Cheat Sheet: Anti-Defection Law | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The Anti-Defection Law, introduced through the 52nd Amendment Act of 1985, aims to curb political defections by disqualifying legislators who switch parties, ensuring stability in governance. Later refined by the 91st Amendment Act of 2003, it addresses the issue of political loyalty and democratic integrity. This chapter outlines the law’s provisions, advantages, criticisms, amendments, and challenges, providing a concise reference for understanding its role in India’s political system.
Provisions of the Anti-Defection Law
The Tenth Schedule, added by the 52nd Amendment Act of 1985, outlines rules for disqualifying legislators who defect from their political party, with exceptions for specific cases.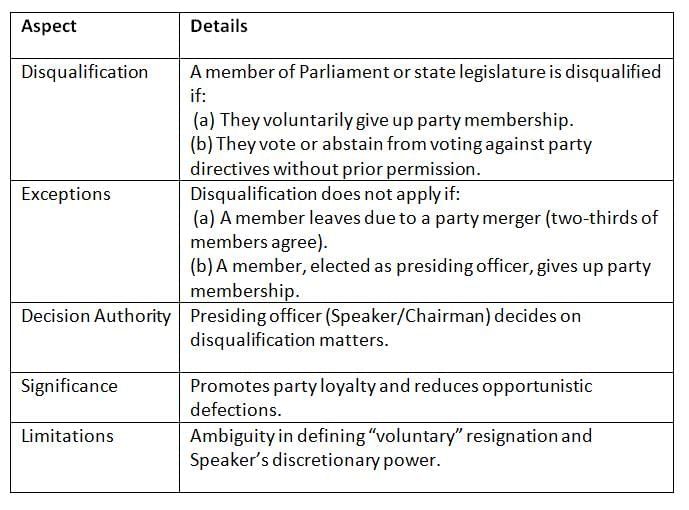
Key Points: The law discourages defections by imposing disqualification, with exceptions for mergers and presiding officers, but relies heavily on the Speaker’s judgment.
Advantages of the Anti-Defection Law
The law was enacted to stabilize governments and strengthen democratic processes by curbing frequent party-switching.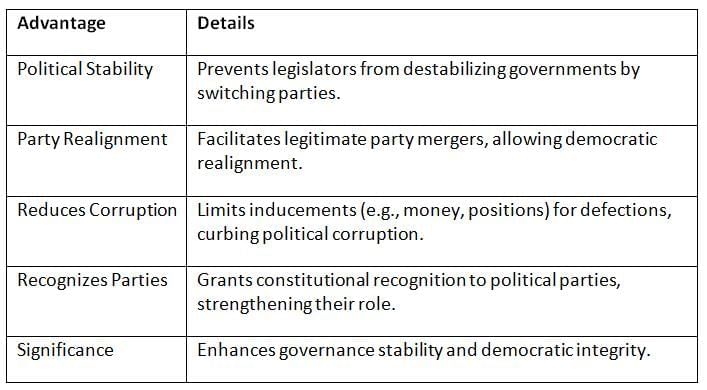 Key Points: The law promotes stability, reduces corrupt practices, and acknowledges the importance of political parties in democracy.
Key Points: The law promotes stability, reduces corrupt practices, and acknowledges the importance of political parties in democracy.
Criticisms of the Anti-Defection Law
Despite its objectives, the law has faced criticism for limiting legislators’ freedom and failing to fully address defection issues.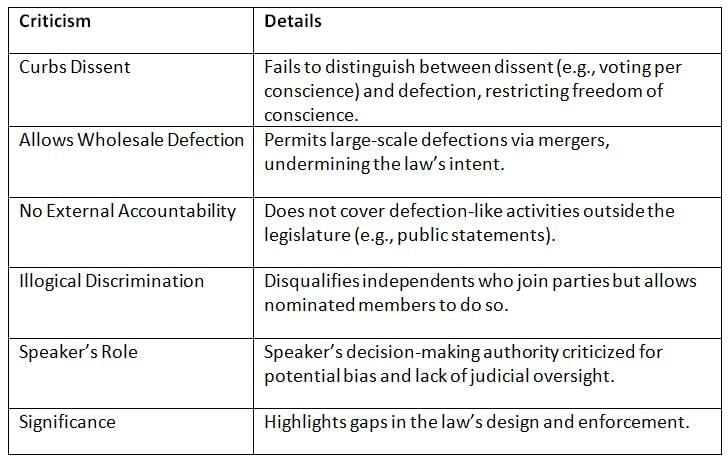
Key Points: The law restricts legitimate dissent, allows loopholes for mass defections, and raises concerns about the Speaker’s impartiality.
91st Amendment Act (2003)
The 91st Amendment Act addressed shortcomings in the original law, responding to recommendations from various committees and commissions.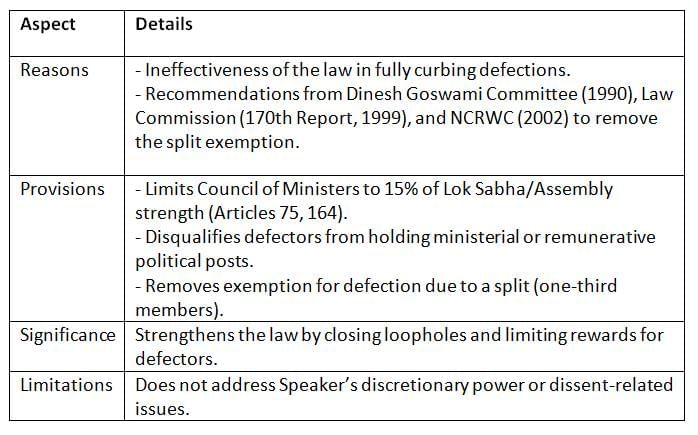
Key Points: The 91st Amendment tightened anti-defection rules by eliminating the split exemption and restricting defectors’ rewards, but some gaps remain.
Challenges and Issues (The Big Picture)
Recent political crises, such as in Karnataka and Goa, highlight ongoing challenges with the law, particularly around resignations and Speaker’s powers.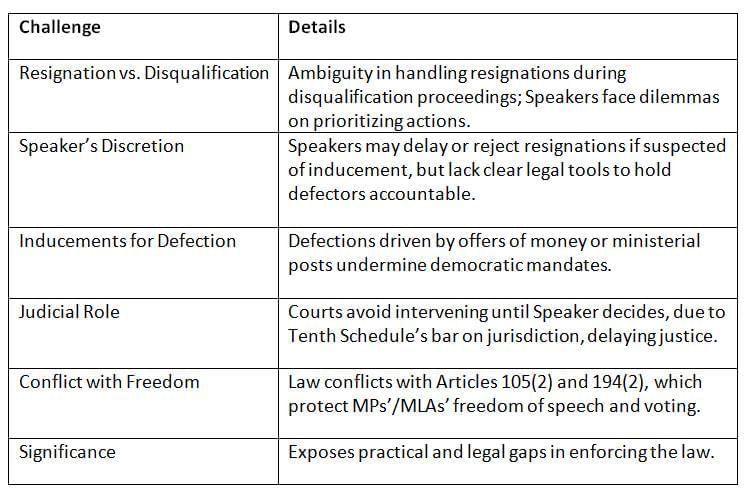 Key Points: Challenges like resignation-disqualification conflicts and Speaker’s discretion reveal enforcement weaknesses, as seen in Karnataka’s political crisis.
Key Points: Challenges like resignation-disqualification conflicts and Speaker’s discretion reveal enforcement weaknesses, as seen in Karnataka’s political crisis.
Way Forward
Addressing the law’s shortcomings requires reforms to balance party loyalty with legislators’ freedom and ensure impartial enforcement.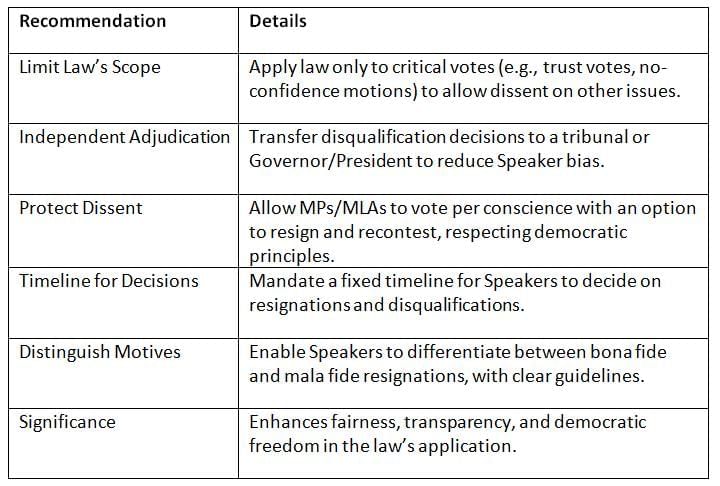
Key Points: Reforms like independent adjudication and protecting dissent can strengthen the law while respecting legislators’ rights.
Chronology of Key Developments
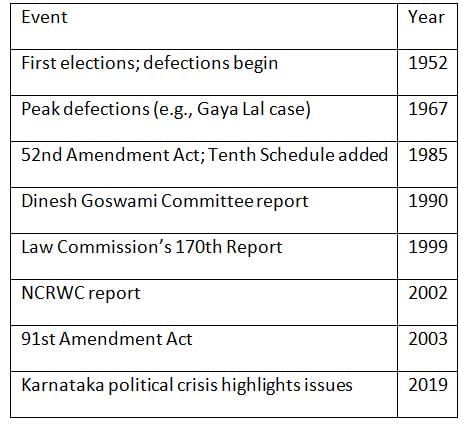
Conclusion
The Anti-Defection Law, introduced to ensure political stability and curb opportunistic defections, has significantly shaped India’s legislative framework. While it promotes party loyalty and reduces corruption, it faces criticism for stifling dissent and allowing loopholes like wholesale defections. The 91st Amendment addressed some issues, but challenges, as seen in crises like Karnataka, underscore the need for reforms. By refining its scope and enforcement, the law can better balance democratic principles with governance stability.
|
162 videos|999 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Anti-Defection Law - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the primary purpose of the Anti-Defection Law in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key provisions outlined in the Anti-Defection Law? |  |
| 3. What are some advantages of implementing the Anti-Defection Law? |  |
| 4. What are the main criticisms against the Anti-Defection Law? |  |
| 5. What changes were introduced by the 91st Amendment Act regarding the Anti-Defection Law? |  |
















