UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Cheat Sheet: Fundamental Rights
Cheat Sheet: Fundamental Rights | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This document provides a detailed chronology of the Fundamental Rights as outlined in Part III of the Indian Constitution. The purpose of this document is to give a clear understanding of the different Fundamental Rights, their application, and how they have evolved over time. The structure of the document is organized into various sections for each right, followed by a summary of key points. This format allows for easy reading and quick revision, making it suitable for both study and reference.
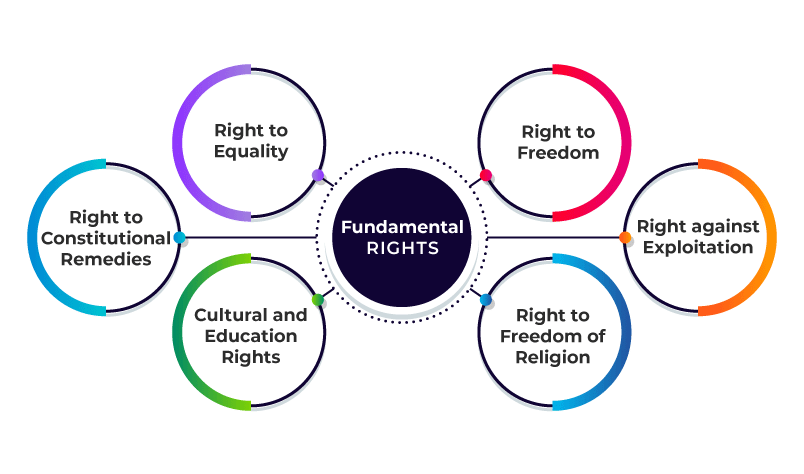
Fundamental Rights Overview
Article 12: Definition of State

Article 13: Laws Inconsistent with Fundamental Rights

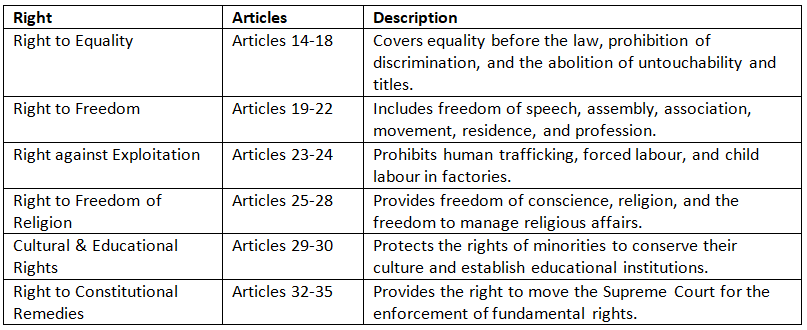
Right to Equality (Articles 14-18)

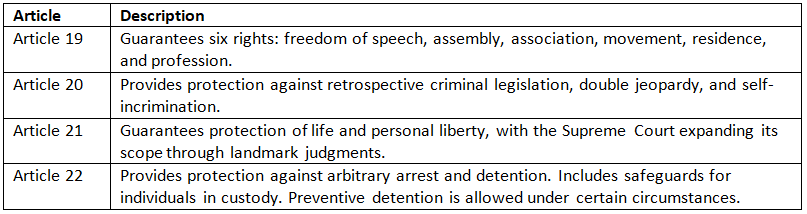
Right to Freedom (Articles 19-22)
Right against Exploitation (Articles 23-24)

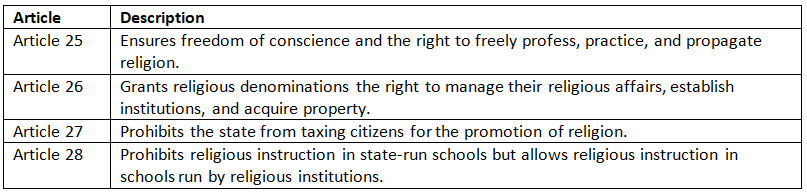
Right to Freedom of Religion (Articles 25-28)
Cultural & Educational Rights (Articles 29-30)

Right to Constitutional Remedies (Articles 32-35)

The document Cheat Sheet: Fundamental Rights | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
154 videos|998 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Fundamental Rights - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are fundamental rights and why are they important? |  |
Ans.Fundamental rights are a set of legal protections and freedoms that are guaranteed to individuals by the constitution or legal framework of a nation. They are essential because they ensure individuals can live freely and with dignity, protecting them from abuse by the state and ensuring equality before the law. These rights often include the right to equality, freedom of speech and expression, the right to privacy, and protection against discrimination, among others.
| 2. How are fundamental rights different from legal rights? |  |
Ans.Fundamental rights are inherent and are typically enshrined in the constitution, meaning they cannot be easily altered or taken away. Legal rights, on the other hand, are granted by legislation and can be modified or revoked by the government. While both types of rights aim to protect individuals, fundamental rights hold a higher status as they are essential for the maintenance of democracy and individual freedom.
| 3. Can fundamental rights be restricted? If so, under what conditions? |  |
Ans.Yes, fundamental rights can be restricted, but such restrictions must meet certain criteria. Generally, limitations can be imposed for reasons such as national security, public order, morality, or the rights of others. However, any restriction must be reasonable, proportional, and not arbitrary, ensuring that the essence of the fundamental rights is preserved.
| 4. What role do courts play in protecting fundamental rights? |  |
Ans.Courts play a crucial role in safeguarding fundamental rights by interpreting the law and adjudicating disputes related to these rights. Individuals can approach the judiciary if they believe their fundamental rights have been violated. Courts have the authority to review laws and government actions to ensure they comply with constitutional provisions, thus providing a check on governmental power.
| 5. How do fundamental rights evolve over time? |  |
Ans.Fundamental rights can evolve through judicial interpretations and societal changes. Courts may expand the scope of these rights based on contemporary values and norms, thereby adapting to new challenges such as technological advancements or social movements. Legislative amendments can also play a role in this evolution, as new rights may be recognized or existing ones revised to reflect the changing needs of society.
Related Searches
















