Cheat Sheet: Prime Minister | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter explains the role, powers, and significance of the Prime Minister in India’s parliamentary system. It covers the constitutional framework, appointment process, duties, and historical context, providing a clear understanding of the Prime Minister’s position as the real executive authority compared to the President’s nominal role. The content is organized for quick reference and easy comprehension.
Constitutional Roles of the President and Prime Minister
India’s parliamentary system, as outlined in the Constitution, distinguishes between the President, who is the nominal head of state (de jure), and the Prime Minister, who is the real head of government (de facto). This separation ensures a balance between ceremonial and executive functions.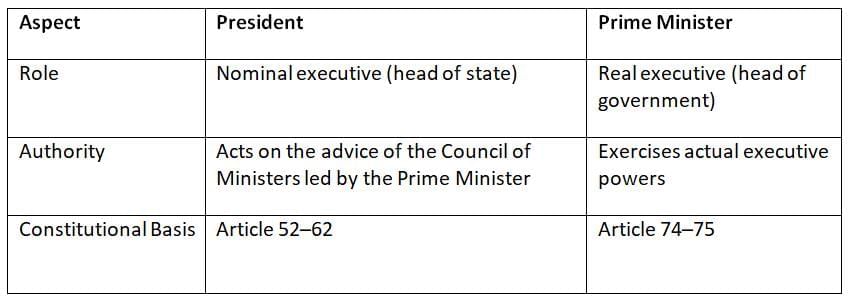
Key Points:
The President represents the nation but has limited discretionary powers.
The Prime Minister leads the government, making key decisions and guiding policy.
Appointment of the Prime Minister
The appointment of the Prime Minister is a critical process governed by constitutional provisions and conventions. While the Constitution provides flexibility, the President’s role is pivotal in ensuring a stable government.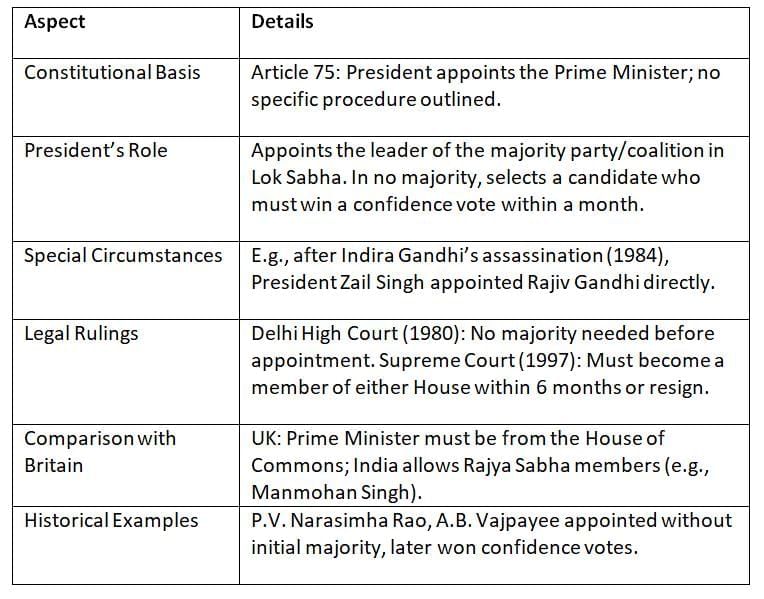
Key Points:
The President’s discretion is limited but significant in unclear majority situations.
Flexibility in India’s system allows non-Lok Sabha members to become Prime Minister, unlike the UK.
Oath, Tenure, and Salary
Before assuming office, the Prime Minister takes oaths to uphold the Constitution and perform duties impartially. The tenure and benefits are designed to support effective governance.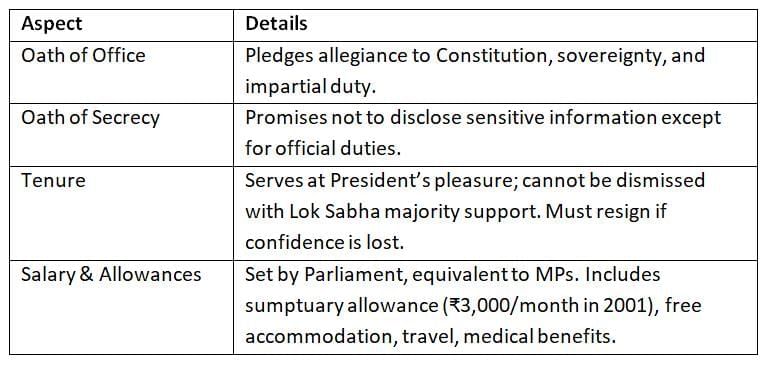
Key Points:
Oaths ensure accountability and confidentiality.
Tenure depends on Lok Sabha’s confidence, ensuring democratic accountability.
Allowances support the Prime Minister’s role without excessive privileges.
Powers and Functions of the Prime Minister
The Prime Minister wields extensive powers, influencing the government’s functioning across multiple domains, from the Council of Ministers to foreign policy.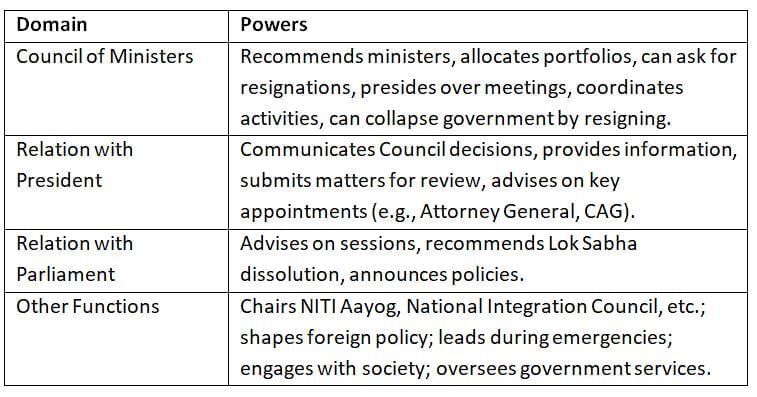
Key Points:
The Prime Minister is central to government coordination and decision-making.
Acts as a bridge between the President, Parliament, and the public.
Leadership extends to policy, emergencies, and national representation.
Role Descriptions by Scholars
Scholars have used vivid metaphors to describe the Prime Minister’s pivotal role in the parliamentary system, emphasizing their leadership and influence.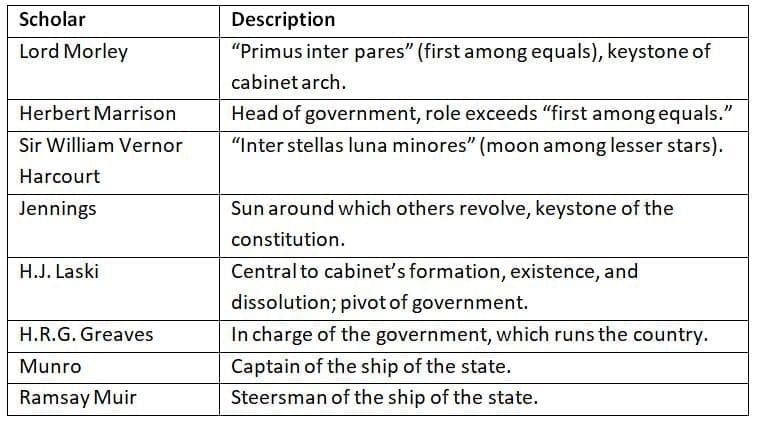
Key Points:
Descriptions highlight the Prime Minister’s dominance and centrality.
Metaphors like “sun” and “captain” underscore leadership and control.
Relationship with the President
The Prime Minister and President work closely, with the Constitution defining their interactions to ensure smooth governance.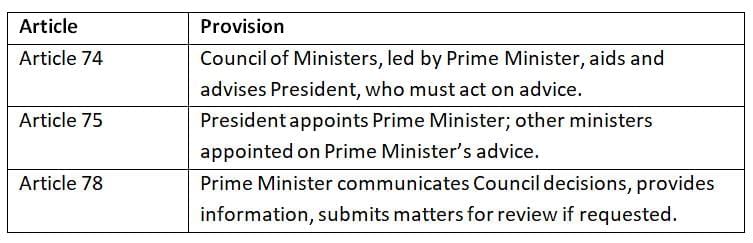
Key Points:
The Prime Minister is the primary link between the President and the government.
Constitutional provisions ensure the President acts on the Prime Minister’s advice, reinforcing the latter’s executive authority.
Chief Ministers Who Became Prime Ministers
Several leaders transitioned from state-level Chief Minister roles to become Prime Minister, showcasing political experience at both levels.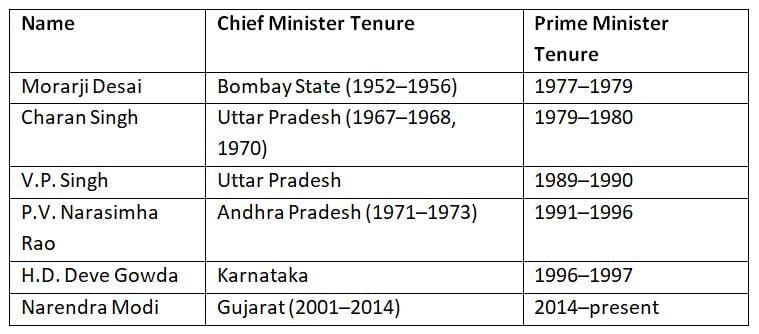
Key Points:
Experience as Chief Minister provides valuable administrative and political skills.
Narendra Modi’s long tenure as Chief Minister highlights sustained regional leadership before national office.
Caretaker Government
A caretaker government is a temporary arrangement to manage routine administration during transitions, particularly after Lok Sabha dissolution or loss of confidence.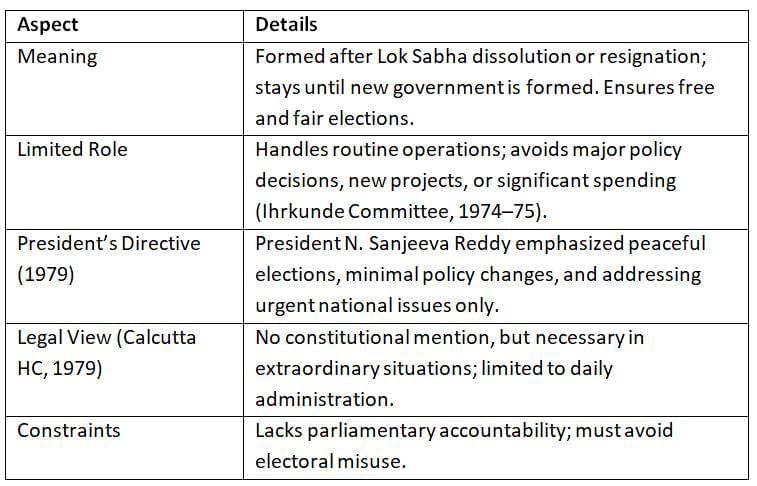
Key Points:
Caretaker governments ensure stability during transitions.
Their role is strictly limited to maintain fairness and neutrality.
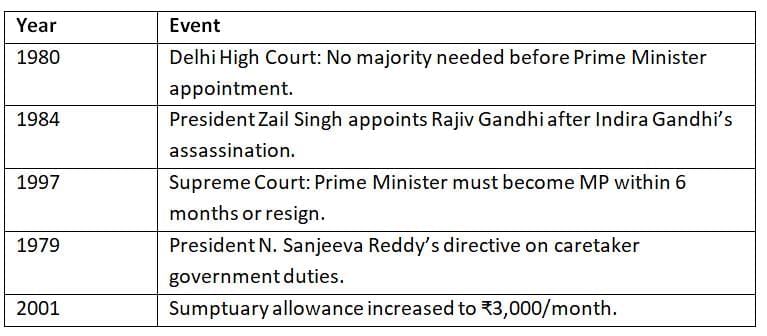
Chronology of Key Events
Conclusion
This chapter highlights the Prime Minister’s central role in India’s parliamentary system as the real executive authority, contrasting with the President’s nominal role. It covers the appointment process, powers, and historical context, emphasizing the Prime Minister’s influence over governance, policy, and national leadership. Understanding this role is essential for grasping how India’s government functions effectively within its constitutional framework.
|
162 videos|999 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Prime Minister - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the constitutional roles of the President and Prime Minister in India? |  |
| 2. How is the Prime Minister appointed in India? |  |
| 3. What are the powers and functions of the Prime Minister? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between the Prime Minister and the President? |  |
| 5. What is a caretaker government in India? |  |
















