Cheat Sheet: Elections, Electoral Laws & Reforms | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Elections in India |

|
| Election Laws |

|
| Electoral Reforms |

|
| Chronology of Key Developments |

|
Introduction
Elections are the foundation of India’s democratic system, enabling citizens to elect representatives and shape governance. This chapter examines the electoral framework, key election laws, and proposed reforms to strengthen the democratic process. It provides a clear and concise reference for understanding the legal and procedural aspects of elections and the ongoing efforts to enhance their fairness and efficiency.
Elections in India
Elections in India, governed by constitutional provisions and managed by the Election Commission of India (ECI), ensure democratic representation through free and fair processes for electing representatives to Parliament, state legislatures, and key offices.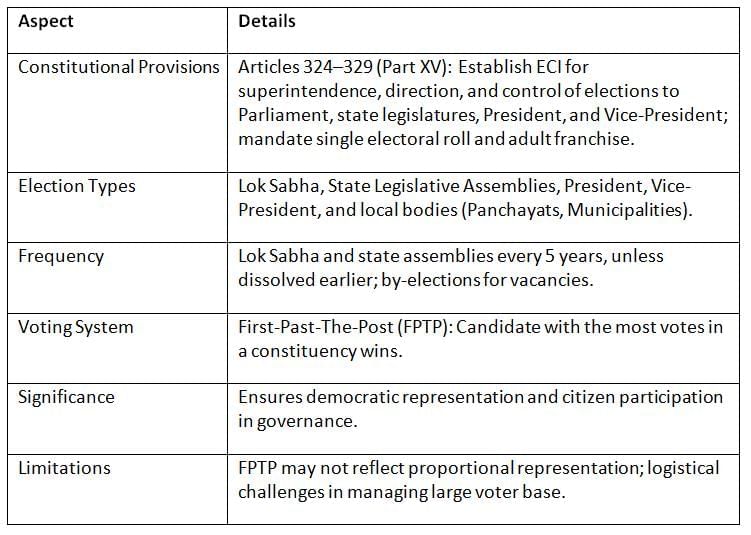 Key Points: India’s electoral system, rooted in the Constitution, promotes inclusive democracy through universal adult franchise, but the FPTP system and scale pose challenges.
Key Points: India’s electoral system, rooted in the Constitution, promotes inclusive democracy through universal adult franchise, but the FPTP system and scale pose challenges.
Election Laws
Election laws in India provide the legal framework for conducting elections, ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability, with the ECI overseeing their implementation.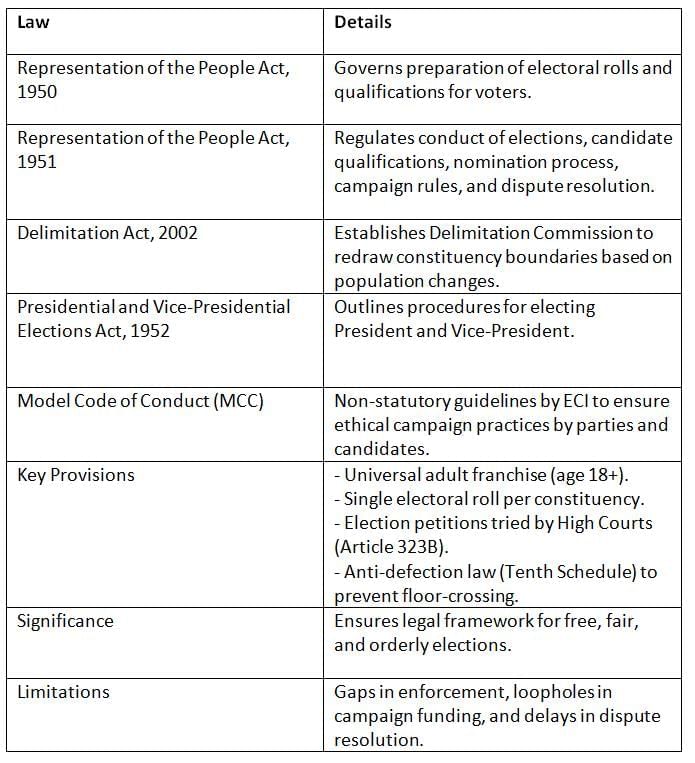
Key Points: Election laws provide a robust framework for democratic processes, but issues like enforcement and funding transparency need attention.
Electoral Reforms
Electoral reforms aim to address shortcomings in the electoral system, enhancing transparency, fairness, and inclusivity. Various committees and the ECI have proposed reforms to tackle issues like criminalization, funding, and voter participation.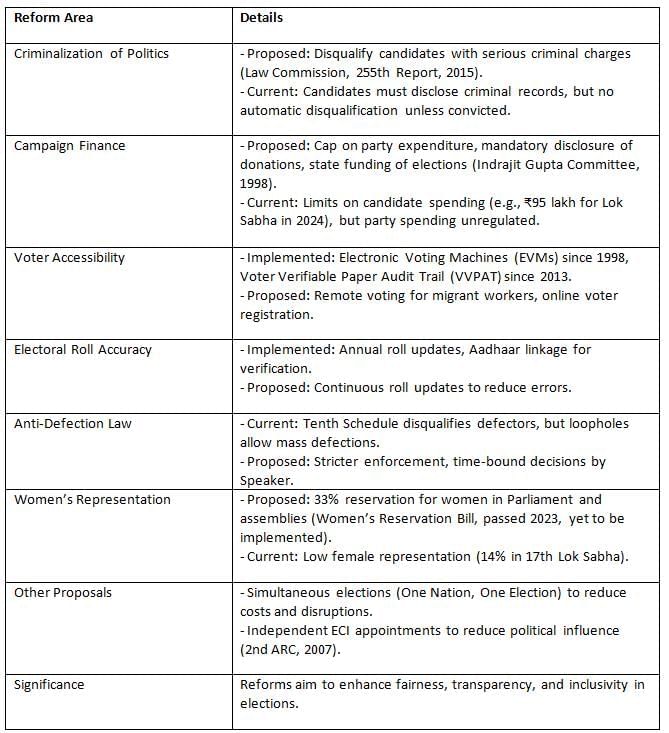
Key Points: Electoral reforms address critical issues like criminalization and funding but face hurdles due to political opposition and logistical complexities.
Chronology of Key Developments
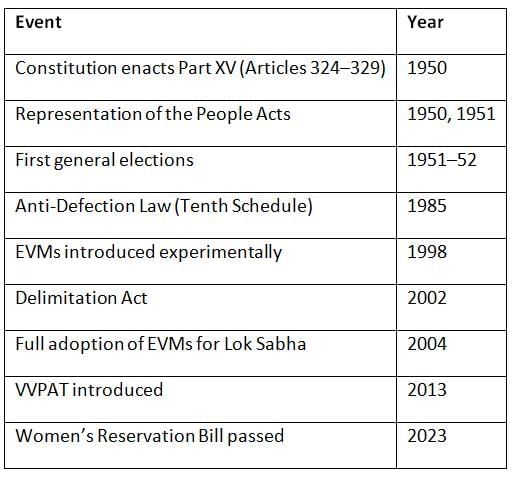
Conclusion
Elections in India, governed by a robust constitutional and legal framework, are central to its democratic ethos. The Election Commission, supported by key laws, ensures free and fair elections, while proposed reforms aim to address challenges like criminalization, funding transparency, and voter inclusivity. Understanding these aspects is essential for appreciating India’s electoral system and the ongoing efforts to strengthen its democratic processes.
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Elections, Electoral Laws & Reforms - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key features of the electoral system in India? |  |
| 2. What are the major election laws governing elections in India? |  |
| 3. What are some significant electoral reforms that have been implemented in India? |  |
| 4. How does the Election Commission of India ensure free and fair elections? |  |
| 5. Can you provide a timeline of key developments in Indian electoral history? |  |




















