Local Governments Class 11 Political Science
What Exactly is a Local Government?
Local self-government involves transferring authority to the lowest tiers of the political structure. This system represents democratic decentralization, allowing all society members, including the most basic, to engage in governance. Local self-government is characterized by local entities, elected by the community, managing local matters. This governance structure encompasses both rural and urban administrations and represents the government's third tier.
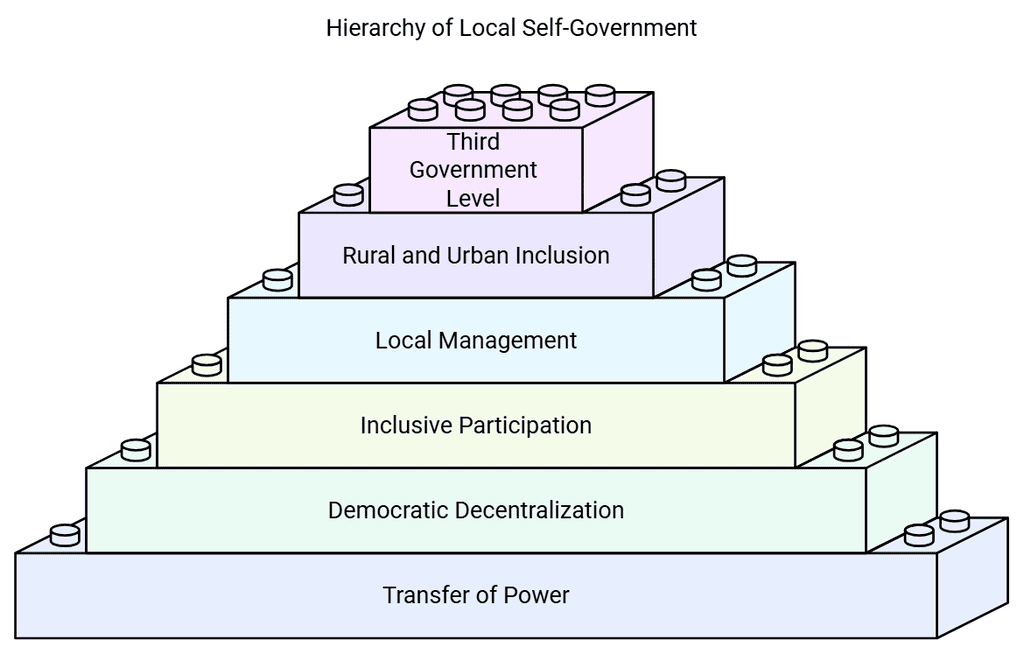
- Transfer of Power: Local self-government transfers authority to the political hierarchy's lowest levels.
- Democratic Decentralization: It embodies democratic decentralization, enabling broad societal participation in administration.
- Inclusive Participation: Even the most fundamental society members are involved in the administrative process.
- Local Management: Management of local affairs is done by local bodies elected by the local populace.
- Rural and Urban Inclusion: The system includes both rural and urban government structures.
- Third Government Level: Local self-government constitutes the third level of government.
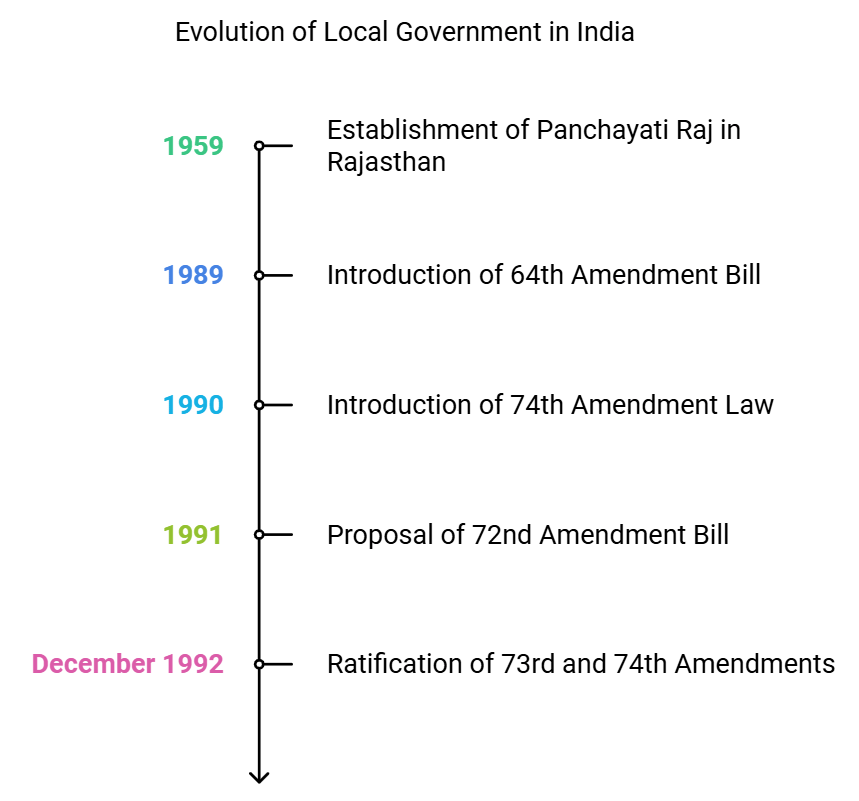
Local Government Evolution
- Establishment of Panchayati Raj (1959): Rajasthan pioneered the Panchayati Raj system in India in Nagaur district. Soon after, Andhra Pradesh followed, with other states adopting the system.
- Key Concerns: The design of local self-government, the extent of power devolution, and financial considerations were major challenges.
- Formation of Committees:To address these challenges, the union government formed several committees, including:
- Balwant Rai Mehta Committee
- Ashok Mehta Committee
- G V K Rao Committee
- L M Singhvi Committee
- Thungon Committee
- Gadgil Committee
- Emphasis on Constitutional Status: Committees, particularly the L M Singhvi, Thungon, and Gadgil Committees, highlighted the need for constitutional recognition of Panchayat Raj Institutions (PRIs).
- Constitutional Amendment Efforts:
- 64th Amendment Bill (1989): Introduced by Rajiv Gandhi to empower PRIs, but rejected by the Rajya Sabha.
- Constitution (74th Amendment) Law (1990): Aimed at both PRIs and municipalities, introduced but not debated.
- Constitution 72nd Amendment Bill (1991): Under P.V. Narasimha Rao's prime ministership, a comprehensive amendment was proposed.
- Ratification of Amendments (1992): Parliament ratified the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments in December 1992, leading to the establishment of local self-government in both rural and urban India.
Local Government Structure in India
Types of Local Government in India: There are two main categories:
- Panchayati Raj
- Municipalities
The Panchayati Raj system
- Panchayati Raj Definition: A system of rural local self-government in India.
- Constitutionalization: Established by the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992, which institutionalized democracy at the grassroots level.
- First Implementations: Rajasthan and Andhra Pradesh were the first states to implement Panchayati Raj in 1959.
- Panchayati Raj Institution (PRI): Established for rural development and fostering grassroots democracy.
- 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act: This act introduced Part-IX to the Constitution, titled ‘The Panchayats’, encompassing Articles 243 to 243 O.
- Addition of Eleventh Schedule: Included 29 functional items for panchayats under Article 243-G.
- Current Status: PRI has been operational for 30 years in its present form, with an ongoing need for further decentralization and strengthening of grassroots democracy.
Municipalities
- Municipalities Definition: Urban local self-government units in India.
- Urban Local Government: Governance of urban areas by elected representatives.
- Purpose of Urban Local Governments: Facilitate democratic decentralization in urban areas.
- Types of Urban Local Governments: There are eight types in India:
- Municipal Corporation
- Municipality
- Notified Area Committee
- Town Area Committee
- Cantonment Board
- Township
- Port Trust
- Special Purpose Agency
- Central Oversight Ministries:
- Ministry of Urban Development (now Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs), established in 1985.
- Ministry of Defense for Cantonment Boards.
- Ministry of Home Affairs for Union Territories.
- 74th Amendment Act (1992): Passed during P.V. Narasimha Rao’s government, effective from June 1, 1993.
- Added Part IX-A to the Constitution, with provisions from Articles 243-P to 243-ZG.
- Included a 12th Schedule with 18 municipal functional items, under Article 243 W.
- Jurisdiction: Urban local governments have jurisdiction within specific urban areas as delineated by state governments. The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Ministry of Defence, and Ministry of Home Affairs oversee these governments in states, cantonment boards, and Union Territories, respectively.
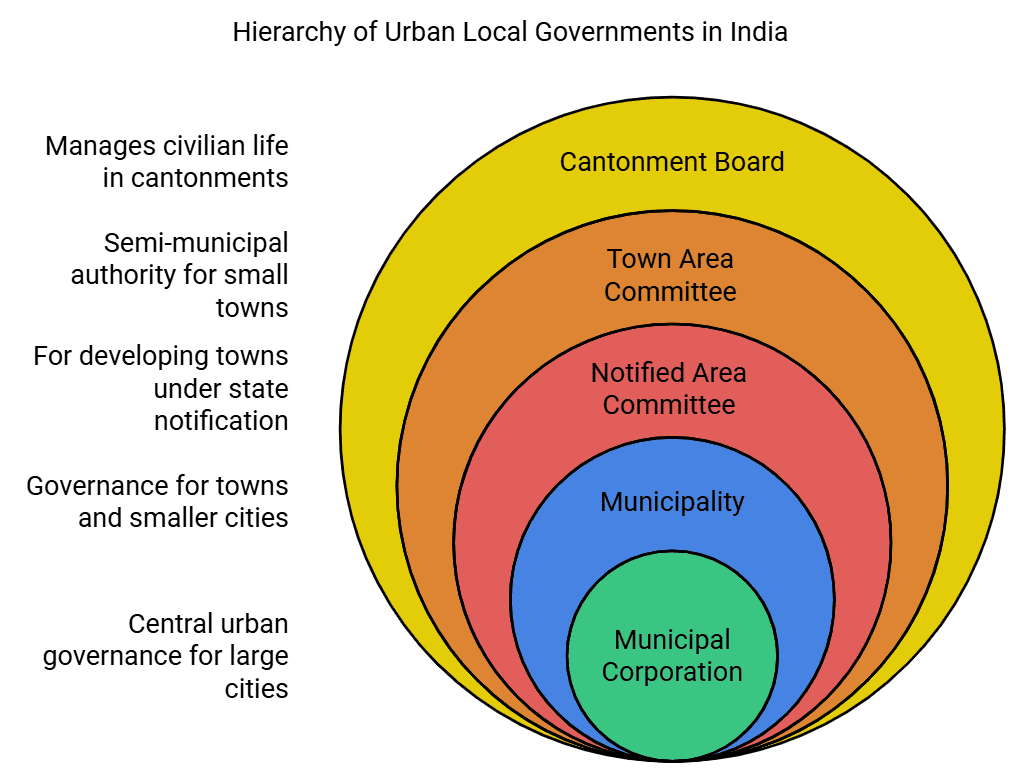
Eight Types of Urban Local Governments in India
Municipal Corporation
- For big city administration.
- Structure: Council (legislative), Standing Committee, and Commissioner (executive).
- Council: Directly elected councilors led by a Mayor.
Municipality
- For towns and smaller cities.
- Variants: Known as municipal council, committee, board, borough municipality, city municipality.
- Leadership: Headed by a President/Chairman; a Chief Executive Officer/Chief Municipal Officer instead of a commissioner.
Notified Area Committee
- For fast-developing towns not meeting municipality criteria.
- Formation: By state government notification.
- Structure: Nominated body, neither statutory nor elected.
Town Area Committee
- For small town administration.
- Nature: Semi-municipal authority with limited civic functions.
- Composition: May be elected, nominated, or both as per state government.
Cantonment Board
- Manages civilian population in cantonment areas.
- Established under Cantonment Act, 2006.
- Oversight: Defence Ministry.
- Composition: Partly elected, partly nominated.
- Leadership: President (military officer), Vice President (elected member), Executive Officer (appointed by President of India).
Township
- Created by public enterprises for staff and workers.
- Structure: Non-elected, members appointed by the enterprise.
Port Trust
- Manages ports and provides civic amenities.
- Structure: Combination of elected and nominated members.
- Establishment: By Act of Parliament.
Special Purpose Agency
- For specific functions or activities.
- Nature: Known as single purpose, uni-purpose, or functional local bodies (e.g., Delhi Metro Rail Corporation).
- Formation: Either statutory body by state act or department by executive resolution.
- Independence: Autonomous, not subordinate to local municipal bodies.
Note: Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) do not exist in Arunachal Pradesh.
Metropolitan Area
Criteria for Area Classification (Article 243P)
- An area with a population exceeding 10 Lakh.
Tribal Areas (As of 2019)
- Total of ten autonomous districts in four states:
- Assam: Three tribal areas.
- Meghalaya: Three tribal areas.
- Tripura: One tribal area.
- Mizoram: Three tribal areas.
- Governance: Administered under the 6th Schedule of the Constitution, focusing on these four states.
Census Definition Of Urban Areas In India
- Population Requirement: A minimum of 5,000 inhabitants.
- Employment Criterion: At least 75% of the male working population engaged in non-agricultural activities.
- Population Density: A minimum of 400 individuals per square kilometer.
Central Council Of Local Government
- Establishment Year: Set up in 1954.
- Constitutional Basis: Constituted under Article 263 (Inter-state Council) of the Indian Constitution by a Presidential order as an advisory body.
- Chairperson: The Union Minister for Urban Development.
- Composition: Includes the Minister in the Government of India and the ministers responsible for local self-government in states.
Salient Features of the 73rd Constitutional Amendment
Mandatory Provisions
- Gram Sabha Organization: Formation is required.
- Three-Tiered Structure: Establishment of Panchayati Raj at Zila, Block, and Village levels.
- Direct Elections: Positions at all levels to be filled through direct elections.
- Minimum Age for Candidacy: 21 years for Panchayati Raj institutions elections.
- Indirect Election of Chairpersons: At Zila and Block levels, chairpersons are elected indirectly.
- Reservation of Seats:
- For Scheduled Castes/Scheduled Tribes: Proportional to their population.
- For Women: Up to one-third of the seats in Panchayats.
- State Election Commission: Each state to establish a commission for overseeing Panchayati Raj elections.
- Tenure and Elections:
- Five-year tenure for Panchayati Raj institutions.
- New elections within six months if dissolved earlier.
- State Finance Commission: Convenes every five years in each state.
Voluntary Provisions
- Voting Rights: To members of Central and State legislatures in these bodies.
- Backward Classes Reservation: Provision for reservations.
- Financial Powers and Autonomy:
- Panchayati Raj institutions should have authority over taxes, levies, etc.
- Efforts for making Panchayats autonomous bodies.
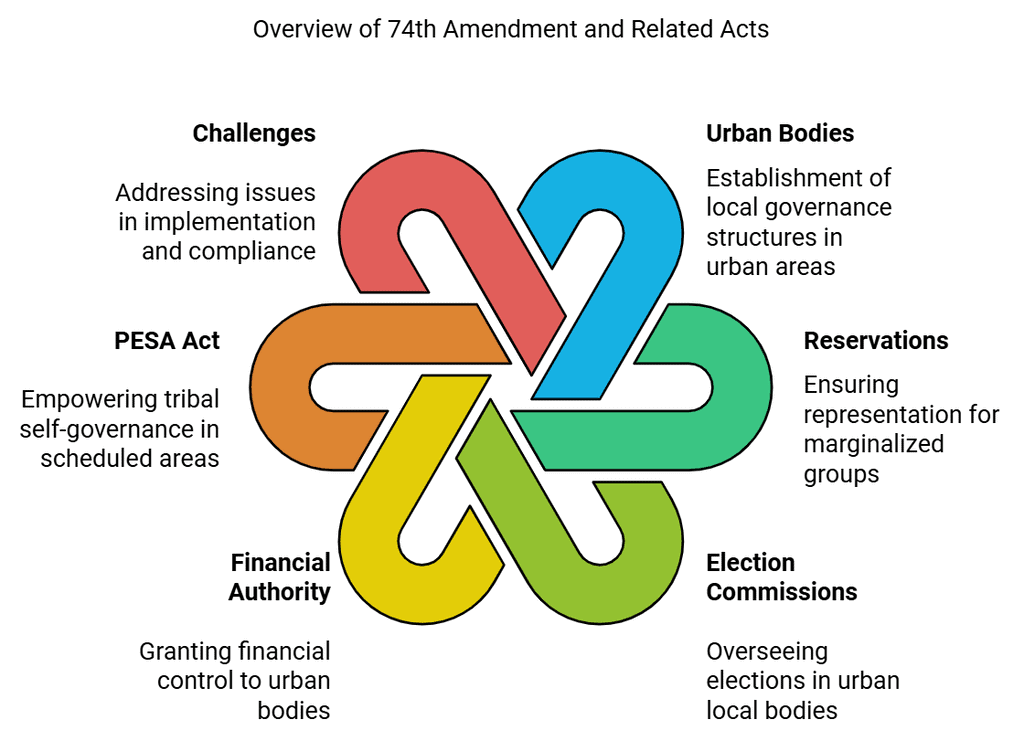
Salient Features of the 74th Amendment Act
Compulsory Provisions- Establishment of Urban Bodies: Constitution of nagar panchayats, municipal councils, and municipal corporations in small, medium, and large urban areas.
- Reservation for SC/ST: Seats in urban local bodies reserved for Scheduled Castes / Scheduled Tribes based on population.
- Women's Reservation: Up to one-third of seats reserved for women.
- State Election Commission Role: Oversee elections in both Panchayati Raj bodies (as per the 73rd Amendment) and urban local self-government bodies.
- State Finance Commission Duties: Manage financial affairs of both Panchayati raj bodies and local urban self-government bodies.
- Tenure of Urban Bodies: Fixed at five years; new elections within six months if dissolved earlier.
Voluntary Provisions
- Voting Rights: For members of Union and State Legislatures in these bodies.
- Backward Classes Reservation: Provision for reservations.
- Financial Authority: Granting urban bodies control over taxes, duties, tolls, fees, etc.
- Municipal Autonomy and Powers:
- Make municipal bodies autonomous.
- Delegate powers to perform functions listed in the Twelfth Schedule added by this Act.
- Empower them to prepare economic development plans.
Panchayat (Extension of the Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996
- 73rd and 74th Amendments (1992): Extended the three-tier Panchayati Raj governance structure to both rural and urban India, effective April 1993.
- Exemption of Scheduled Areas: Areas predominantly inhabited by tribal populations were exempt from these amendments.
- Demand for Empowerment in Scheduled Areas: Recognizing low human development indicators, there was a call for local governance empowerment in these areas.
- Committee Formation (1994): The Indian government established a committee to evaluate the need for such laws in scheduled areas and the modalities of their extension.
- Committee Chair: Dilip Singh Bhuria, a Member of Parliament from Madhya Pradesh, led the committee.
- Committee's Focus: Addressed the challenges and exploitation faced by tribal communities.
- Recommendations Submission (1995): The committee presented its findings and recommendations in 1995.
Panchayat Extension to Scheduled Areas Act, 1996
Background
- 73rd and 74th Amendments (1992): Extended Panchayati Raj to rural and urban areas; effective April 1993.
- Exemption: Scheduled areas with tribal populations exempted from these amendments.
- Demand for Empowerment: Call for local governance in scheduled areas.
- Dilip Singh Bhuria Committee (1994): Assessed the need for laws in scheduled areas.
- Committee’s Recommendations (1995): Addressed tribal communities' exploitation and rights.
PESA Act 1996
- Enactment and Implementation: Passed in 1996, effective from 24th December 1996.
- Applicability: In Fifth Schedule areas across 10 states: Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Telangana.
Objectives
- Extension of Part IX: Apply Panchayat provisions to Scheduled Areas with modifications.
- Self-Rule: Empower the majority of the tribal population.
- Village Governance: Make Gram Sabha the center of all activities.
- Traditional Practices: Respect and integrate traditional practices.
- Preservation: Safeguard tribal customs and traditions.
Powers of Gram Sabhas under PESA
- Regulation of Intoxicants: Control the sale and consumption of intoxicants.
- Ownership of Forest Produce: Manage minor forest produce.
- Land Protection: Prevent and restore alienated tribal land.
- Market Management: Handle village markets.
- Money Lending Control: Oversee lending to Scheduled Tribes.
- Institutional Control: Over social sector institutions and functionaries.
- Local Planning: Handle local plans and resources, including tribal sub-plans.
Supreme Court Case (2013)
- Niyamgiri Hills Mining: Supreme Court directed Odisha to seek Gram Sabha permission.
- Result: Gram Sabha denied permission, leading to project cancellation.
- Milestone: Demonstrated Gram Sabha's power under PESA.
Significance
- Decentralization: Empower indigenous communities and promote participatory democracy.
- Gandhian Concept: Based on Gram Swaraj, operationalized by PESA.
- Self-Governance: Strengthen village autonomy and local decision-making.
Challenges
- Implementation Issues: Act termed “toothless” with inadequate rule formulation.
- Lack of State Compliance: Incomplete or absent Panchayat Raj Act amendments.
- Legislative Overlap: Other laws like Land Acquisition Act and Forest Right Act overshadow PESA.
- Infringements: Violations of self-governance rights, especially in resource management.
Way Forward
- Adherence to Sixth Schedule: Pattern structures above Gram Sabha on it.
- Empowerment of Gram Sabha: Allocate state powers without overriding Gram Sabha.
- Implementation Focus: Commit to implementing PESA effectively.
- Harmonizing Conflicts: Resolve inconsistencies between Gram Sabhas and Panchayats.
- Law Amendments: State governments to align laws with PESA.
- Serious Implementation Efforts: Recognize pitfalls and promote tribal self-rule policies.
Successes of Decentralisation in India
Introduction
- Democratic Decentralization: Devolving state functions and resources to lower levels for direct citizen participation in governance.
- Indian Constitution View: Devolution is more than delegation, including defined functions, financial grants, tax handles, and staff for local governments.
Related Constitutional Provisions
- State Subject: Local government, including panchayats, is under state jurisdiction.
- Election Mandate: Panchayats and municipalities must be elected every five years.
- 73rd and 74th Amendments: Mandated elected local governments in India, establishing PRIs.
- Constitutional Parts: Part IX “The Panchayats” and Part IXA “The Municipalities” added.
- Schedules: Powers and responsibilities of Panchayats in 11th Schedule, Municipalities in 12th Schedule.
- Article 40: Establishment of village panchayats.
Major Achievements of Local Bodies
- Female Representation: Increased significantly post-73rd Amendment.
- Current Statistics: 260,512 Panchayats, 3.1 million representatives, 1.3 million women.
- Comparison: Women's representation higher in local bodies than in Parliament and State Assemblies.
Issues with Local Governments in India
- Inadequate Funding: Insufficient funds and rigid budget spending.
- Infrastructure Issues: Lack of dedicated buildings and basic amenities for Gram Panchayats.
- Internet Accessibility: Operational issues with internet access in GPs.
- Personnel Shortage: Insufficient staff, leading to inefficiency.
- Election Delays: Frequent postponements, violating constitutional mandate.
- Role Reduction: Local governments seen as implementers, not policy-makers.
- Corruption: Involvement of criminal elements and contractors, no proof of increased corruption due to decentralization.
Way Forward
- Revitalize Gram Sabhas: Essential for real-world participation.
- Strengthen Organizational Structure: Ensure adequate manpower in local governments.
- Taxation Mechanism: Implement comprehensive local taxation systems.
- Funding Management: Monitor Finance Commission grants’ release and expenditure.
- Local Audits: Encourage Panchayats to conduct regular audits for financial accountability.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Local Governments Class 11 Political Science
| 1. What is the role of local government in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the 73rd Constitutional Amendment? |  |
| 3. How are urban local bodies structured in India? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the 74th Amendment Act? |  |
| 5. What is the Panchayat (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996? |  |






















