Cheat Sheet: Union Public Service Commission | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter explains the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC), India’s key body for recruiting government officials. It covers the UPSC’s structure, functions, independence, limitations, and role as outlined in Articles 315 to 323 of the Constitution. The chapter shows how the UPSC ensures a merit-based system for civil service recruitment while highlighting its advisory nature.
Composition of the Union Public Service Commission
The UPSC is an independent constitutional body led by a chairman and members appointed by the President, with flexible membership to meet recruitment needs.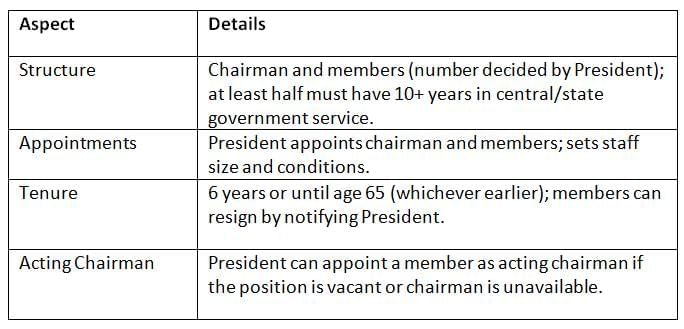
Key Points: The UPSC’s flexible composition, led by a chairman, ensures experienced leadership for civil service recruitment, with terms set by the President.
Removal of UPSC Members
The Constitution provides strict conditions for removing UPSC members to protect their independence, with misbehaviour cases requiring Supreme Court inquiry.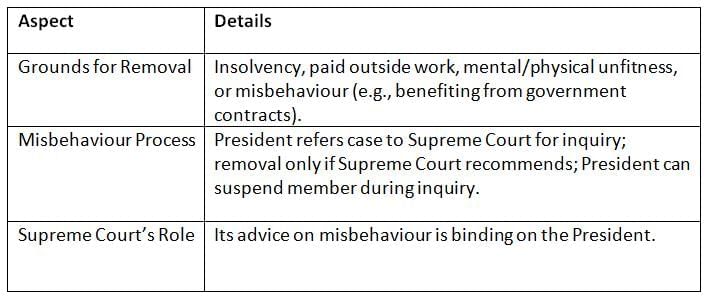
Key Points: Removal safeguards, especially for misbehaviour, ensure UPSC members’ independence through a rigorous, judicially overseen process.
Functions of the Union Public Service Commission
The UPSC conducts exams and advises on civil service matters, supporting merit-based recruitment and governance, though its role is advisory.
Key Points: The UPSC’s core functions include recruitment and advisory services, ensuring merit in civil services, with its scope expandable by Parliament.
Limitations of the Union Public Service Commission
The UPSC’s advisory role has specific exclusions, and its recommendations are not binding, limiting its authority in certain areas.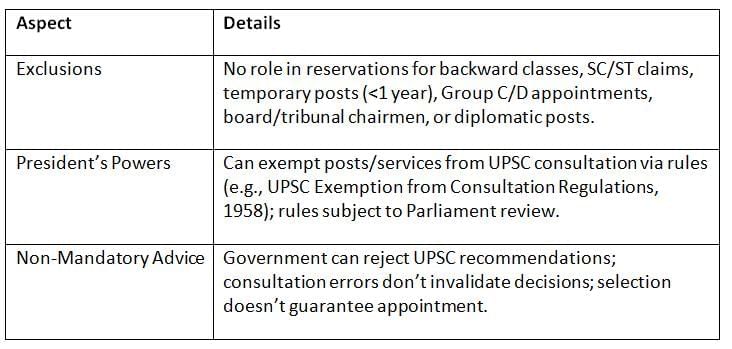
Key Points: The UPSC’s role is limited by exclusions, non-binding advice, and presidential exemptions, restricting its influence over certain recruitment matters.
Role of the Union Public Service Commission
The UPSC acts as a merit system watchdog, focusing on recruitment and advisory roles, but its scope is narrower than personnel management, which is handled elsewhere.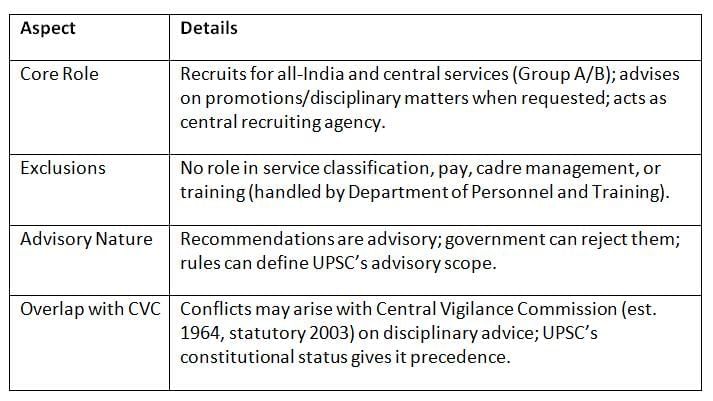
Key Points: The UPSC ensures merit-based recruitment but has a limited, advisory role, distinct from broader personnel management, with potential overlap with the CVC.
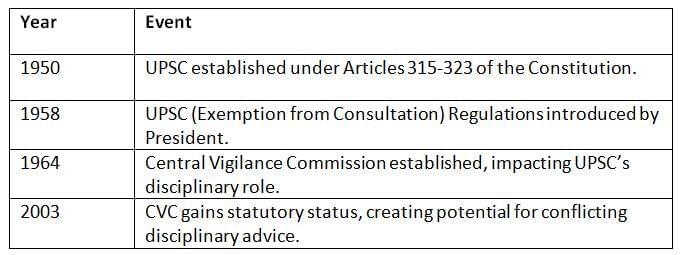
Chronology for Quick Revision
Conclusion
This chapter highlights the Union Public Service Commission’s crucial role in upholding India’s merit-based civil service system. As an independent constitutional body, the UPSC ensures fair recruitment and provides advisory support for government services. Despite its limited scope, non-binding recommendations, and exclusions from certain matters, it remains a cornerstone of transparent governance. Strengthening its advisory influence and clarifying overlaps with bodies like the CVC can enhance its effectiveness in sustaining India’s administrative integrity.
|
154 videos|998 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Union Public Service Commission - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the composition of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)? |  |
| 2. How can members of the UPSC be removed from their position? |  |
| 3. What are the primary functions of the Union Public Service Commission? |  |
| 4. What limitations does the Union Public Service Commission face? |  |
| 5. What role does the Union Public Service Commission play in Indian governance? |  |
















