Cheat Sheet: Public Interest Litigation (PIL) | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
PIL is a way for courts to help protect the public’s rights on issues like pollution, safety, or worker exploitation. We’ll cover what PIL is, how it started, key cases, why it grew, who can file it, its importance, and its challenges. Everything is in tables for quick learning, with short main points for each topic.
What is Public Interest Litigation?
PIL is when someone files a case in court to protect the public’s interests, like clean air, safe roads, or workers’ rights. It started in the USA to help groups like the poor or minorities and was adopted in India.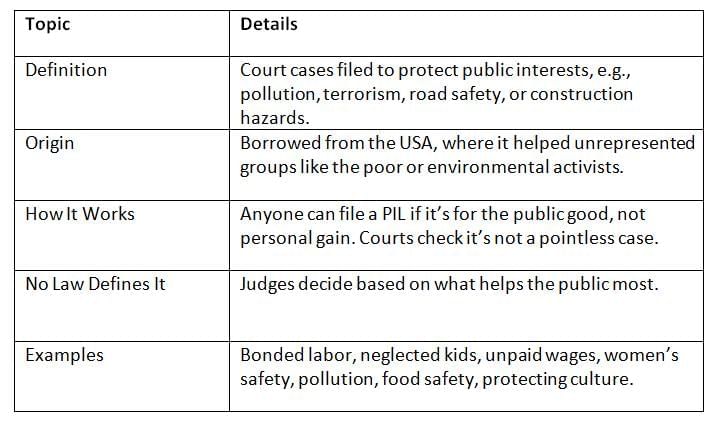
PIL Lets courts tackle big public issues, giving power to people to fight for everyone’s rights, but it must be genuine, not for personal benefit.
How PIL Started in India: Key Cases
PIL began in India in the 1970s through important court cases that helped the poor, prisoners, and the environment.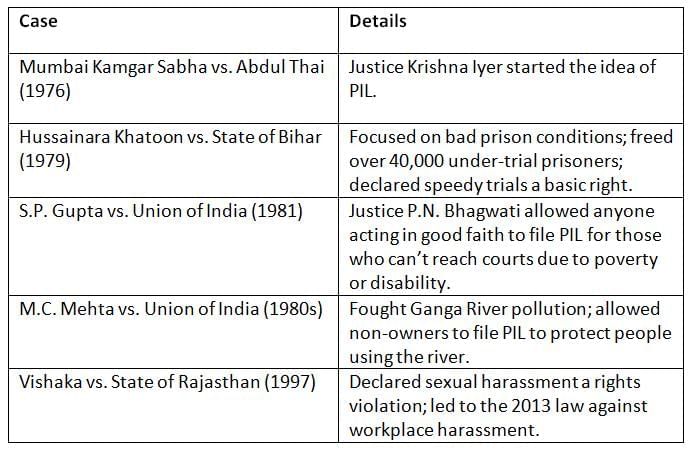
PIL grew through landmark cases that protected prisoners, rivers, and women, showing courts can fight for the public’s rights.
Why PIL Grew in India
PIL became popular because of India’s Constitution, strong laws, and judges who wanted to help the poor and marginalized.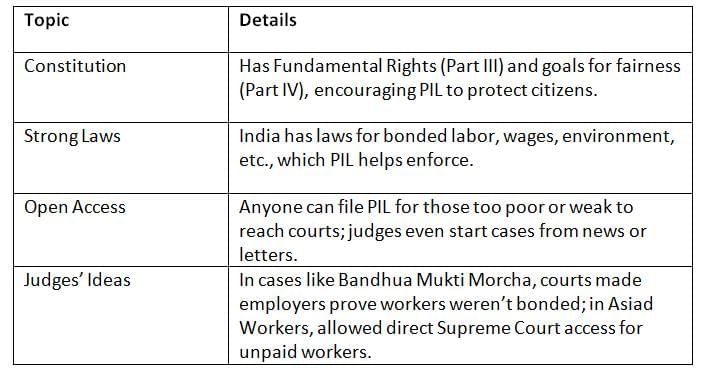
PIL grew because the Constitution, laws, and creative judges made it easier to fight for the poor and enforce rights.
Who Can File a PIL and Against Whom?
Any citizen can file a PIL, but it must be for the public good. It can target government bodies, not private people.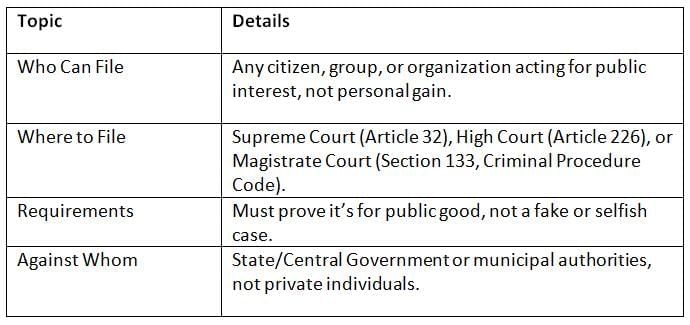
PIL is open to anyone fighting for the public, but it’s only against government bodies and must be serious.
Why PIL is Important
PIL helps ordinary people get justice, protects rights, and keeps the government accountable.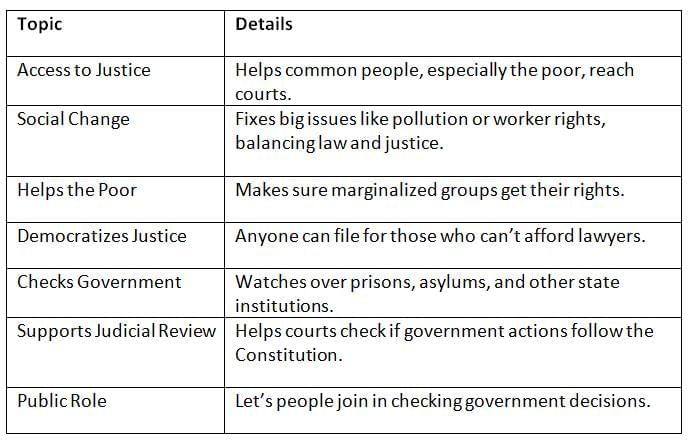 PIL makes justice reachable for everyone, protects rights, and ensures the government respects the law.
PIL makes justice reachable for everyone, protects rights, and ensures the government respects the law.
Challenges of PIL
While PIL does good, it can cause problems like unfair outcomes, fake cases, or too much court work.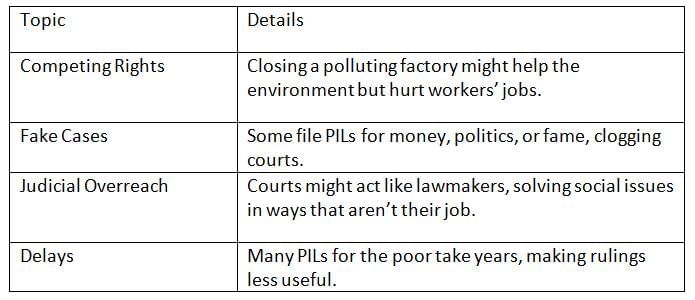
PIL can lead to unfair results, fake cases, or courts overstepping, and slow cases reduce its impact.
Timeline of Key Events

Conclusion
This chapter shows how Public Interest Litigation has changed India by letting courts fight for the public’s rights. From freeing prisoners to cleaning rivers and protecting women, PIL has helped the poor and marginalized. It makes justice open to all and keeps the government in check, but challenges like fake cases and delays need fixing. PIL is a powerful tool for fairness and democracy in India.
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Public Interest Litigation (PIL) - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is Public Interest Litigation (PIL) and its significance in the Indian legal system? |  |
| 2. How did Public Interest Litigation originate in India? |  |
| 3. Who is eligible to file a PIL and against whom can it be filed? |  |
| 4. What are the importance and benefits of PIL in India? |  |
| 5. What challenges does the Public Interest Litigation system face in India? |  |
















