UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Cheat Sheet: Burning Socio-Economic Issues
Cheat Sheet: Burning Socio-Economic Issues | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Unemployment
- Youth Unemployment Rate (2024-25): ~16% (PLFS)
- High incidence of educated unemployment, especially among graduates and postgraduates.
- Rise in gig economy, but concerns over social security, job quality.
- Skewed employment: Agriculture still employs ~45% but contributes <18% to GDP.
- Women’s LFPR (Labour Force Participation Rate) still low (~25%).
Government Initiatives:
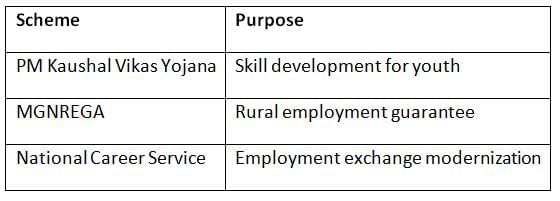
Poverty and Inequality
- Multidimensional Poverty in India reduced from 25% (2015-16) to 11.3% (2019-21), but income inequality has widened.
- Gini coefficient (income inequality): ~0.35 (2024 est.)
- Urban-rural income gap persists; concentration of wealth among top 1% (Oxfam report 2024).
Malnutrition and Hunger
- Global Hunger Index 2024: India ranks 111/125 – "serious" category.
- Child stunting (NFHS-5): 35.5%; wasting: 19.3%
- Low per capita consumption of protein, fruits, and dairy.
Key Schemes:
- POSHAN 2.0
- Mid-Day Meal (PM Poshan)
- National Food Security Act (NFSA) – covers ~75% rural, ~50% urban population.
Health Infrastructure & Access
- Health spending: ~2.1% of GDP (below global average).
- Out-of-pocket expenditure: ~47% of total health expenditure.
- Doctor-population ratio: 1:854 (WHO norm: 1:1000).
- Post-COVID focus on primary health and digital health (Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission).
Education and Skill Gap
- Dropout rates still high in secondary level; digital divide worsens learning outcomes.
- ASER 2023: Learning losses persist in reading/math post-pandemic.
- NEP 2020 implementation ongoing: Focus on early childhood care, vocational training.
Gender Disparities
- Female Labour Force Participation Rate (2024): ~25%
- Gender gap in pay, access to leadership, and land ownership continues.
- Rise in crimes against women and low conviction rates.
- Digital Gender Divide: Only ~30% women in rural areas use smartphones regularly.
Important Scheme: Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao | Mission Shakti | Saksham Anganwadi
Urbanisation & Slum Development
- Urban population (2025): ~37% of total.
- Infrastructure under strain: housing shortage, waste management, pollution.
- Smart Cities Mission progress mixed; many projects delayed due to funding and governance issues.
Migration & Informal Sector
- Informal sector: >80% of India’s workforce.
- Lack of social security, income vulnerability.
- Post-COVID migration led to renewed push for One Nation One Ration Card, e-Shram portal.
Environmental Inequity
- Disproportionate impact of pollution, climate change on the poor.
- Urban poor in slums most affected by heatwaves, water scarcity.
- Crop losses and rural indebtedness linked with climate variability.
Digital Divide
- While digital penetration has increased (~65% Internet users), gaps remain in rural India.
- Challenges: language, affordability, gender, digital literacy.
- Important for access to education, health, financial services.
Caste, Class, and Social Discrimination
- Caste-based discrimination still prevalent in rural areas, manual scavenging persists.
- Economic marginalization of Dalits and Adivasis.
- EWS Reservation (10%) upheld by Supreme Court in 2022—ongoing debates.
Aging Population
- By 2036, ~15% of India's population will be >60 years old.
- Lack of social security and elderly care infrastructure.
- Rise in old-age poverty and abandonment.
Drug Abuse and Mental Health
- Rise in mental health issues post-pandemic (especially among youth and women).
- National Mental Health Programme underfunded.
- Drug abuse in Punjab, NE, metro cities—linked with crime and unemployment.
Rural-Urban Divide
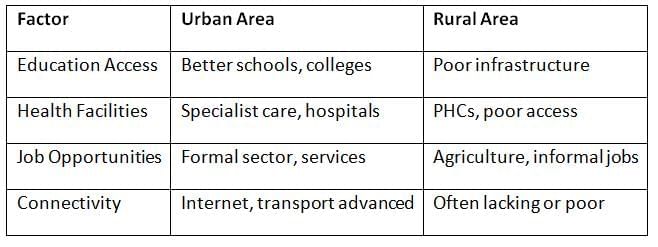
Recent Initiatives & Reports (2024–2025)
- Economic Survey 2024-25: Emphasized human capital investment and reducing inequality.
- NITI Aayog’s SDG India Index 2024: Identified inter-state disparities in health, education, gender.
- Global Gender Gap Report 2024: India ranked 127/146; major gap in political and economic participation.
The document Cheat Sheet: Burning Socio-Economic Issues | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Burning Socio-Economic Issues - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the primary causes of unemployment in contemporary society? |  |
Ans. Unemployment can be attributed to various factors, including economic downturns, technological advancements leading to automation, lack of required skills among the workforce, and structural changes in industries. Additionally, social factors such as discrimination and geographic mobility can also contribute to persistent unemployment rates.
| 2. How does poverty and inequality affect socio-economic development? |  |
Ans. Poverty and inequality hinder socio-economic development by limiting access to essential services such as education and healthcare. They create a cycle where the disadvantaged lack opportunities for upward mobility. High levels of inequality can also lead to social unrest and reduce overall economic growth by creating disparities in consumption and investment.
| 3. What are the impacts of malnutrition and hunger on society? |  |
Ans. Malnutrition and hunger significantly impact public health, leading to higher rates of disease and mortality, particularly among children. These conditions can impair cognitive development, affecting educational outcomes and productivity in adulthood. Furthermore, they strain healthcare systems and reduce economic development potential, perpetuating cycles of poverty.
| 4. How does health infrastructure and access influence quality of life? |  |
Ans. Robust health infrastructure and access to healthcare services are vital for improving the quality of life. They ensure that individuals receive timely medical attention, preventive care, and treatment for diseases. Lack of access can lead to increased morbidity and mortality rates, reduced workforce productivity, and higher healthcare costs for society at large.
| 5. What role does education play in bridging the skill gap in the workforce? |  |
Ans. Education is crucial for bridging the skill gap in the workforce by equipping individuals with the necessary knowledge and competencies to meet job market demands. It fosters critical thinking, technical skills, and adaptability, which are essential in a rapidly changing economy. Effective educational programs can also promote lifelong learning, enhancing employability and career advancement opportunities.
Related Searches





















