- Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the blood and do not have ducts.
- The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland because it releases hormones like thyroxine directly into the bloodstream.
- Sweat and salivary glands are exocrine glands because they release their secretions through ducts.
- The pancreas is both an endocrine (insulin, glucagon) and exocrine (digestive enzymes) gland, but in general examples of pure endocrine glands, the thyroid is a standard choice.
Chemical Coordination In Animals - Endocrine System | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Hormones in Animals |

|
| Hormones |

|
| Difference between Nervous and Hormonal Coordination |

|
| Some Important Endocrine Glands and Hormones |

|
Hormones in Animals
- The branch of biology which deals with the study of the endocrine system and its physiology is known as"endocrinology".
- "Thomas Addison" is known as the Father of Endocrinology.
- The glands which pour their secretion directly into the blood are called endocrine glands. These glands lack ducts, so these glands are called ductless glands. Example: Thyroid gland, parathyroid gland.
- On the other hand, the glands with ducts are called exocrine glands. Example: Sweat gland, salivary gland.
Pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine part, so it is also called mixed gland or common gland or heterocrine gland.
Hormones
- Chemicals secreted by endocrine glands are called "hormones".
- The term hormone was coined by Starling.
- Hormones are also called "primary messengers" or "chemical messengers".
Discovery
- First discovered hormone was secretin.
- It was discovered by Bayliss and Starling.
Physical & Chemical Properties of Hormones
- These are secreted by endocrine glands.
- Hormones are secreted only when required.
- Their secretion is regulated by feedback mechanisms.
- These are generally released in the bloodstream.
- The molecules of most of the hormones are small.
- Their molecular weight is low.
- The secretion of a hormone is always in very small quantity.
- Hormones are destroyed after use i.e. hormones can not be stored in the body. Thyroxine is an exception.
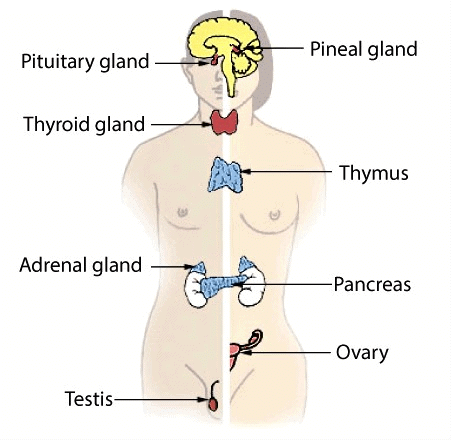 Male Endocrine Glands
Male Endocrine Glands
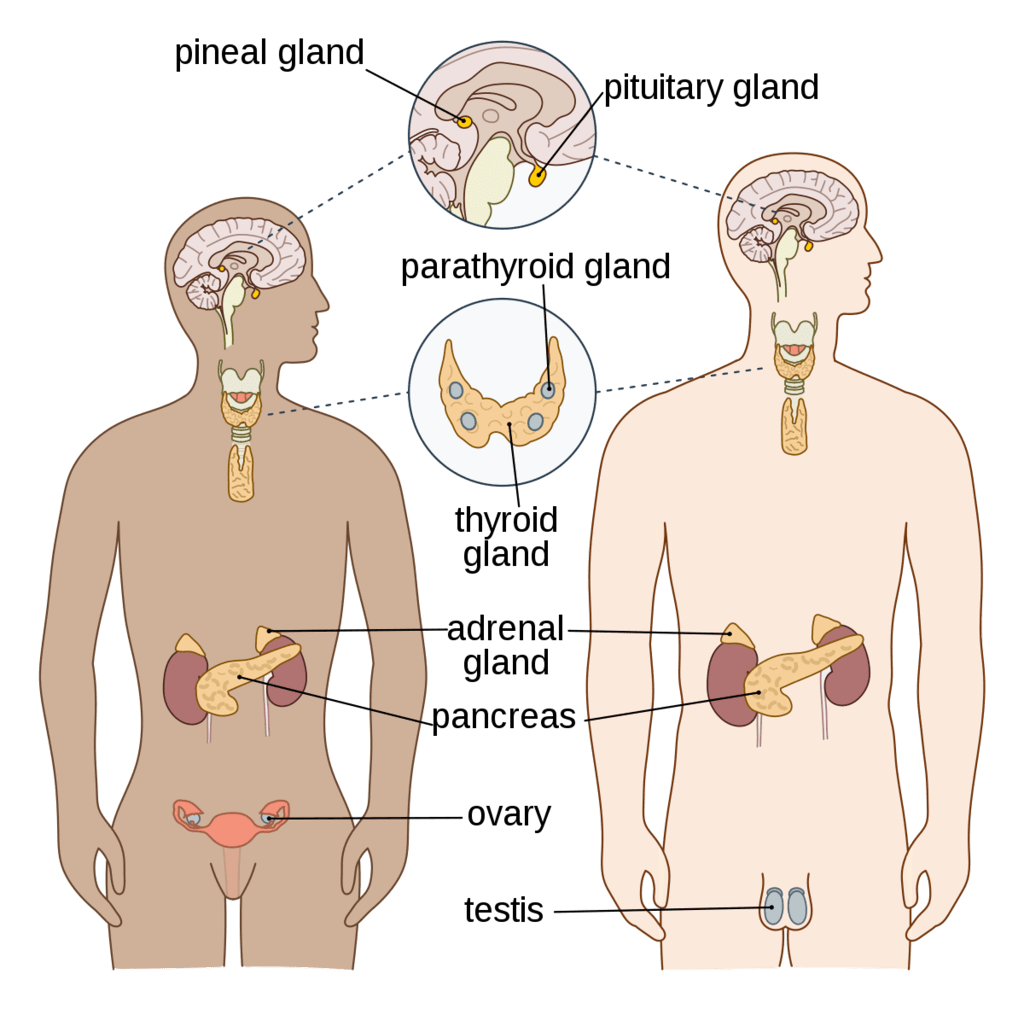 Major Endocrine Glands
Major Endocrine Glands
Difference between Nervous and Hormonal Coordination
| S. NO. | Nervous Coordination | Hormonal Coordination |
| 1 | It is sent as an electrical impulse along axons, and as a chemical across synapse. | It is sent as a chemical messenger via blood stream. |
| 2 | Information travels rapidly, in milliseconds. | Information travels slowly. |
| 3 | Information is directed to specific receptors–one or a few nerve fibres, gland cells or other neurons. | Information is spread throughout the body by blood from which the target cells or organs pick it up. |
| 4 | It gets response immediately. | It gets response usually slowly. |
| 5 | Its effects are short-lived. | Its effects are generally more prolonged. |
Some Important Endocrine Glands and Hormones
| S. No. | Nature of Endocrine gland | Position in body | Hormone(s) | Chemical Nature of Hormones | Function(s) | Hypo/Hypersection Causes | Special Points |
| 1 | Hypothalamus | Below thalamus in brain | Releasing and inhibiting hormones | Protein | Regulate the release of pituitary hormones | Ectodermal in orgin | |
| 2 | Pituitary - Anterior gland | Below hypothalamus attached to it with a stalk called infundibulum
| GH (Growth Hormone) | Protein | Body Growth | Hyposecretion in children causes dwarfism | Also called master gland of the body |
| Growth of Muscles and bones | Hypersecretion in children causes gigantism and in adults causes acromegaly | ||||||
| TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) | Protein | Regulate the secretion of hormones from thyroid | |||||
| ACTH (Adreno Cortico Tropic Hormone) | Protein | Secretion of hormones from adrenal cortex | |||||
| FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) | Protein | stimulate spermatogenesis and oogenesis | |||||
| LH (Luteinising Hormone) | Protein | It causes ovulatiin and formation of corpus luteum | - LH in males is called ICSH | ||||
| LTH (Luteotropic Honnone) | Protein | Stimulate growth of mammary glands during pregnancy and promotes lactation alter parturition (delivery) | - Also Known as Prolactin. | ||||
Middle lobe | MSH (Melanocyte Stimulating Honnone) | Protein | Metachrosis (colour change) in poikilothermals (cold blooded animals) | - In human MSH is secreted by anterior lobe is merged in anterior lobe | |||
| Posterior lobe | Oxytoxin | Protein | -Function in human is not known. - Contraction of uterine muscles during pregnancy - Causes release of milk after delivery | Also called birth hormone | |||
Vasopressin | Protein | - Reabsorption of water from DCT of nephron and collecting duct | -Hyposecretion causes Diabetes insipidus | Also called ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) | |||
| 3 | Thyroid | Located in the neck between the trachea and larynx | Thyroxine | Amine | Regulate BMR of body | - Hyposecretion in children causes cretinism | Thyroxine is the only hormone stored in our body |
| - Calcitonin | Protein | -Decreases the level of calcium in blood | - Hyposecretion in adults causes myxoedema - Generally say hyposecretion of thyroxine causes simple goitre - Hypersecretion of Thyroxine causes exophthalmic goitre | Element in thyroxine is iodine | |||
| 4 | Parathyroid | Attached to thyroid | Parathormone (PTH) | Protein | Increases the level of calcium in blood | Hypersecretion of PTH causes osteoporosis Hyposecretion causes tetany | Also called Collip's Hormone |
| 5 | Pineal gland | Attached to epithalamus in brain | Melatonin | Amine | - Metachrosis in poikibthermals - Control sexual behaviour in mammals | - Also called epiphysis cerebri - Also called as third eye in frog - Ectodermal in origin | |
| 6 | Pancreas | In the loop of duodenum | - Insulin | - Protein | - Decreases the level of glucose in blood | - Hyposecretion of insulin causes Diabetes mellitus | World Diabetes Day 14 November
|
| - Glucagon | - Protein | - Increases the level of glucose in blood | - Endocrine part of pancreas is called Islets of Langerhans. - Endodennal in origin | ||||
| 7 | Adrenal Gland | Above Kidney | Corticoids | Steroid | Hyposecretion of corticoids causes Addison's disease | Ectomesodennal in origin | |
| Adrenal Cortex | Mineralo corticoids | Maintain the level of Na+, K+ and Cl- body | Hypersecretion of corticoids causes Cushing's and Conn's disease | Also called 3-F gland, Life saving gland, 4-S gland, Emergency gland | |||
| Gluco corticoids | Carbohydrate metabolism | ||||||
| Sex corticoids | Secrete androgens and estrogens | ||||||
| Adrenaline | Amine | Increases heart beat, blood pressure and blood glucose level | |||||
| 8 | Testes | Outside the abdominal cavity | Testosterone | Steroid | -Stimulate spermatogenesis -Promote secondary sexual | ||
| 9 | Ovaries | Inside the abdominal cavity | Estrogen | Steroid | Stimuate oogenesis | ||
| Progestrone | Steroid | - Promote secondary sexual characters in females | |||||
| - Maintain pregnancy | Progesterone is also called anti abortion hormone | ||||||
| 10 | Thymus | Near Heart | Thymosin | Protein | Increase immunity of body | - Endodermal in origin -Also called Throne of Immunity or training School of T-lymphocytes |
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Coordination In Animals - Endocrine System - Science Class 10
| 1. What are hormones? |  |
| 2. How are nervous and hormonal coordination different? |  |
| 3. What are some important endocrine glands and hormones in animals? |  |
| 4. How does the endocrine system regulate the body? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of hormonal disorders in animals? |  |
















