Cheat Sheet: Parliamentary System | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This document provides a detailed chronology of the parliamentary and presidential systems of government, focusing on their application in India. It highlights the evolution of India's parliamentary system, the features of both the parliamentary and presidential models, and the reasons behind adopting the parliamentary system. Additionally, the document explores the advantages and disadvantages of the parliamentary system, its challenges, and the distinction between the Indian and British models of governance. The information is organized for easy revision and clarity, particularly for understanding the structure of governance in India.

Parliamentary System in India: Overview

Features of the Parliamentary Government

Features of the Presidential Government
Merits of the Parliamentary System


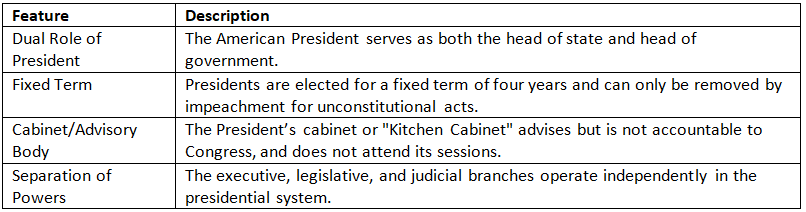
Demerits of the Parliamentary System
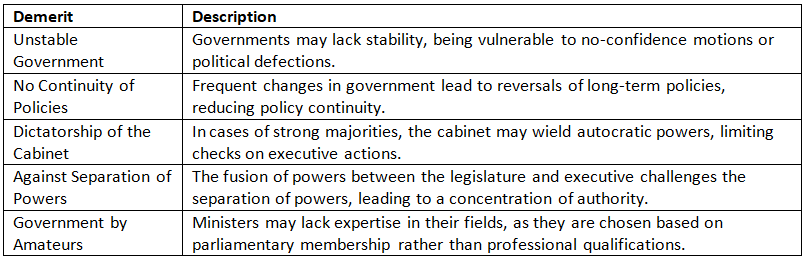
Reason for Adopting the Parliamentary System
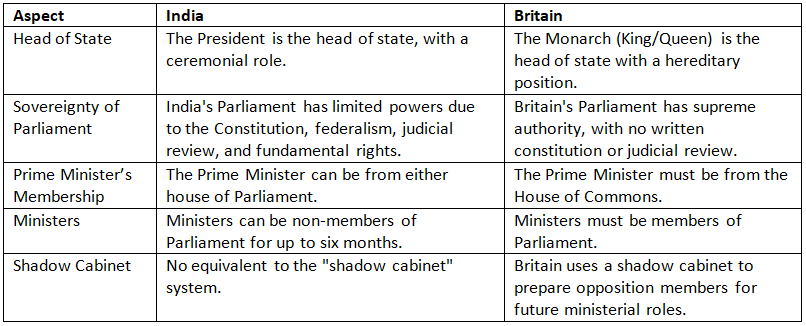
Distinction Between Indian and British Models
Conclusion
India's parliamentary system reflects a blend of both British and Indian governance traditions, ensuring that the executive remains accountable to the legislature. This system, however, faces challenges such as instability and potential concentration of power in the cabinet. Despite these drawbacks, the system provides for greater representation and responsibility. The choice of a parliamentary system was driven by historical familiarity, the need for unity in a diverse society, and a desire to avoid the conflicts seen in other forms of government. Understanding these dynamics is essential for a deeper appreciation of India's political framework and its evolution.
|
150 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
















