Cheat Sheet: Era of Militant Nationalism-(1905-1909) | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The period from the late 19th century to the early 20th century witnessed a significant transformation in the Indian nationalist movement, marked by the transition from moderate methods to more militant forms of nationalism. Various factors, such as repressive British policies, dissatisfaction with moderate strategies, international influences, and the emergence of a trained leadership, contributed to the growth of militant nationalism. One pivotal event during this time was the Swadeshi Movement, which had its roots in the anti-partition movement against the division of Bengal. This chronology document aims to provide a structured overview of the key events leading to the growth of militant nationalism, focusing on the Swadeshi Movement and its aftermath.
Recognition of the True Nature of British Rule

Growth of Confidence and Self-Respect
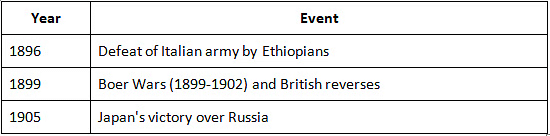
Reaction to Increasing Westernisation and Dissatisfaction with Moderates

Emergence of a Trained Leadership
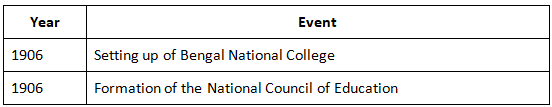
The Swadeshi and Boycott Movement
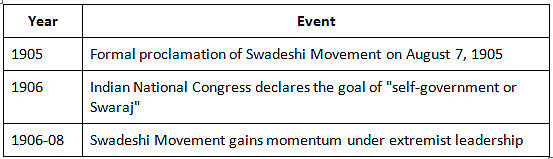
Impact in Different Spheres

Movements Across India in Support of Bengal
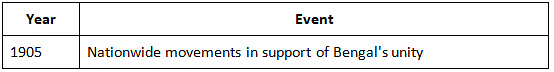
Annulment of Partition and Evaluation of Swadeshi Movement

Conclusion
The period under consideration, characterized by the growth of militant nationalism, saw the Indian nationalist movement evolve from moderate approaches to more assertive and widespread forms of resistance. The Swadeshi Movement, emerging from the anti-partition movement, played a crucial role in mobilizing various sections of society. Despite facing severe repression and internal challenges, the movement marked a turning point in Indian political consciousness, setting the stage for future struggles. The Morley-Minto Reforms of 1909, while acknowledging some Indian representation, fell short of the demand for self-government, highlighting the continued struggle for true autonomy. The chronology presented here underscores the complex dynamics that shaped the trajectory of Indian nationalism during this transformative period.
|
210 videos|853 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Era of Militant Nationalism-(1905-1909) - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What were the main causes of militant nationalism during the period of 1905-1909? |  |
| 2. Which significant events marked the era of militant nationalism from 1905 to 1909? |  |
| 3. How did militant nationalism manifest in different regions during the 1905-1909 period? |  |
| 4. What role did ideology play in the development of militant nationalism in this era? |  |
| 5. How did the international political climate influence militant nationalism from 1905 to 1909? |  |
















