Chemical Reactions and Equations - 1 Class 10 Worksheet Science
Q1. Which of the following is not a physical change? (1 Mark)
(A) Boiling of water to give water vapour
(B) Melting of ice to give water
(C) Dissolution of salt in water
(D) Combustion of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
Ans: Option D
Explanation: Combustion of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) forms CO2 and H2O (chemical change), while in other cases, there's just a change of state (or physical change).
Q2. Read the given passage and answer the following questions.
In the following chemical reaction, ‘‘zinc oxide reacts with carbon to produce zinc metal and carbon monoxide.’’
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
(a) The substance getting oxidized is ________ and the one getting reduced is ________. (1 Marks)
(b) State the reason for choosing the carbon. (1 Marks)
(c) Name the type of reaction. (1 Marks)
(d) Give another example of a similar type of reaction. (1 Marks)
Ans.
(a) The substance getting oxidized is carbon, and the one getting reduced is zinc oxide.
- Carbon gains oxygen → forms carbon monoxide (CO) → oxidized
- Zinc oxide loses oxygen → forms zinc (Zn) → reduced
(b) Reason for choosing carbon:
Carbon is a good reducing agent. It removes oxygen from metal oxides like ZnO, converting them into pure metal (Zn), while itself getting oxidized to CO.
(c) It is a redox reaction or oxidation and reduction reaction.
(d) CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O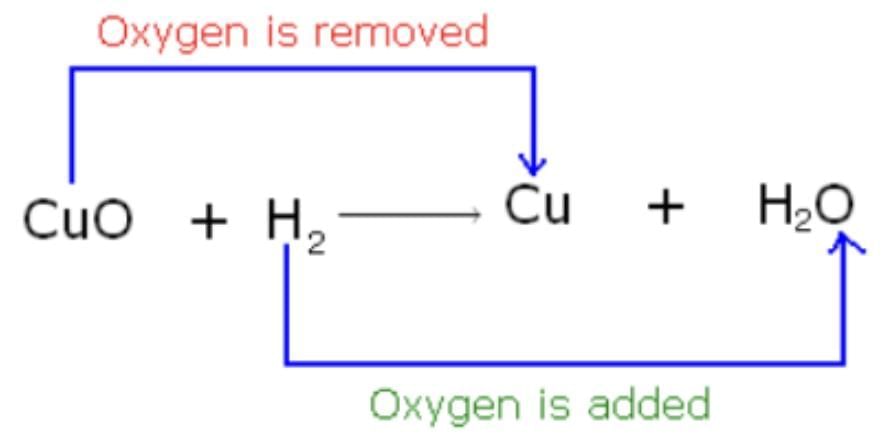
Q3. Which one is a chemical change–rusting of iron or melting of iron?
Ans. Rusting of iron
Q4. What happens when quick lime is added to water? (1 Marks)
Ans. When quick lime (CaO) is added to water, it reacts vigorously to form slaked lime (Ca(OH)₂) and releases a large amount of heat.
Reaction:
CaO(s) (quick lime) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (Slaked lime) + Heat
This is an exothermic reaction.
Q5. Identify the type of reactions taking place in each of the following cases and write the balanced chemical equation for the reactions.
(a) Zinc reacts with silver nitrate to produce zinc nitrate and silver.
(b) Potassium iodide reacts with lead nitrate to produce potassium nitrate and lead iodide. (3 Marks)(CBSE Marking Scheme, 2019)
Ans.
(a) Displacement reaction i.e. Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn (NO3)2 + 2Ag
(b) Double displacement reaction i.e. 2KI + Pb(NO3)2 → PbI2 + 2KNO3
Q6. (i) Define corrosion. What name is given to the corrosion of iron?
(ii) Name the color of the coating formed on silver and copper articles when exposed to air.
(iii) List two damages caused by corrosion and suggest how corrosion can be prevented. (5 Marks)
Ans.
(i) Corrosion is a process in which metals are deteriorated by air, moisture, chemicals, etc. Corrosion of iron is Rusting.
(ii) Silver - black, copper - green.
(iii) Causes: Car bodies, bridges, railing, etc. (Any two)
Prevention: Painting, alloying, greasing, etc. (Any two)
Q7. Identify the type of chemical reaction in the following statements and define each of them :
(i) Digestion of food in our body
(ii) Rusting of iron
(iii) Heating of manganese dioxide with aluminum powder.
(iv) Blue color of copper sulphate solution disappears when iron filings are added to it.
(v) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride and water. (5 Marks)
Ans.
(i) Decomposition Reaction: Carbohydrates are broken down to form glucose.
(ii) Oxidation Reaction: When an iron object is left in moist air for a considerable time, it gets covered with a red-brown flaky substance called rust.
(iii) Displacement reaction: More reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its salt solution.
(iv) Displacement reaction: More reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its salt solution.
(v) Double displacement reaction: Reaction in which two compounds react by exchanging ions to form two new compounds. (CBSE Marking Scheme, 2016)
Q8. What happens when :
(i) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to solid sodium carbonate.
(ii) Quicklime is treated with water.
(iii) Sodium chloride solution is added to the lead nitrate solution.
Also, write the chemical equation in each case. (3 Marks)
Ans.
(i) Na2CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
(ii) CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
(iii) Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaCl(aq) → PbCl2(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
Q9.The following diagram displays a chemical reaction. Observe and answer the following questions:
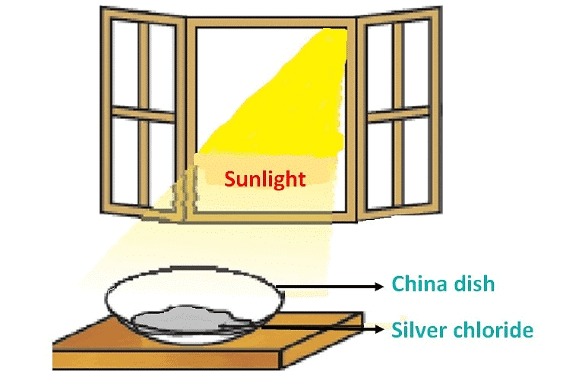
(a) The type of chemical reaction that will take place is
(i) Photochemical decomposition
(ii) Displacement reaction
(iii) Reduction reaction
(iv) Combination reaction (1 Marks)
(b) What happens to the silver chloride? (1 Marks)
(c) Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved. (1 Marks)
(d) Mention one commercial use of this salt. (1 Marks)
Ans. (a) (i) Photochemical decomposition
(b) White silver chloride changes to grey as it decomposes to silver and chlorine in the presence of sunlight.
(c) 2AgCl (s)  2Ag (s) + Cl₂ (g)
2Ag (s) + Cl₂ (g)
White Gray
(d) Black and white photography.
Q11. When a copper wire was left in silver nitrate solution for some time, it was observed that the solution turned bluish-green.
(i) Explain the observation.
(ii) Write the balanced chemical equation to represent the change. (3 Marks)
Ans.
(i) Copper is more reactive than silver. Hence, when the copper wire is dipped in silver nitrate solution, it displaces silver from AgNO3 solution forming copper nitrate, which is bluish-green in color.
(ii) Cu + 2AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
Q12. (i) Solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for testing carbon dioxide. Write the equation of the reaction of ‘X’ with carbon dioxide.
(ii) How is ‘X’ obtained? Write chemical equations. (3 Marks)
Ans.
(i) Substance X-Calcium Hydroxide.
Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s) + H2O(l)
CaCO3(s)are white precipitates formed during the reaction.
(ii) Calcium hydroxide is obtained by reaction of calcium oxide and water.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
Q.13. Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a reason (R).
Assertion (A): Carbon dioxide turns lime water milky.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide sullies the water.
Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both assertion (a) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (a).
(B) Both assertion (a) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (a).
(C) Assertion (a) is true but reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (a) is false but reason (R) is true.
Ans: Option C
Explanation: Carbon dioxide reacts with lime water (calcium hydroxide) to form a milky precipitate of calcium carbonate.
Q14. Name and state the law kept in mind while we balance a chemical equation. (1 Marks)
Ans. Law of conservation of mass: Mass can neither be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Q15. 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube.
Answer the following :
(i) List any two observations.
(ii) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction. (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) Two observations are :
(a) Change in state and color.
(b) Evolution of gas
(ii) Decomposition reaction
(iii) FeSO₄ (s)  Fe₂O₃ (s) + SO₂ (g) + SO₃ (g)
Fe₂O₃ (s) + SO₂ (g) + SO₃ (g)
Reason (R): At higher temperatures, molecular motion becomes more rapid.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Reactions and Equations - 1 Class 10 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are the types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 2. How do you balance a chemical equation? |  |
| 3. What is the law of conservation of mass in relation to chemical reactions? |  |
| 4. What are some common indicators of a chemical reaction occurring? |  |
| 5. How can I identify reactants and products in a chemical equation? |  |






















