Cheat Sheet: Non-Constitutional Bodies | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of key Non-Constitutional Bodies in India, which are established by statutes, executive resolutions, or government orders but are not enshrined in the Constitution. These bodies play critical roles in governance, addressing issues like human rights, corruption, transparency, and development. Unlike Constitutional Bodies, they can be modified or dissolved by the government. This chapter aims to offer a clear, concise reference for understanding their structure, functions, and significance, particularly for exam preparation or general knowledge of Indian polity.
NITI Aayog
NITI Aayog, formed in 2015, replaced the Planning Commission to foster cooperative federalism and drive India’s development through policy formulation and state collaboration.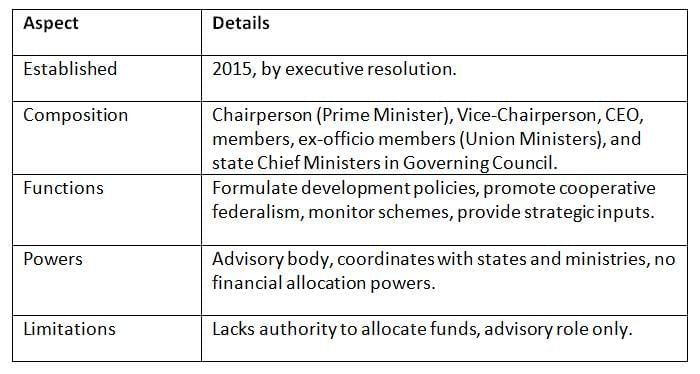
Key Points: NITI Aayog emphasizes state involvement in policy-making, unlike the top-down approach of the Planning Commission, but its lack of financial powers limits its influence.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
The NHRC was established under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993, to protect and promote human rights, addressing violations like torture and discrimination.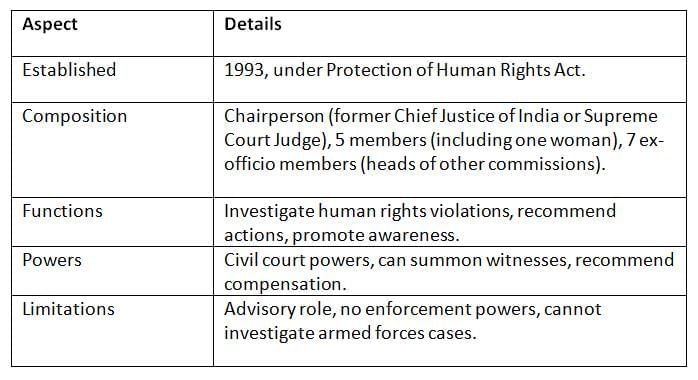 Key Points: The NHRC is a vital watchdog for human rights but is often called a “toothless tiger” due to its advisory nature and limited investigative authority.
Key Points: The NHRC is a vital watchdog for human rights but is often called a “toothless tiger” due to its advisory nature and limited investigative authority.
State Human Rights Commission (SHRC)
SHRCs, established under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993, operate at the state level to address human rights violations within their jurisdiction.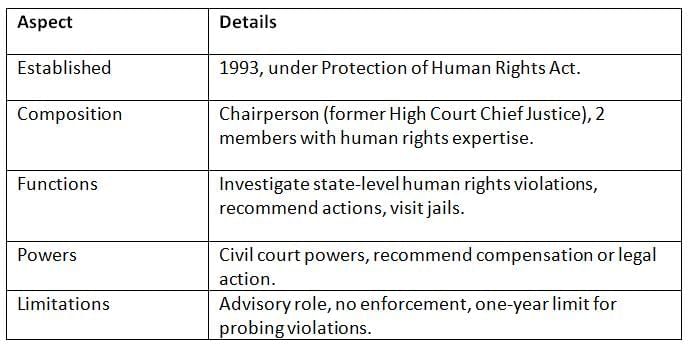
Key Points: SHRCs complement NHRC efforts but face similar limitations in enforcement and are constrained by state government cooperation.
National Commission for Women (NCW)
The NCW, set up in 1992, focuses on protecting and promoting women’s rights, addressing gender-based issues through legal and policy interventions.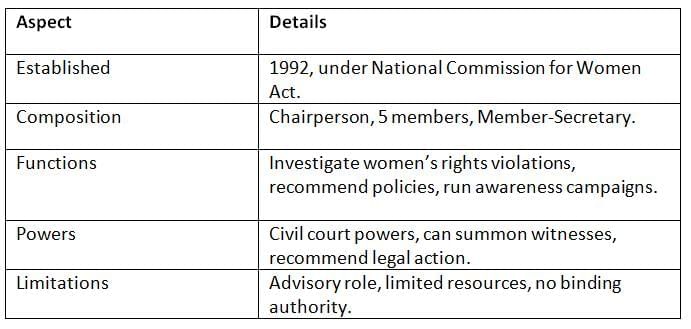
Key Points: The NCW drives gender equality but struggles with resource constraints and lack of enforcement power.
National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR)
The NCPCR, established in 2007, ensures the protection of child rights under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005.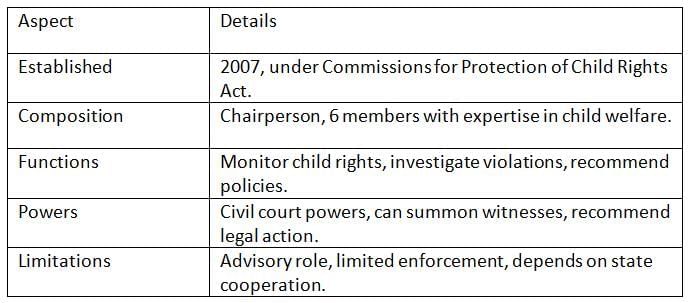
Key Points: The NCPCR safeguards children’s welfare but is constrained by its advisory nature and reliance on state governments.
National Commission for Minorities (NCM)
The NCM, formed in 1992, promotes the welfare of minority communities under the National Commission for Minorities Act.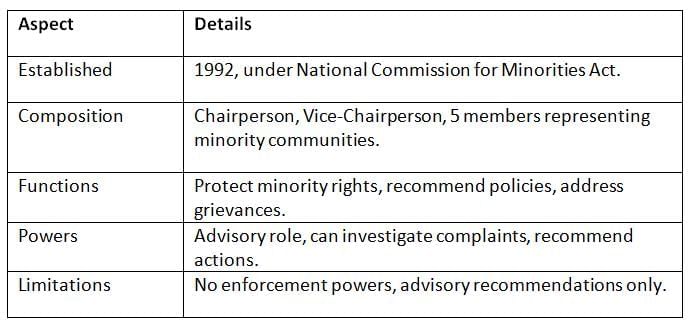
Key Points: The NCM ensures minority representation but is limited by its advisory role and lack of binding authority.
Central Information Commission (CIC)
The CIC, established under the Right to Information Act, 2005, ensures transparency by facilitating access to government information.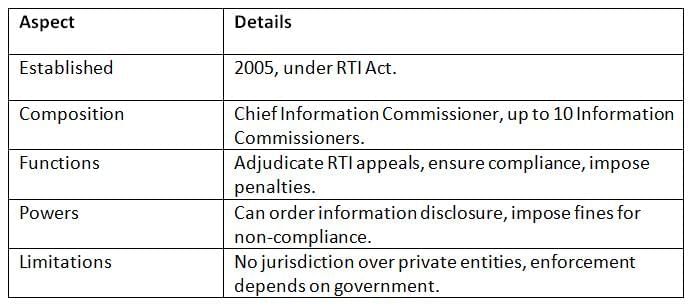
Key Points: The CIC empowers citizens through transparency but faces challenges in enforcement and limited scope over private bodies.
State Information Commission (SIC)
SICs, also set up under the RTI Act, 2005, handle RTI appeals and complaints at the state level to promote transparency.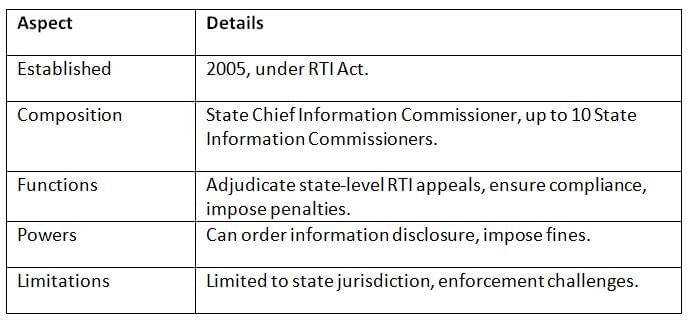
Key Points: SICs enhance state-level transparency but share similar enforcement limitations as the CIC.
Central Vigilance Commission (CVC)
The CVC, established in 1964 and made statutory in 2003, oversees anti-corruption efforts in government offices.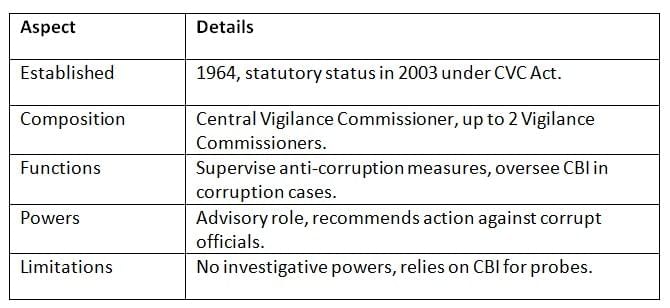 Key Points: The CVC promotes integrity but is limited by its advisory role and dependence on other agencies like the CBI.
Key Points: The CVC promotes integrity but is limited by its advisory role and dependence on other agencies like the CBI.
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
The CBI, established in 1963 under the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, investigates corruption and major crimes.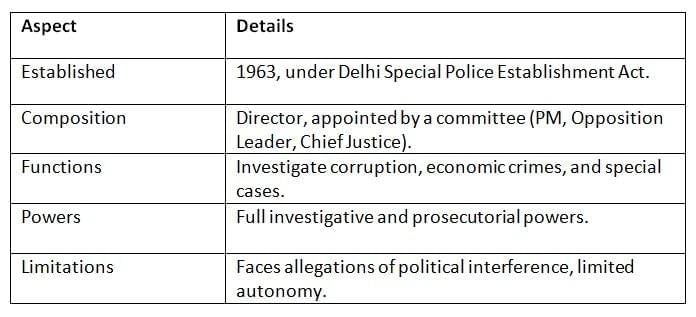
Key Points: The CBI is a key investigative agency but struggles with autonomy and political pressures.
Lokpal and Lokayuktas
The Lokpal (central) and Lokayuktas (state), established under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013, combat corruption among public servants.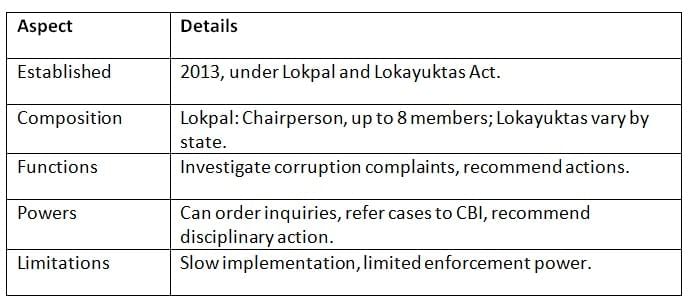
Key Points: Lokpal and Lokayuktas enhance accountability but face delays and enforcement challenges.
National Investigation Agency (NIA)
The NIA, formed in 2008 under the NIA Act, investigates terrorism-related cases to strengthen national security.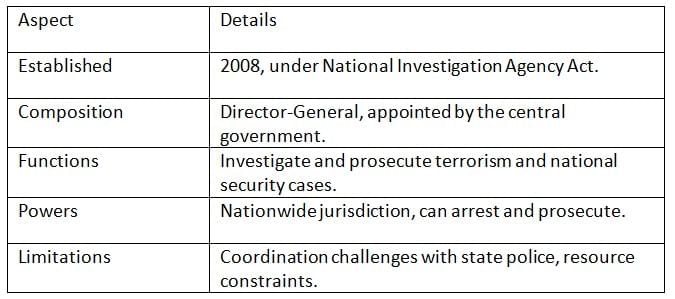
Key Points: The NIA is crucial for counter-terrorism but faces issues with state coordination and resources.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
The NDMA, established in 2005 under the Disaster Management Act, coordinates disaster preparedness and response.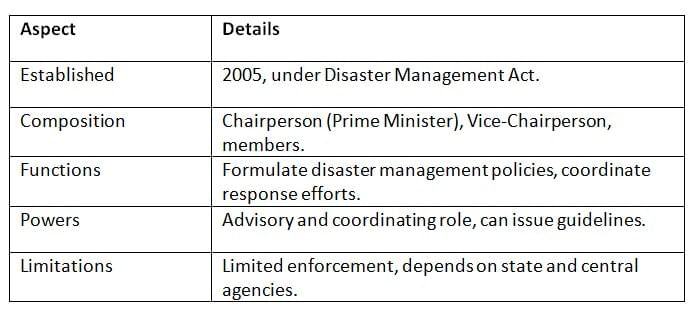
Key Points: The NDMA enhances disaster resilience but relies heavily on inter-agency coordination.
Bar Council of India (BCI)
The BCI, set up under the Advocates Act, 1961, regulates legal education and practice in India.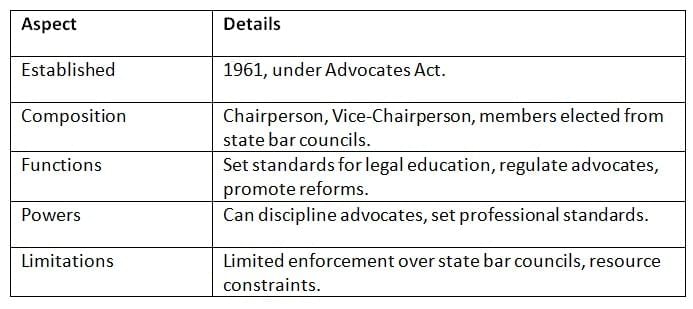
Key Points: The BCI ensures professional standards in law but faces challenges in uniform enforcement.
Law Commission of India
The Law Commission, a non-statutory body, advises on legal reforms and modernization of laws.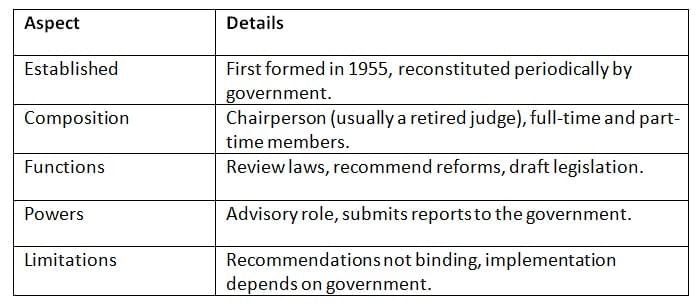
Key Points: The Law Commission drives legal modernization but lacks authority to enforce reforms.
Delimitation Commission
The Delimitation Commission, set up periodically under the Delimitation Act, redraws electoral constituency boundaries.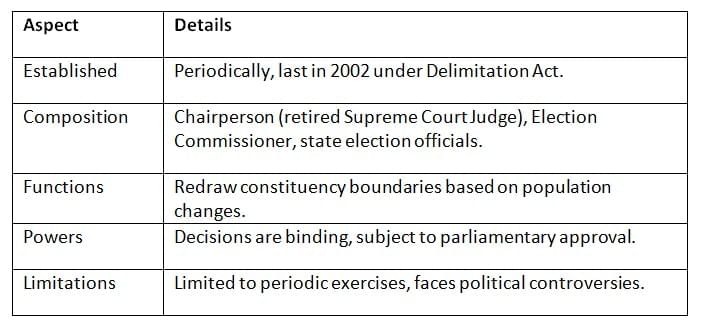 Key Points: The Delimitation Commission ensures fair representation but often faces political resistance.
Key Points: The Delimitation Commission ensures fair representation but often faces political resistance.
Chronology of Establishment
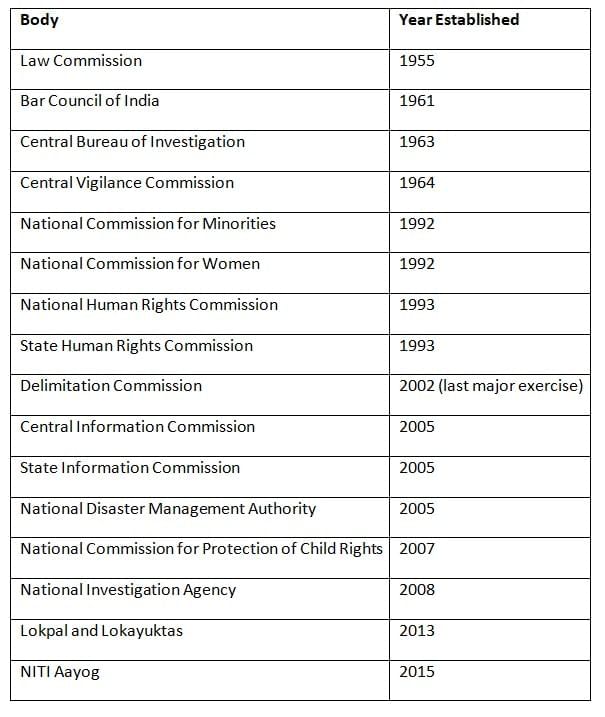
Conclusion
This chapter covers the major Non-Constitutional Bodies in India, highlighting their roles in areas like human rights, anti-corruption, transparency, disaster management, legal reforms, and electoral fairness. These bodies are essential for addressing specific governance challenges but are often limited by their advisory nature or reliance on other agencies. Understanding their functions and limitations is crucial for appreciating their contributions to India’s administrative and social framework.
|
154 videos|998 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Non-Constitutional Bodies - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the role of NITI Aayog in India's governance framework? |  |
| 2. How does the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) function in India? |  |
| 3. What are the main functions of the National Commission for Women (NCW)? |  |
| 4. How does the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) contribute to combating corruption in India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR)? |  |
















