NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Chemical Coordination & Integration | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Match List- I with List-II. (NEET 2025)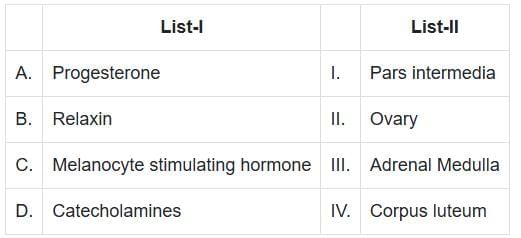
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(b) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(d) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
Ans: (c)
A. Progesterone - IV (Corpus luteum):
- Progesterone is a steroid hormone primarily produced by the corpus luteum in the ovaries.
- It plays a critical role in regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining pregnancy by preparing the uterine lining for implantation of the fertilized egg.
- During pregnancy, the placenta also produces progesterone to support fetal development.
B. Relaxin - II (Ovary):
- Relaxin is a hormone secreted mainly by the ovary, specifically by the corpus luteum, during pregnancy.
- It helps relax the ligaments in the pelvis and softens the cervix to prepare for childbirth.
- It also plays a role in inhibiting uterine contractions during early pregnancy.
C. Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH) - I (Pars intermedia):
- MSH is produced by the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland (a part of the intermediate lobe of the pituitary).
- It regulates the production and release of melanin in the skin, which affects pigmentation.
D. Catecholamines - III (Adrenal Medulla):
- Catecholamines such as adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) are produced by the adrenal medulla.
- These hormones are part of the body's response to stress ("fight-or-flight" response), increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels.
- Catecholamines also stimulate the breakdown of glycogen resulting in an increased concentration of glucose in blood. In addition, they also stimulate the breakdown of lipids and proteins.
Q2: Consider the following statements regarding function of adrenal medullary hormones: (NEET 2025)
A. It causes pupilary constriction
B. It is a hyperglycemic hormone
C. It causes piloerection
D. It increases strength of heart contraction
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) A, C and D only
(b) D only
(c) C and D only
(d) B, C and D only
Ans: (d)
- A. It causes pupillary constriction: This statement is incorrect. Adrenal medullary hormones cause pupillary dilation (mydriasis) to allow more light into the eyes and enhance vision during stressful situations. Pupillary constriction (miosis) is associated with the parasympathetic response, not the sympathetic response mediated by the adrenal medulla.
- B. It is a hyperglycemic hormone: Adrenal medullary hormones, particularly adrenaline, increase blood glucose levels by stimulating glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen into glucose) in the liver. This ensures that the body has an immediate supply of energy during stressful situations. Hence, this statement is correct.
- C. It causes piloerection: Piloerection, or the "goosebumps" phenomenon, is caused by the contraction of arrector pili muscles in response to adrenaline. This is part of the fight-or-flight response. Hence, this statement is correct.
- D. It increases the strength of heart contraction: Adrenaline and noradrenaline stimulate beta-adrenergic receptors in the heart, leading to increased heart rate and stronger heart contractions. This ensures better blood circulation during stress or emergency. Hence, this statement is correct.
Q3: Which of the following hormones released from the pituitary is actually synthesized in the hypothalamus? (NEET 2025)
(a) Follicle - stimulating hormone (FSH)
(b) Adenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
(c) Luteinizing hormone (LH)
(d) Anti - diuretic hormone (ADH)
Ans: (d)
- Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary gland.
- Vasopressin acts mainly at the kidney and stimulates resorption of water and electrolytes by the distal tubules and thereby reduces loss of water through urine (diuresis). Hence, it is also called as anti- diuretic hormone (ADH).
- An impairment affecting synthesis or release of ADH results in a diminished ability of the kidney to conserve water leading to water loss and dehydration. This condition is known as Diabetes Insipidus.
Other Options
Luteinizing hormone (LH):
- LH is synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
- It plays a key role in regulating the reproductive system, including ovulation in females and testosterone production in males.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH):
- FSH is also synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
- It is involved in the regulation of reproductive processes, such as the maturation of ovarian follicles in females and spermatogenesis in males.
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH):
- ACTH is synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
- It stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, which are vital for stress response and metabolism.
Q4: Match the List-I with List-II (NEET 2025)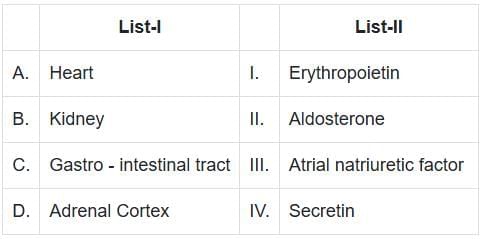
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(c) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Ans: (b)
A. Heart - III. Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF):
- The atrial wall of our heart secretes a very important peptide hormone called atrial natriuretic factor (ANF), which decreases blood pressure.
- When blood pressure is increased, ANF is secreted which causes dilation of the blood vessels. This reduces the blood pressure.
- ANF helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance by promoting sodium excretion and reducing water reabsorption in the kidneys.
- This hormone counteracts the effects of aldosterone and reduces blood volume, thereby lowering blood pressure.
B. Kidney - I. Erythropoietin:
- The juxtaglomerular cells of kidney produce a peptide hormone called erythropoietin which stimulates erythropoiesis (formation of RBC).
C. Gastro-intestinal Tract - IV. Secretin:
- Endocrine cells present in different parts of the gastro-intestinal tract secrete four major peptide hormones, namely gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK) and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP).
- Secretin acts on the exocrine pancreas and stimulates secretion of water and bicarbonate ions.
D. Adrenal Cortex - II. Aldosterone:
- The adrenal cortex produces aldosterone, a steroid hormone that is part of the mineralocorticoid group.
- Aldosterone regulates sodium and potassium levels in the body by increasing sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in the kidneys.
- This hormone is crucial for maintaining blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
Q5: Why can't insulin be given orally to diabetic patients? (NEET 2025)
(a) Because of structural variation
(b) Its bioavailability will be increased
(c) Human body will elicit strong immune response
(d) It will be digested in Gastro-Intestinal (GI) tract
Ans: (d)
- Insulin is a protein-based molecule, and like other proteins consumed in food, it is broken down into amino acids by digestive enzymes in the stomach and intestines.
- This enzymatic breakdown prevents insulin from retaining its functional structure and biological activity, rendering it ineffective if taken orally.
- Since oral delivery is not feasible, insulin is typically given via injections (subcutaneous, intravenous, or intramuscular).
- Research is ongoing for alternative delivery methods, such as inhalable insulin, transdermal patches, and oral formulations with protective coatings or encapsulations.
Other Options:
Human body will elicit a strong immune response:
- The human immune system does not typically produce a strong immune response to insulin, especially if it is human recombinant insulin, which mimics the natural hormone produced in the body. Immune responses are more relevant in cases of non-human insulin or impurities in synthetic formulations, which are rare in modern medicine.
Because of structural variation:
- Insulin’s structure is not a limiting factor for its administration. Its molecular structure is well-suited for interaction with insulin receptors, and it performs its function effectively once in the bloodstream.
Its bioavailability will be increased:
- This statement is incorrect because oral administration of insulin would result in extremely low bioavailability due to enzymatic breakdown in the GI tract. Bioavailability refers to the proportion of a drug that enters circulation and can have an active effect. Oral insulin delivery significantly reduces this proportion.
2024
Q1: Which of the following is not a steroid hormone? (NEET 2024)(a) Cortisol
(b) Testosterone
(c) Progesterone
(d) Glucagon
Ans: (d)
Steroid hormones are a class of hormones that are derived from cholesterol and are lipophilic (fat-soluble) in nature. They can easily pass through the cell membranes of target cells to bind with intracellular receptors. Common examples of steroid hormones include cortisol, testosterone, and progesterone, each involved in different regulatory functions in the body.
Cortisol (Option A) is a glucocorticoid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex. It is involved in the regulation of metabolism, immune response, and stress response.
Testosterone (Option B) is an androgen hormone primarily produced in the testes in males and in smaller quantities in the ovaries in females. It plays a key role in developing male reproductive tissues and promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as muscle and bone mass, and the growth of body hair.
Progesterone (Option C) is a hormone released by the ovaries and is important in the regulation of menstruation and maintaining the early stages of pregnancy.
Glucagon (Option D) is fundamentally different from the mentioned hormones. It is a peptide hormone, not a steroid hormone. Glucagon is produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas and works to raise the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in the liver. Unlike steroid hormones, glucagon does not pass through cell membranes but binds to receptors on the cell surface.
Thus, the correct answer to the question is Option D: Glucagon, as it is not a steroid hormone.
Q2: Match List I with List II :
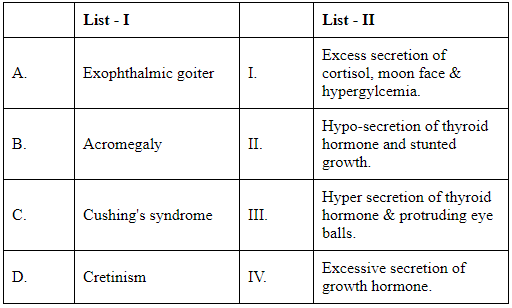 Choose the correct answer from the options given below : (NEET 2024)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below : (NEET 2024)
(a) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Ans: (d)
To solve the matching question, we need to correctly link each disease (List-I) with their corresponding characteristics (List-II). Here is the breakdown of each disease and its effects:
Exophthalmic goiter: Also known as Graves' disease, this is an autoimmune disorder that involves an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) and is characterized by symptoms such as protruding eyeballs. Therefore, this matches with "Hyper secretion of thyroid hormone & protruding eye balls." - from List II (III).
Acromegaly: This condition is caused by excessive secretion of growth hormone, usually from a benign tumor in the pituitary gland, leading to enlarged features (bones, especially in the hands, feet, and face). Thus, it corresponds with "Excessive secretion of growth hormone." - from List II (IV).
Cushing's syndrome: This syndrome is the result of prolonged exposure to high levels of the hormone cortisol. It features symptoms including obesity majorly centered around the abdomen and upper back, moon face, and hyperglycemia. Therefore, it fits "Excess secretion of cortisol, moon face & hyperglycemia." - from List II (I).
Cretinism: This is a condition arising from the deficiency of thyroid hormone in childhood, which causes impaired neurological function, stunted physical growth, and possibly other symptoms. It matches with "Hypo-secretion of thyroid hormone and stunted growth." - from List II (II).
Now, compare these with the available options:
Therefore, the correct answer is Option D.
Q3: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R : (NEET 2024)
Assertion A : FSH acts upon ovarian follicles in female and Leydig cells in male.
Reason R : Growing ovarian follicles secrete estrogen in female while interstitial cells secrete androgen in male human being.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans: (d)
Sol:
- Assertion A states that FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) acts on ovarian follicles in females and Leydig cells in males.
- In females, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles, which is essential for oocyte development and the production of estrogen.
- In males, FSH actually acts on Sertoli cells, not Leydig cells. Sertoli cells support sperm development, while Leydig cells produce testosterone, influenced by Luteinizing Hormone (LH).
Reason R accurately describes hormone secretion:
- Growing ovarian follicles secrete estrogen, which is vital for regulating the female reproductive cycle and secondary sexual characteristics.
- In males, Leydig cells (also known as interstitial cells) secrete androgens, including testosterone, important for male reproductive functions.
Thus, Assertion A is false because it incorrectly states that FSH acts on Leydig cells in males. However, Reason R is true as it correctly describes the hormone secretion by ovarian follicles and Leydig cells. Therefore, the correct answer is: Option D: A is false but R is true.
Q4: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)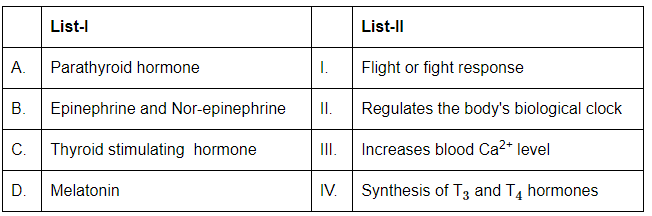 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(c) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(d) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
Ans: (a)
- A. Parathyroid hormone: This hormone is responsible for increasing blood calcium levels by promoting calcium release from bones and increasing calcium absorption in the kidneys and intestines. Thus, it corresponds to III (Increases blood Ca²⁺ level).
- B. Epinephrine and Nor-epinephrine: These hormones are involved in the fight or flight response, increasing heart rate, blood flow to muscles, and energy supply during stressful situations. Therefore, B corresponds to I (Flight or fight response).
- C. Thyroid stimulating hormone: This hormone stimulates the synthesis of T₃ and T₄ hormones, which regulate metabolism. Thus, C corresponds to IV (Synthesis of T₃ and T₄ hormones).
- D. Melatonin: This hormone regulates the body's biological clock, influencing sleep-wake cycles and seasonal rhythms. Therefore, D corresponds to II (Regulates the body's biological clock).
Thus, the correct match is:
- A-III: Parathyroid hormone increases blood Ca²⁺ levels.
- B-I: Epinephrine and nor-epinephrine regulate the fight or flight response.
- C-IV: Thyroid stimulating hormone stimulates the synthesis of T₃ and T₄ hormones.
- D-II: Melatonin regulates the biological clock.
Q5: With regard to hormones, identify the correct statements. (NEET 2024)
A. Epinephrine is a peptide hormone.
B. Progesterone is a peptide hormone.
C. Hormones that interact with membrane-bound receptors normally do not enter the target cell, but generate second messengers.
D. Hormones that interact with intracellular receptors mostly regulate gene expression.
E. Insulin is an amino acid derivative hormone.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) C and E only
(c) C and D only
(d) B and C only
Ans: (c)
- A. Epinephrine is a peptide hormone: This statement is incorrect. Epinephrine (also known as adrenaline) is a catecholamine hormone, derived from the amino acid tyrosine, and not a peptide hormone.
- B. Progesterone is a peptide hormone: This statement is incorrect. Progesterone is a steroid hormone, derived from cholesterol, not a peptide hormone.
- C. Hormones that interact with membrane-bound receptors normally do not enter the target cell, but generate second messengers: This statement is correct. Peptide hormones and other hydrophilic hormones bind to membrane-bound receptors, which then activate second messenger systems (like cAMP or calcium ions) inside the cell to carry out their effects.
- D. Hormones that interact with intracellular receptors mostly regulate gene expression: This statement is correct. Steroid hormones and thyroid hormones pass through the cell membrane and bind to intracellular receptors, typically affecting gene transcription and regulating gene expression.
- E. Insulin is an amino acid derivative hormone: This statement is incorrect. Insulin is a peptide hormone, not an amino acid derivative.
Thus, the correct statements are C and D, making the correct answer (c).
Q6: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
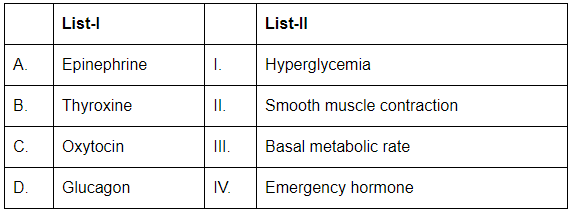
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II,B-I,C-IV,D-III
(b) A-III,B-II,C-I,D-IV
(c) A-IV,B-III,C-II,D-I
(d) A-I,B-IV,C-III,D-II
Ans: (c)
- A. Epinephrine: Epinephrine is often referred to as the emergency hormone because it prepares the body for the "fight or flight" response, increasing heart rate and blood flow. Thus, A corresponds to IV (Emergency hormone).
- B. Thyroxine: Thyroxine (T₄) regulates the basal metabolic rate (BMR), influencing metabolism and energy production in the body. Thus, B corresponds to III (Basal metabolic rate).
- C. Oxytocin: Oxytocin is involved in smooth muscle contraction, particularly during childbirth (uterine contractions) and in milk ejection during lactation. Thus, C corresponds to II (Smooth muscle contraction).
- D. Glucagon: Glucagon raises blood glucose levels by promoting the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, leading to hyperglycemia. Thus, D corresponds to I (Hyperglycemia).
Thus, the correct match is:
- A-IV: Epinephrine is the emergency hormone.
- B-III: Thyroxine regulates basal metabolic rate.
- C-II: Oxytocin promotes smooth muscle contraction.
- D-I: Glucagon leads to hyperglycemia.
Q7: Diuresis is prevented by: (NEET 2024)
(a) Renin from JG cells via switching off the osmoreceptors.
(b) ANF from atria of the heart.
(c) Aldosterone from adrenal medulla.
(d) Vasopressin from Neurohypophysis.
Ans: (d)
Vasopressin (also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH)) is secreted by the neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary). It plays a key role in regulating water balance in the body by increasing the reabsorption of water in the kidneys, thus preventing diuresis (excessive urination). When vasopressin is released, it acts on the kidneys to reduce urine output and conserve water, thereby preventing diuresis.
Why the other options are incorrect:
- (a) Renin from JG cells via switching off the osmoreceptors: Renin is involved in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance, but it does not directly prevent diuresis in the same way as vasopressin.
- (b) ANF from atria of the heart: Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) actually promotes diuresis by increasing the excretion of sodium and water, thereby lowering blood volume and blood pressure.
- (c) Aldosterone from adrenal medulla: Aldosterone, secreted by the adrenal cortex (not the adrenal medulla), helps regulate sodium and water balance, but it does not directly prevent diuresis; instead, it promotes sodium retention, which indirectly helps control blood volume and pressure.
Thus, (d) Vasopressin from Neurohypophysis is the correct answer as it directly prevents diuresis by promoting water reabsorption in the kidneys.
Q8: Identify the wrong statements: (NEET 2024)
A. Erythropoietin is produced by juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney.
B. Leydig cells produce Androgens.
C. Atrial Natriuretic factor, a peptide hormone, is secreted by the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
D. Cholecystokinin is produced by the gastrointestinal tract.
E. Gastrin acts on the intestinal wall and helps in the production of pepsinogen.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) D and E only
(b) A and B only
(c) C and E only
(d) A and C only
Ans: (c)
- A. Erythropoietin is produced by juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney: This statement is incorrect. Erythropoietin is actually produced by the peritubular capillary cells in the kidneys (primarily in response to low oxygen levels), not by the juxtaglomerular cells, which secrete renin.
- B. Leydig cells produce Androgens: This statement is correct. Leydig cells in the testes are responsible for producing androgens, primarily testosterone, which is crucial for male reproductive function and secondary sexual characteristics.
- C. Atrial Natriuretic factor, a peptide hormone, is secreted by the seminiferous tubules of the testes: This statement is incorrect. Atrial Natriuretic factor (ANF) is produced by the atria of the heart, not the seminiferous tubules of the testes. ANF helps regulate blood pressure by promoting sodium excretion and water loss.
- D. Cholecystokinin is produced by the gastrointestinal tract: This statement is correct. Cholecystokinin (CCK) is a peptide hormone produced by the duodenum in the gastrointestinal tract. It stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder and digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
- E. Gastrin acts on intestinal wall and helps in the production of pepsinogen: This statement is incorrect. Gastrin is produced by the stomach and stimulates the secretion of gastric juices, including hydrochloric acid (HCl). It does not act on the intestinal wall to produce pepsinogen; pepsinogen is produced by chief cells in the stomach lining and is activated to pepsin by the acidic environment created by gastrin.
Thus, the wrong statements are C and E, making the correct answer (3).
2023
Q1: Which of the following are NOT under the control of thyroid hormone? (NEET 2023)
A. Maintenance of water and electrolyte balance
B. Regulation of basal metabolic rate
C. Normal rhythm of sleep-wake cycle
D. Development of immune system
E. Support the process of RBCs formation
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and D only
(b) B and C only
(c) C and D only
(d) D and E only
Ans: (c)
Option (C) is the correct answer because thyroid hormones play an important role in the regulation of basal metabolic rate, maintenance of water and electrolyte balance and support the process of RBCs formation, whereas this hormone is not involved in regulating normal rhythm of sleep-wake cycle and development of immune system.
Q2: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2023)
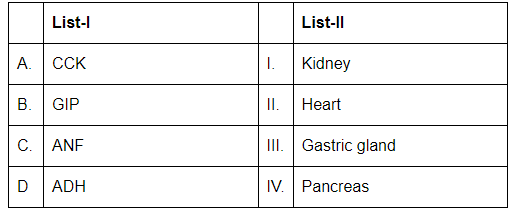 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)IV, (B)II ,(C)III, (D)I
(b) (A)IV, (B)III,(C)II ,(D)I
(c) (A)III (B)II (C)IV (D)I
(d) (A)II (B)IV (C)I (D)III
Ans: (b)
- A. CCK (Cholecystokinin): CCK is a hormone produced in the pancreas that stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder and digestive enzymes from the pancreas. Thus, A corresponds to IV (Pancreas).
- B. GIP (Gastric Inhibitory Peptide): GIP is produced by the gastric gland and inhibits gastric secretion, as well as stimulating insulin release. Thus, B corresponds to III (Gastric gland).
- C. ANF (Atrial Natriuretic Factor): ANF is a hormone produced in the heart that helps to regulate blood pressure by promoting sodium and water excretion. Thus, C corresponds to II (Heart).
- D. ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone): ADH plays a role in regulating water balance by increasing water reabsorption in the kidneys. Thus, D corresponds to I (Kidney).
Q3: Which of the following statements are correct with respect to the hormone and its function? (NEET 2023)
A: Thyrocalcitonin (TCT) regulates the blood calcium level.
B: In males, FSH and androgens regulate spermatogenesis.
C: Hyperthyroidism can lead to goitre.
D: Glucocorticoids are secreted in Adrenal Medulla.
E: Parathyroid hormone is regulated by circulated levels of sodium ions.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (C) and (E) only
(b) (A) and (B) only
(c) (B) and (C) only
(d) (A) and (D) only
Ans: (b)
- A: Thyrocalcitonin (TCT) regulates the blood calcium level: This statement is correct. Thyrocalcitonin (also called calcitonin) is produced by the thyroid gland and helps to lower blood calcium levels by inhibiting calcium release from bones and promoting calcium excretion in the kidneys.
- B: In males, FSH and androgens regulate spermatogenesis: This statement is correct. In males, Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and androgens (e.g., testosterone) regulate the process of spermatogenesis (the production of sperm in the testes).
- C: Hyperthyroidism can lead to goitre: This statement is incorrect. Goitre is typically associated with hypothyroidism (underproduction of thyroid hormones), where the thyroid gland enlarges due to lack of iodine or insufficient thyroid hormone production. Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, is an overproduction of thyroid hormones.
- D: Glucocorticoids are secreted in the Adrenal Medulla: This statement is incorrect. Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol) are secreted by the adrenal cortex, not the medulla. The adrenal medulla produces catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine).
- E: Parathyroid hormone is regulated by circulated levels of sodium ions: This statement is incorrect. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates calcium levels in the blood, not sodium. It increases blood calcium levels by promoting calcium release from bones, reabsorption in the kidneys, and activation of vitamin D.
Thus, the correct statements are (A) and (B), making the answer (b).
Q4: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: Parathyroid hormone acts on bones and stimulates the process of bone resorption.
Statement II: Parathyroid hormone along with Thyrocalcitonin plays a significant role in carbohydrate metabolism.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is false
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
Ans: (a)
- Statement I: Parathyroid hormone acts on bones and stimulates the process of bone resorption: This statement is correct. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates bone resorption by activating osteoclasts, which break down bone tissue and release calcium into the blood. This helps to increase the blood calcium levels.
- Statement II: Parathyroid hormone along with Thyrocalcitonin plays a significant role in carbohydrate metabolism: This statement is false. Parathyroid hormone and thyrocalcitonin (calcitonin) are primarily involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphate levels in the body, not carbohydrate metabolism. While they have important roles in maintaining bone health and calcium balance, they do not directly regulate carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin, glucagon, and other hormones are primarily responsible for carbohydrate metabolism.
Thus, the correct answer is (a): "Statement I is correct but Statement II is false."
2022
Q1: Which of the following are not the effects of parathyroid hormone? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(A) Stimulates the process of bone resorption.
(B) Decreases Ca2+ level in blood.
(C) Reabsorption of Ca2+ by renal tubules.
(D) Decreases the absorption of Ca2+ from digested food.
(E) Increases metabolism of carbohydrates.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (D) and (E) only
(b) (A) and (E) only
(c) (B) and (C) only
(d) (A) and (C) only
Ans: (a)
Parathyroid glands are located at the back of the thyroid glands.They secrete a hormone known as parathyroid hormone or parathormone (PTH). It regulates the level of calcium in the blood. PTH increases the level of calcium in the blood when it’s too low. It increases bone resorption by increasing the activity of osteoclasts and thus adding more calcium to blood. It also increases the reabsorption of calcium ions from renal tubules and digested food. PTH also decreases the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Q2: Give below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): FSH which interacts with membrane bound receptors does not enter the target cell.
Reason (R): Binding of FSH to its receptors generates second messenger (cyclic AMP) for its biochemical and physiological responses.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
(a) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Ans: (c)
- Assertion (A) is correct because FSH, or follicle-stimulating hormone, is a peptide hormone that does not enter the target cell. Instead, it interacts with membrane-bound receptors on the surface of the target cell. This is a common feature of peptide hormones, as they are too large and hydrophilic to pass through the cell membrane.
- Reason (R) is also correct. When FSH binds to its receptor, it triggers a cascade of intracellular events, including the production of second messengers like cyclic AMP (cAMP). The second messengers then go on to activate various biochemical and physiological responses within the target cell, such as cell growth and hormone production. This is a typical process for signal transduction initiated by the binding of a hormone to its cell surface receptor.
- However, (R) is not the correct explanation of (A) because it doesn't directly address why FSH doesn't enter the target cell. The reason FSH does not enter the target cell is that it is a peptide hormone, which cannot cross the cell membrane. Instead, it interacts with cell surface receptors to initiate a signaling cascade. The generation of second messengers, like cAMP, is a part of the signaling process that takes place after FSH binds to its receptor, but it is not the reason why FSH doesn't enter the cell.
2021
Q1: Erythropoietin hormone which stimulates R.B.C. formation is produced by: (NEET 2021)
(a) The cells of bone marrow
(b) Juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney
(c) Alpha cells of the pancreas
(d) The cells of the rostral adenohypophysis
Ans: (b)
- Option (b) is correct because The juxtaglomerular cells of kidney produce peptide hormone called erythropoietin which stimulates (erythropoiesis). It stimulates the stem cells of the bone marrow to increase red blood cell production.
- Alpha cells of pancreas produce hormone glucagon.
- The cells of rostral adenohypophysis synthesizes hormones of anterior lobe of pituitary.
- The cells of bone marrow are responsible for formation of formed elements.
2020
Q1: Match the following columns and select the correct option. (NEET 2020)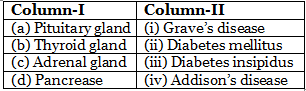
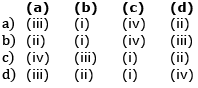
Ans: (a)
Grave’s disease is due to excess secretion of thyroid hormones (T3 & T4). Diabetes mellitus is due to hyposecretion of insulin from beta-cells of pancreas. Diabetes insipidus is due to hyposecretion of ADH from posterior pituitary. Addison’s disease is due to hyposecretion of hormone from adrenal cortex.
Q2: Select the correct statement. (NEET 2020)
(a) Insulin acts on pancreatic cells and adipocytes.
(b) Insulin is associated with hyperglycemia.
(c) Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis.
(d) Glucagon is associated with hypoglycemia.
Ans: (c)
Glucagon is associated with hyperglycemia. Insulin acts on hepatocytes and adipocytes and is associated with hypoglycemia. Glucocorticoid stimulates gluconeogenesis, so increase blood sugar level.
2019
Q1: Match the following hormones with their respective disease:
| (A) Insulin | (i) Addison’s disease |
| (B) Thyroxin | (ii) Diabetes insipidus |
| (C) Corticoids | (iii) Acromegaly |
| (D) Growth hormone | (iv) Goitre |
| (v) Diabetes mellitus |
Select the correct option. (NEET 2019)
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) | |
| (a) | (ii) | (iv) | (i) | (iii) |
| (b) | (v) | (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
| (c) | (ii) | (iv) | (iii) | (i) |
| (d) | (v) | (iv) | (i) | (iii) |
Ans: (d)
- Diabetes mellitus is caused due to deficiency of insulin.
- Goite is caused due to deficiency of Iodine which leads to less secretion of thyroxine.
- Addison’s disease is caused due to hyposecretion of corticoids.
- Acromegaly is caused due to hypersecretion of growth hormones after puberty.
2018
Q1: Which of the following is an amino acid derived hormone? (NEET 2018)
(a) Epinephrine
(b) Ecdysone
(c) Estradiol
(d) Estriol
Ans: (a)
Epinephrine is derived from amino acid tyrosine by the removal of carboxylic group.
2017
Q1: GnRH, a hypothalamic hormone, needed in reproduction, acts on (NEET 2017)
(a) Anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and FSH
(b) Posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of oxytocin and FSH
(c) Posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and relaxin
(d) Anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and oxytocin.
Ans: (a)
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) is secreted by the hypothalamus which stimulates the anterior lobe of pituitary gland to secrete luteinising hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
Q2: A temporary endocrine gland in the human body is (NEET 2017)
(a) Corpus cardiacum
(b) Corpus luteum
(c) Corpus allatum
(d) Pineal gland.
Ans: (b)
Corpus luteum is the temporary endocrine gland formed in the ovary after ovulation. It release hormones like progesterone, oestrogen etc.
2016
Q1: Graves’ disease is caused due to (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Hyposecretion of thyroid gland
(b) Hypersecretion of thyroid gland
(c) Hyposecrction of adrenal gland
(d) Hypersecretion of adrenal gland.
Ans: (b)
Exophthalmic goitre or Graves’ disease is a thyroid enlargement (goitre) in which the thyroid secretes excessive amount of thyroid hormone. It is characterised by exophthalmia (protrusion of eye balls because of fluid accumulation behind them), loss of weight, slightly rise in the body temperature, excitability, rapid heart beat, nervousness and restlessness.
Q2: Name a peptide hormone which acts mainly on hepatocytes, adipocytes and enhances cellular glucose uptake and utilisation. (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Insulin
(b) Glucagon
(c) Secretin
(d) Gastrin
Ans: (a)
Insulin is a peptide hormone, secreted by the β cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas, that promotes the uptake of glucose by body cells, particularly in the liver (hepatocytes) and muscles (adipocytes) and thereby controls its concentration in the blood.
Q3: The posterior pituitary gland is not a true endocrine gland because (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) It is provided with a duct
(b) It only stores and releases hormones
(c) It is under the regulation of hypothalamus
(d) It secretes enzymes.
Ans: (b)
Posterior lobe of pituitary gland does not secrete any hormone. Its hormones are synthesised by the hypothalamus. It only stores and releases these hormones. Hence, it cannot be considered as true gland.
Q4: Changes in GnRH pulse frequency in females is controlled by circulating levels of (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Estrogen and progesterone
(b) Estrogen and inhibin
(c) Progesterone only
(d) Progesterone and inhibin
Ans: (a)
At the pituitary, GnRH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of the gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH). These processes are controlled by the size and frequency of GnRH pulses, as well as by feedback from progesterone and estrogens. Low-frequency GnRH pulses are required for FSH release, whereas highfrequency GnRH pulses stimulate LH pulses in a one to one manner.
2015
Q1: Which one of the following hormones is not involved in sugar metabolism? (AIPMT 2015)
(a) Aldosterone
(b) Insulin
(c) Glucagon
(d) Cortisone
Ans: (a)
Aldosterone is produced by adrenal cortex and plays an important role in the regulation of Na+ and K+ levels in body.
Q2: Which one of the following hormones though synthesised elsewhere is stored and released by the master gland? (AIPMT 2015)
(a) Luteinizing hormone
(b) Prolactin
(c) Melanocyte stimulating hormone
(d) Antidiuretic hormone
Ans: (d)
ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin are produced by hypothalamus and stored in posterior pituitary.
Q3: A chemical signal that has both endocrine and neural roles is? (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Calcitonin
(b) Epinephrine
(c) Cortisol
(d) Melatonin
Ans: (b)
Epinephrine acts as both a hormone and a neurotransmitter. It is crucial for the body's fight-or-flight response.
Functions include: Increasing heart rate, Enhancing alertness, Boosting energy availability.
2014
Q1: Identify the hormone with its correct matching of source and function: (AIPMT 2014)
(a) Oxytocin - posterior pituitary, growth and maintenance of mammary glands.
(b) Melatonin - pineal gland, regulates the normal rhythm of sleepwake cycle.
(c) Progesterone - corpus-luteum, stimulatiuon of growth and activities of female secondary sex orgAns:
(d) Atrial natriuretic factor - ventricular wall increases the blood pressure.
Ans: (b)
- Melatonin is produced by the pineal gland. It is essential for regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Melatonin helps maintain our body's natural circadian rhythms.
- Oxytocin is produced by hypothalamus and generally secreted by posterior pituitary. It stimulates secretion of milk from mammary glands; causes contraction of uterus at the time of child birth.
- Progesterone is secreted by corpus luteum. It stimulates uterus for pregnancy, implantation, formation of placenta and development of mammary glands.
- Atrial natriuretic factor is secreted by atrial wall in response to an increased return of the venous blood. This hormone regulates the blood volume through increased excretion of ions and water.
|
169 videos|524 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Chemical Coordination & Integration - Biology Class 11
| 1. How does chemical coordination play a role in the integration of the human body? |  |
| 2. Which glands are responsible for the chemical coordination in the human body? |  |
| 3. How do hormones travel in the body to exert their effects on target organs? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the hypothalamus in chemical coordination and integration? |  |
| 5. How does the dysfunction of the endocrine system affect the overall health of an individual? |  |






















