UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Cheat Sheet: Climatology
Cheat Sheet: Climatology | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Temperature and Pressure Belts of the World
Major Temperature Belts:
- Equatorial (0°–10°): Hot & humid
- Tropical (10°–25°): High insolation
- Temperate (25°–66.5°): Moderate
- Polar (66.5°–90°): Cold
Pressure Belts: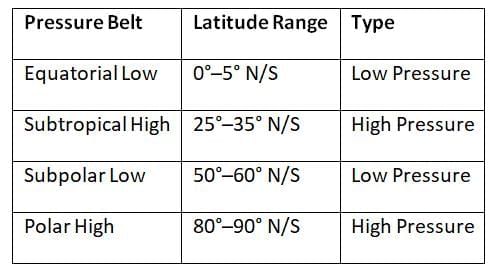
Heat Budget of the Earth
Incoming Solar Radiation (Insolation) = 100 units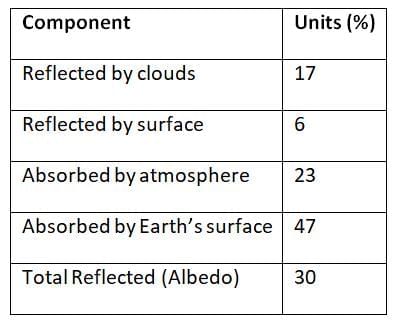
Earth radiates heat as long-wave radiation → partly absorbed by greenhouse gases
Atmospheric Circulation
Three-Cell Model (by Ferrel):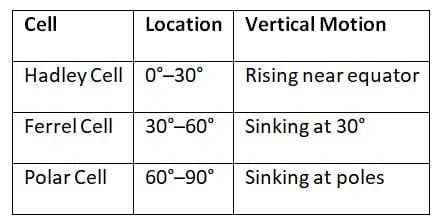 Air moves from high to low pressure, deflected by Coriolis force.
Air moves from high to low pressure, deflected by Coriolis force.
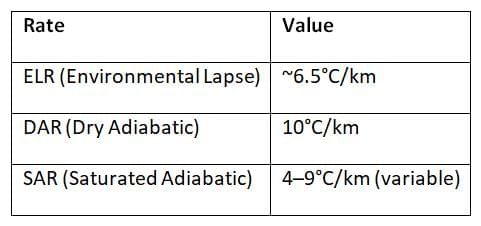
Atmospheric Stability and Instability
Stability:
- Occurs when ELR < DAR
- Resists vertical motion
Instability:
- Occurs when ELR > DAR
- Promotes convection, clouds, storms
Planetary and Local Winds
Planetary Winds (Permanent):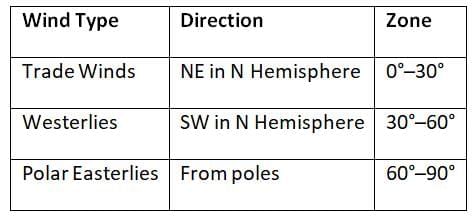
Local Winds: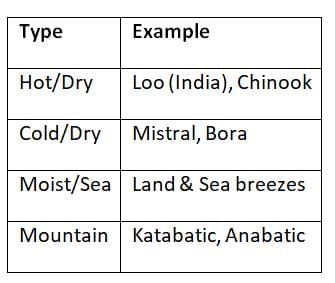
Monsoons and Jet Streams
Monsoons:
- Seasonal winds caused by differential heating of land and sea
Reversal in direction:
- Summer: SW Monsoon (sea to land)
- Winter: NE Monsoon (land to sea)
Jet Streams:
- High-speed, upper-tropospheric winds
Types:
- Subtropical Westerly Jet (STWJ)
- Tropical Easterly Jet (TEJ)
Air Masses and Fronts
Air Masses (by Source Region):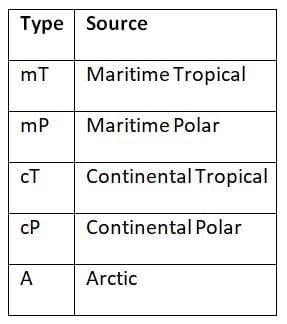 Fronts:
Fronts: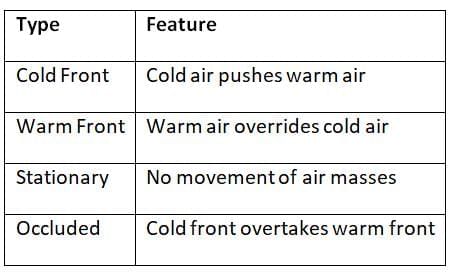
Temperate and Tropical Cyclones
Tropical Cyclones: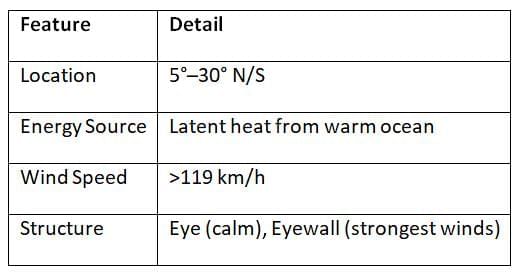
Temperate Cyclones: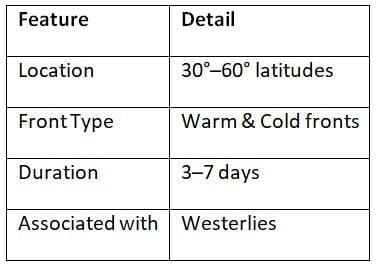
Types and Distribution of Precipitation
Types: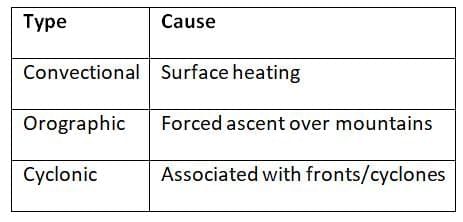
Distribution:
- Equatorial: High rainfall
- Subtropical: Arid (descending air)
- Temperate: Moderate (cyclonic)
- Polar: Low (cold, dry air)
Weather and Climate
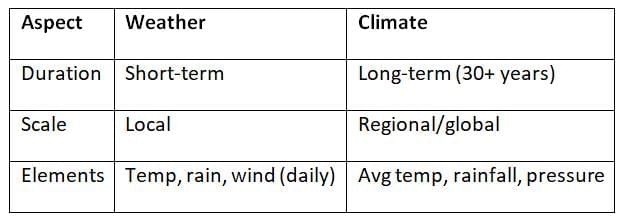
Climate Classification Systems
Köppen’s Classification:
- Based on temperature & precipitation
- 5 major groups: A (Tropical), B (Dry), C (Warm temperate), D (Cold), E (Polar)
- India: Aw (tropical savanna), Am (monsoon), BSh (semi-arid)
Thornthwaite’s Classification:
- Based on moisture index, PET (Potential Evapotranspiration)
- Suitable for agriculture & water balance
Trewartha’s Classification:
- Modified Köppen with more focus on vegetation and human settlement
- Divides temperate climate more precisely
Hydrological Cycle
Major Processes:
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- Precipitation
- Runoff
- Infiltration
- Transpiration
Forms a closed system but influenced by climate change & human activity
Global Climatic Change
Major Causes:
- Natural: Solar variability, volcanic activity
- Anthropogenic: Greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4), deforestation, urbanization
Impacts:
- Sea-level rise
- Melting glaciers
- Extreme weather events
- Biodiversity loss
Role and Response of Man in Climatic Changes
Human Contributions:
- Industrialization
- Fossil fuel burning
- Land-use changes
Responses:
- International Agreements: Kyoto Protocol, Paris Agreement
- Adaptation strategies: Afforestation, Renewable energy
- Mitigation: Carbon trading, green technologies
Applied Climatology
- Urban Planning (heat islands)
- Agriculture (crop suitability)
- Aviation (wind, visibility, storms)
- Disaster Management (cyclone prediction)
Urban Climate
Urban Heat Island (UHI):
- Urban areas are warmer due to concrete, traffic, pollution
- Affects local wind, humidity, rainfall patterns
Mitigation:
- Green roofs, reflective materials, tree plantation
The document Cheat Sheet: Climatology | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Climatology - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main temperature and pressure belts of the world? |  |
Ans. The world's temperature and pressure belts are classified into several key areas: the equatorial low-pressure belt, the subtropical high-pressure belt, the subpolar low-pressure belt, and the polar high-pressure belt. The equatorial belt, also known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), experiences high temperatures and significant rainfall throughout the year. The subtropical high-pressure belt, located around 30 degrees latitude, is characterized by dry and stable conditions, leading to deserts. The subpolar low-pressure area, around 60 degrees latitude, experiences variable weather with the convergence of warm and cold air masses. Finally, the polar high-pressure belts are cold and dry, with minimal precipitation.
| 2. How does the Earth's heat budget function? |  |
Ans. The Earth's heat budget refers to the balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing infrared radiation. Approximately 30% of solar energy is reflected back into space by clouds, atmospheric particles, and the Earth's surface, while the remaining 70% is absorbed, warming the planet. This absorbed energy is then released back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation. Factors such as greenhouse gases, ocean currents, and land cover also influence the heat budget, affecting climate patterns. A balanced heat budget is crucial for maintaining stable climate conditions on Earth.
| 3. What is atmospheric circulation, and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Atmospheric circulation refers to the large-scale movement of air across the Earth, driven by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by the sun. This circulation is crucial for distributing heat and moisture around the globe, influencing weather patterns and climate. The primary components include the trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies. The circulation patterns also play a significant role in the formation of high and low-pressure systems, impacting local weather conditions and long-term climate trends.
| 4. What are the characteristics of stable and unstable atmospheric conditions? |  |
Ans. Atmospheric stability refers to the tendency of air parcels to rise or sink in the atmosphere. A stable atmosphere resists vertical motion, where warm air is trapped beneath cooler air, leading to clear skies and calm weather. Conversely, unstable conditions occur when warm, buoyant air rises rapidly, often resulting in clouds, thunderstorms, and severe weather. Factors such as temperature gradients, humidity, and wind shear influence atmospheric stability, making it a critical aspect of weather forecasting and climate analysis.
| 5. How do monsoons and jet streams impact global weather patterns? |  |
Ans. Monsoons are seasonal wind patterns that bring significant changes in precipitation, particularly in South Asia, where they produce heavy rains during the summer months. Jet streams are fast-flowing air currents in the upper atmosphere that influence weather systems by steering them along their paths. Both phenomena play a vital role in shaping climate and weather conditions worldwide. Monsoons can lead to agricultural productivity but also pose risks of flooding, while jet streams can enhance storm development or influence temperature extremes in various regions.
Related Searches
















