is called atmospheric refraction.(i) Apparent flickering of objects placed behind a hot object or fire.
(ii) Stars near the horizon appear slightly higher than their actual position.
(iii) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset.
(iv) Twinkling of stars.
(i) An object placed behind the fire or a hot surface appears to flicker when seen through the air.
- The air above the hot surface becomes hot and rises. The space is occupied by cool air. The refractive index of hot air is less than that of cool air.
- So, the physical condition of the medium is not constant.
- Due to the changing Refractive Index (RI) of the medium, the light appears to come from different directions.
- It results in fluctuation in the apparent position of the object.
(ii) Stars, when seen near the horizon, appear slightly higher than their actual position due to atmospheric refraction.

- The refractive index of the earth’s atmosphere, in general, increases from top to bottom.
- So, the light coming from a star near the horizon has to travel from rarer to denser medium and it bends towards the normal.
- As a result, the star appears higher.
(iii) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset
- The sun appears about two minutes earlier than the actual sunrise, and it remains visible for about two minutes after the actual sunset.
- When the sun is below the horizon, the rays have to pass from rarer to denser medium.
- The time difference between the actual sunset and the apparent sunset is approximately 2 minutes.
- So, rays bend towards the normal. As a result, the sun appears higher than its actual position.
(iv) Twinkling of stars
- The twinkling of a star is due to the way starlight is refracted by Earth's atmosphere.
- As starlight enters the atmosphere, it bends continuously because the refractive index of the air changes gradually.
- This bending of light makes the star appear slightly higher in the sky than its actual position, particularly when it is near the horizon.
 Twinkling of Stars
Twinkling of Stars
- Additionally, the star’s apparent position shifts because the atmosphere's conditions are always changing.
- Since stars are so far away that they appear as point sources of light, these slight variations in light paths cause the star's brightness to fluctuate.
- This fluctuation, where the star seems to brighten and dim, creates the twinkling effect.
Why don't the planets twinkle?
- Planets, being much closer to Earth, are viewed as extended sources of light rather than point sources.
- When a planet is considered as a collection of numerous tiny point sources of light, the variations in light from these individual sources average out to zero.
- As a result, the overall light intensity entering our eyes remains relatively stable, which eliminates the twinkling effect seen with stars.
Scattering of Light
- Light interacts with objects to create remarkable natural phenomena, such as the blue sky, the color of deep sea water, and the red hues of sunrise and sunset.
- While the path of light in a true solution is invisible, it becomes visible in a colloidal solution due to the larger particle sizes.
Tyndall Effect
- Earth's atmosphere contains a diverse mix of tiny particles such as smoke, water droplets, dust, and air molecules.
- When light interacts with these fine particles, it becomes visible due to the scattering phenomenon.
- The Tyndall effect is a result of the diffuse reflection of light by colloidal particles in the atmosphere.
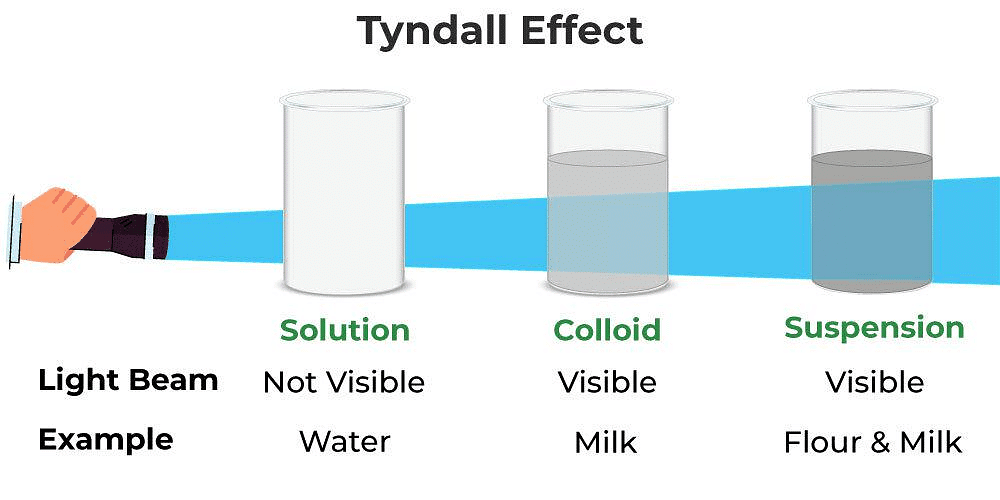 Examples of the Tyndall effect include a sunbeam entering a smoke-filled room, making particles visible, and sunlight passing through a misty forest canopy, where tiny water droplets scatter light.
Examples of the Tyndall effect include a sunbeam entering a smoke-filled room, making particles visible, and sunlight passing through a misty forest canopy, where tiny water droplets scatter light.- The colour of scattered light depends on particle size, with very fine particles primarily scattering the blue light, while larger particles scatter light of longer wavelengths.
- If the scattering particles are large enough, the scattered light may appear white.
Why is the Color of the Clear Sky Blue?
Size of Particles: Molecules of air and fine particles in the atmosphere are smaller than the wavelength of visible light.
Scattering Effectiveness: These particles scatter light of shorter wavelengths (blue) more effectively than light of longer wavelengths (red).
Wavelength Comparison: Red light has a wavelength approximately 1.8 times greater than blue light.

Sunlight and Scattering: As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, blue light (shorter wavelength) is scattered more strongly than red light (longer wavelength).
Sky Color: The scattered blue light is what makes the sky appear blue to us.
Absence of Atmosphere: Without an atmosphere, there would be no scattering, and the sky would appear dark.
High Altitudes: At very high altitudes, the atmosphere is thinner, resulting in less scattering and a darker sky for passengers.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 10
| 1. What are the common defects of vision and how can they be corrected? |  |
| 2. How does refraction of light occur when it passes through a prism? |  |
| 3. What is the phenomenon of dispersion of white light through a glass prism? |  |
| 4. What is atmospheric refraction and how does it affect our perception of objects? |  |
| 5. What is the scattering of light, and why is the sky blue? |  |

















