UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Cheat sheet: Sustainability and Climate Change: India & the World
Cheat sheet: Sustainability and Climate Change: India & the World | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Sustainable Development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations.
Core Principles:
- Intergenerational equity
- Precautionary principle
- Inclusive growth
- Environmental stewardship
India’s Efforts:
- SDG India Index by NITI Aayog – benchmarks states’ performance on Sustainable Development Goals.
- Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) – nudges citizens towards pro-planet behaviours.
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) – umbrella program with 8 missions (e.g., Solar Mission, Energy Efficiency Mission).
Environmental Policy Framework
Key Legislations:
- Environment Protection Act, 1986
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- Forest Conservation Act, 1980 (recently amended to ease strategic projects)
Other Instruments:
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notifications
- National Environment Policy (under review)
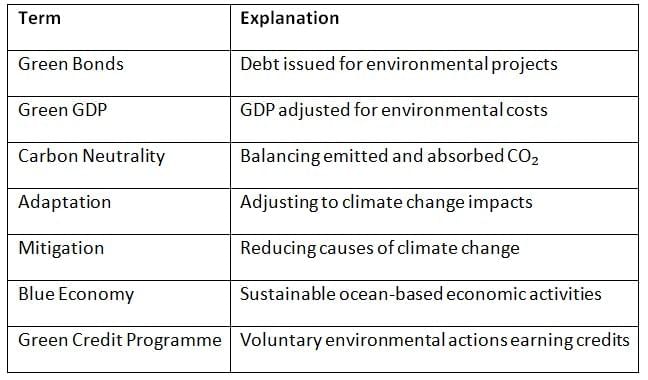
Green & Climate Finance
- Green Finance: Flows directed to projects with positive environmental impact.
- Climate Finance: International transfers for mitigation and adaptation.
- Global Mechanisms:
- Green Climate Fund (GCF)
- Global Environment Facility (GEF)
- Adaptation Fund
- Loss and Damage Fund – created under COP27, operational modalities advanced in COP28.
- Indian Developments:
- Launch of Sovereign Green Bonds
- Introduction of Green Credit Programme – incentivises voluntary pro-environment actions.
- Climate Budget Tagging initiated for sectoral integration
Climate Change: Mitigation & Adaptation
- Mitigation: Reduction of emissions through renewable energy, e-mobility, and afforestation.
- Adaptation: Coping strategies – resilient agriculture, climate-proof housing, early warning systems.
- Major Indian Schemes:
- National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC)
- FASTER Adoption of Electric Vehicles (FAME)
- PAT Scheme (Perform, Achieve, Trade for industries)
- UJALA (LED bulb distribution), Unnat Jyoti
Renewable Energy Transition
Target: 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030.
Progress:
- Solar: ~80 GW
- Wind: ~45 GW
- Hydropower and bioenergy significant contributors
Key Missions & Schemes:
- National Solar Mission
- Rooftop Solar Programme
- PM-KUSUM (solarisation of agricultural pumps)
- National Green Hydrogen Mission – 5 MMT production target
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) for solar PV and green technologies
India and Global Climate Commitments
UNFCCC – India is a signatory
Paris Agreement – India’s Updated NDCs:
- Reduce GDP emission intensity by 45% by 2030
- 50% cumulative power capacity from non-fossil sources
- Enhance forest carbon sink by 2.5–3 billion tonnes
- Net-Zero Commitment: India to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070
COP28 Highlights:
- Operationalisation of Loss and Damage Fund
- Calls for phasing down fossil fuels
- Emphasis on Global Stocktake to assess Paris goals progress
Important Terms
The document Cheat sheet: Sustainability and Climate Change: India & the World | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
108 videos|430 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat sheet: Sustainability and Climate Change: India & the World - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of sustainable development in the context of environmental policy? |  |
Ans.Sustainable development is crucial as it aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It balances economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection. Environmental policy frameworks are designed to promote sustainable development by establishing guidelines and regulations that encourage responsible resource use, reduce pollution, and protect ecosystems.
| 2. How does climate finance support green initiatives and adaptation strategies? |  |
Ans.Climate finance refers to investments aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing resilience to climate change. It supports green initiatives such as renewable energy projects, energy efficiency improvements, and sustainable agriculture practices. Additionally, it funds adaptation strategies that help communities adjust to the impacts of climate change, ensuring that vulnerable populations are equipped to handle environmental changes.
| 3. What are the main components of climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts? |  |
Ans.Climate change mitigation involves reducing or preventing the emission of greenhouse gases through strategies like transitioning to renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting carbon capture technologies. Adaptation, on the other hand, focuses on making adjustments to social, economic, and environmental practices to minimize the adverse effects of climate change, such as improving infrastructure, developing drought-resistant crops, and creating early warning systems for extreme weather events.
| 4. What role does India play in global climate commitments, and what are its primary objectives? |  |
Ans.India plays a significant role in global climate commitments, particularly through its participation in international agreements like the Paris Agreement. Its primary objectives include reducing carbon intensity, increasing the share of non-fossil fuel-based energy capacity, and enhancing forest cover. India aims to achieve sustainable growth while fulfilling its development needs and addressing climate change challenges.
| 5. What is the importance of the renewable energy transition in combating climate change? |  |
Ans.The renewable energy transition is essential for combating climate change as it reduces dependence on fossil fuels, which are the primary sources of greenhouse gas emissions. By shifting to renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, countries can lower their carbon footprints, enhance energy security, and create sustainable jobs. This transition also supports the global effort to limit temperature rise and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Related Searches















