Cheat Sheet: Judicial Activism | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter explores the concept of judicial activism, its evolution, and its role in the Indian judiciary. It covers the meaning, aspects, reasons, and concerns of judicial activism, as well as its distinction from judicial review and judicial restraint. The chapter also highlights the Supreme Court’s stance on balancing activism with restraint.
Introduction
Judicial activism, first recognized in the USA, emerged in India in the 1970s as a means for the judiciary to protect citizens’ rights and promote justice. It reflects a proactive judicial approach, contrasting with the self-discipline of judicial restraint.
Key Points:
- Judicial activism empowers the judiciary to actively protect rights and ensure constitutional obligations are met, marking a shift from passive interpretation to dynamic intervention in India.
Aspects of Judicial Activism
In India, judicial activism focuses on issuing directives to protect public interest and expanding the interpretation of fundamental rights, particularly through Public Interest Litigation (PIL) and constitutional rulings.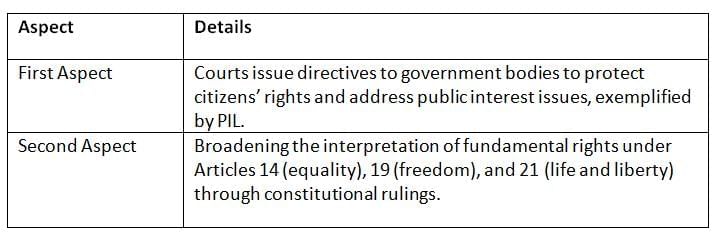
Key Points:
- Judicial activism in India drives public welfare through PIL and enhances the scope of fundamental rights, ensuring broader access to justice and constitutional protections.
Judicial Review vs. Judicial Activism
Judicial review and judicial activism are related but distinct concepts. While judicial review assesses the constitutionality of laws, judicial activism involves shaping policy to reflect societal changes, often sparking debate about judicial roles.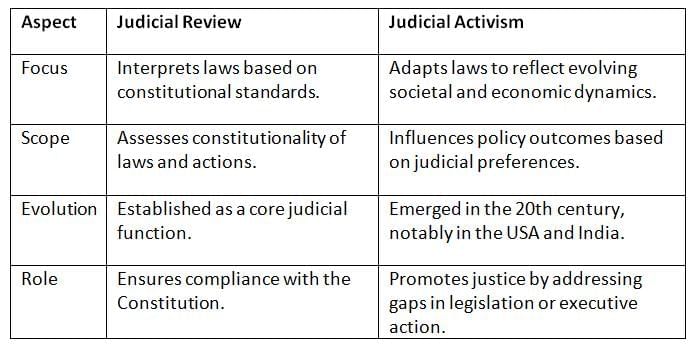
Key Points:
- Judicial activism extends beyond review by actively shaping laws to meet societal needs, but it risks blurring the line between judicial and legislative functions.
Reasons for Judicial Activism
Judicial activism arises due to failures in other government branches, public trust in the judiciary, and constitutional provisions that allow courts to address societal needs.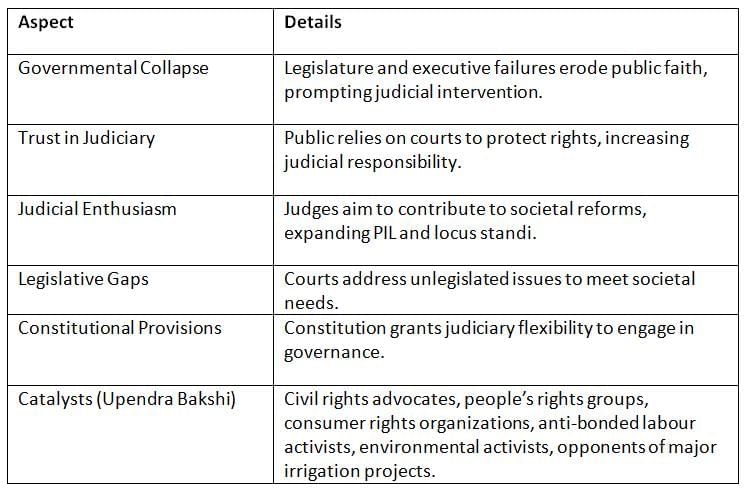
Key Points:
- Judicial activism fills gaps left by legislative and executive inaction, driven by public trust and constitutional mandates, with diverse groups advocating for judicial intervention.
Concerns Regarding Judicial Activism
While judicial activism promotes justice, it raises concerns about overreach, judicial expertise, case backlogs, and legitimacy, as highlighted by legal expert Upendra Bakshi.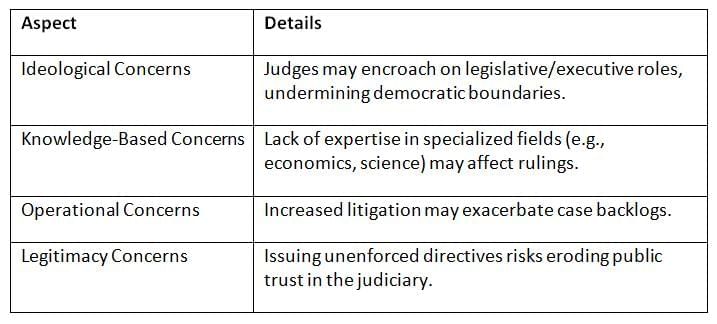
Key Points:
- Judicial activism’s benefits are tempered by risks of overstepping roles, straining judicial resources, and diminishing credibility if directives are ignored.
Judicial Activism vs. Judicial Restraint
Judicial restraint, prominent in the USA, advocates strict adherence to constitutional interpretation without creating laws, contrasting with activism’s proactive approach.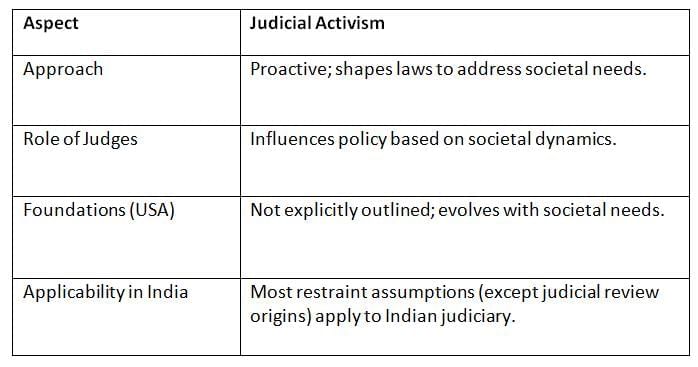
Key Points:
- Judicial restraint prioritizes deference to elected branches, while activism allows judges to address societal gaps, raising debates about judicial boundaries in both India and the USA.
Supreme Court’s Stand on Judicial Restraint
In a 2007 judgment, the Supreme Court of India emphasized judicial restraint to maintain constitutional balance, cautioning against overreach while acknowledging the value of activism.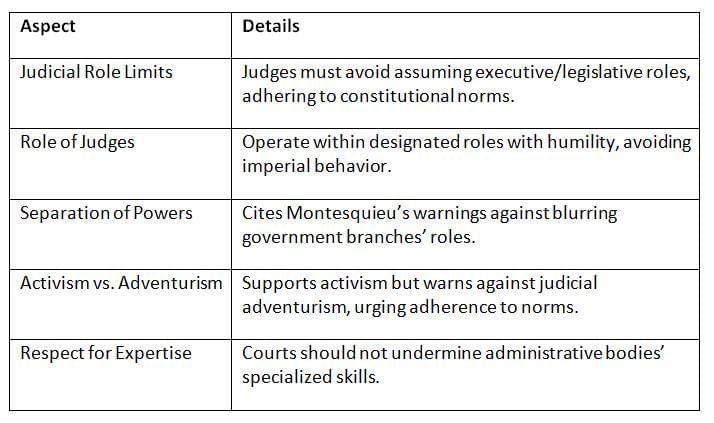
Key Points:
- The Supreme Court advocates a balanced approach, endorsing activism for justice but urging restraint to preserve separation of powers and judicial credibility.
Chronology of Key Events

Conclusion
This chapter underscores the significance of judicial activism in India as a tool for protecting citizens’ rights and addressing governance gaps. While it empowers the judiciary to advance justice through PIL and expanded fundamental rights, it must be balanced with restraint to respect constitutional boundaries. The Supreme Court’s 2007 stance highlights the need for humility and adherence to norms, ensuring the judiciary remains a trusted guardian of democracy and the Constitution.
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Judicial Activism - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is judicial activism and how does it differ from judicial review? |  |
| 2. What are the main reasons that justify judicial activism? |  |
| 3. What concerns are commonly raised about judicial activism? |  |
| 4. How does judicial activism contrast with judicial restraint? |  |
| 5. What is the Supreme Court's stance on judicial restraint? |  |
















