UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Cheat Sheet: Industry and Infrastructure
Cheat Sheet: Industry and Infrastructure | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
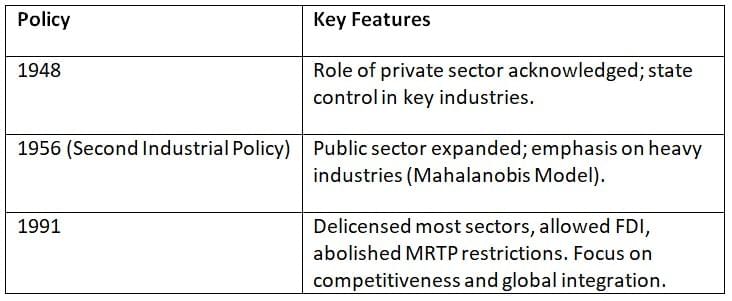
Industrial Development in India
- Pre-1991: License Raj, state-led growth, inefficiencies.
- Post-1991 Reforms: Shift to liberalization, privatization, and globalization. Boost in private investment and FDI.
- 2025 Focus: Balanced industrial development via PLI schemes, digital infrastructure, and green industrial policy.
Industrial Policies
Disinvestment
- Types: Minority Stake Sale, Strategic Sale, Asset Monetization.
- Recent Examples:
- 2021–2023: LIC IPO, Air India privatization.
- 2024–2025: IDBI Bank (strategic), CONCOR (proposed).
- Policy Shift: Government to retain presence only in strategic sectors.
- Debates: Use of proceeds—should it fund fiscal deficit or be reinvested in infrastructure?
MSME Sector
Significance: 30% of GDP, 48% exports, employment to 11 crore.
Schemes:
- Udyam Registration (replaces Udyog Aadhaar).
- Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) – Extended to 2024.
- RAMP Scheme (2022–2026) – Enhances productivity, competitiveness.
Ease of Doing Business (EoDB)
- Improvements: Digitization, single window clearances.
- India’s Focus (Post-WB Rankings): State-level EoDB, industrial clusters, startup facilitation.
- Major Push: National Single Window System (NSWS), decriminalization of business laws (2023–25).
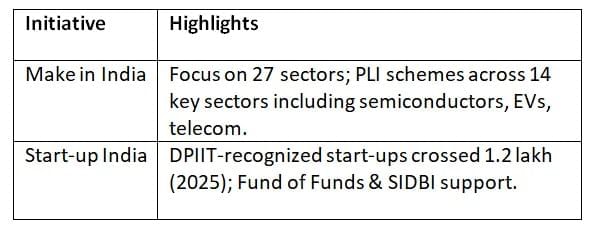
Make in India & Start-up India
Infrastructure Sector
National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
- Outlay: ₹111 lakh crore (2020–25).
- Sectors: Energy (24%), Roads (18%), Railways (12%).
- Monitoring: Dashboard for real-time tracking.
Energy Sector
- Petroleum Sector Challenges: Import dependence (85%), high global oil prices.
- Alternative Push:
- Biofuels Policy 2018 (Updated 2022) – Ethanol blending target of 20% by 2025.
- Green Hydrogen Mission (2023) – ₹19,744 crore investment.
- Renewable Energy:
- Installed RE capacity: ~180 GW (2025 target: 500 GW).
- Solar dominance: Top 5 globally.
Transport Infrastructure
- Roads:
- Bharatmala Phase-II (2024–2028) approved with ~₹10 lakh crore outlay.
- FASTag-led toll collection surge.
- Railways:
- PM Gati Shakti integration.
- Vande Bharat trains, electrification (100% goal by 2030).
- Civil Aviation:
- UDAN Scheme – 500+ routes operational by 2025.
- No. of airports: >150; 220+ targeted by 2030.
Urban Infrastructure
Smart Cities Mission:
- 100 cities, nearing completion in most.
- Emphasis: IT-enabled services, urban mobility, waste management.
Housing:
- PMAY–Urban: 1.18 crore houses sanctioned (as of mid-2025).
- Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHC) for migrants.
PPP Models & Logistics
PPP Models:
- BOT, HAM, EPC prevalent.
- Revamp via Model Concession Agreements.
Logistics:
- National Logistics Policy (2022): Aims to reduce logistics cost to 8% of GDP (currently ~13%).
- Dedicated Freight Corridors expanding rapidly.
Recent Additions & Reforms (2023–2025)
PM Gati Shakti Master Plan: Multi-modal infra, digital planning via GIS mapping.
National Monetization Pipeline (NMP):
- Target: ₹6 lakh crore (2021–25).
- Assets: Roads, power, telecom, airports.
The document Cheat Sheet: Industry and Infrastructure | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Industry and Infrastructure - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key objectives of the Make in India initiative? |  |
Ans. The Make in India initiative aims to transform India into a global manufacturing hub by encouraging both multinational and domestic companies to manufacture their products in India. Key objectives include boosting manufacturing output, creating jobs, enhancing skills, promoting innovation, and increasing the ease of doing business. The initiative also focuses on improving infrastructure and fostering investment in various sectors.
| 2. How does the MSME sector contribute to the Indian economy? |  |
Ans. The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector plays a crucial role in the Indian economy by contributing significantly to GDP, employment, and exports. It accounts for about 30% of India's GDP, provides jobs to millions, and contributes nearly 50% of total exports. The sector is vital for promoting entrepreneurship and reducing regional disparities through the establishment of small enterprises in rural and semi-urban areas.
| 3. What are the major components of India's industrial policy? |  |
Ans. India's industrial policy encompasses various components aimed at promoting industrial growth. These include fostering entrepreneurship, encouraging foreign direct investment (FDI), promoting technology transfer, enhancing infrastructure, and supporting small-scale industries. Policies also focus on sector-specific incentives, skill development initiatives, and measures to improve the overall investment climate in the country.
| 4. What is the significance of the Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) rankings for India? |  |
Ans. The Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) rankings are significant for India as they reflect the country's business environment and regulatory framework. Higher rankings indicate a more favorable environment for businesses, attracting foreign investments and promoting domestic entrepreneurship. Improvements in EoDB rankings can lead to better job creation, economic growth, and increased competitiveness on a global scale.
| 5. What are the recent reforms in the infrastructure sector aimed at enhancing industrial growth? |  |
Ans. Recent reforms in the infrastructure sector include initiatives to improve transportation networks, enhance connectivity through dedicated freight corridors, and develop smart cities. Investments in renewable energy, digital infrastructure, and logistics are also prioritized. These reforms aim to reduce bottlenecks, lower costs for businesses, and create a conducive environment for industrial growth, ultimately supporting the broader economic development of the country.
Related Searches





















