Class 10 Civics Chapter 2 Question Answers - Federalism
Q1. Mention three policies that have strengthened federalism in India.
Ans: The success of federalism in India is largely due to its democratic politics, which promotes respect for diversity and a shared desire for unity. Here are three key policies that have strengthened federalism:
- Linguistic States: - The creation of states based on language was a significant step after independence. - This approach has helped unify the country and simplify administration, despite initial concerns about potential disintegration.
- Language Policy: - While Hindi is the official language, the Constitution protects 21 other scheduled languages. - This policy ensures that no single language dominates, supporting the cultural diversity of the nation.
- Centre-State Relations: - The restructuring of these relations has enhanced federalism. - Post-1990, the rise of regional parties and coalition governments has fostered a culture of power-sharing and respect for state autonomy.
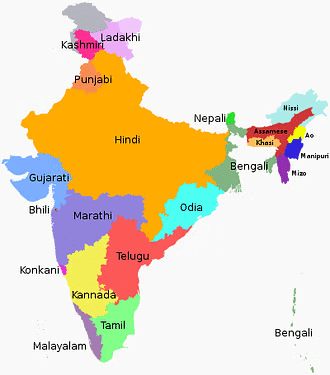
Q2. In which way does the language policy in India help our country avoid the situation that Sri Lanka is in today? (HOTS)
Ans: India's language policy plays a crucial role in maintaining harmony among its diverse linguistic communities. Key aspects include:
- No single national language: The Constitution does not designate any language as the national language, which helps prevent dominance by any one group.
- Official languages: Hindi is the official language, but there are 22 other Scheduled Languages recognised, ensuring representation for various linguistic groups.
- Flexibility in language use: The Central Government allows the use of English alongside Hindi for official purposes, accommodating non-Hindi speaking states.
- State languages: Each state can have its own official language, allowing local governance to operate in the language of the majority.
- Contrast with Sri Lanka: In Sri Lanka, the 1956 Act made Sinhala the only official language, marginalising Tamil speakers and leading to social tensions.
The cautious approach of Indian leaders in promoting Hindi, without imposing it on other states, has helped avoid the ethnic conflicts seen in Sri Lanka.
Q3. How can you say that power-sharing is more effective today than it was in the early years after the Constitution came into force? (HOTS)
Ans: In the early years after the Constitution was enacted, the same party often ruled at both the Centre and in most States. This led to:
- The State Governments not fully exercising their rights as autonomous federal units.
- Central Government misusing its power to dismiss State Governments controlled by rival parties, undermining the spirit of federalism.
However, significant changes occurred after 1990:
- The rise of regional parties in many States.
- The beginning of the era of coalition governments at the Centre, as no single party secured a clear majority in the Lok Sabha.
- Major national parties had to form alliances with regional parties to govern effectively.
This shift fostered:
- A new culture of power-sharing.
- Greater respect for the autonomy of State Governments.
Q4. Why is decentralisation favoured in democracy? Identify any two reasons. (2014)
Ans: Decentralisation is favoured in democracy for several reasons:
- Local Knowledge: People have a better understanding of the issues in their own areas. This local insight allows for more effective solutions.
- Participation: Decentralisation enables direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes, fostering a culture of democratic engagement.
Decentralisation involves transferring power from central and state governments to local authorities. This approach is essential for addressing numerous local problems effectively. The Constitution of India acknowledges the need for decentralisation, leading to significant reforms in 1992 that strengthened local governance.
Key features of these reforms include:
- Mandatory regular elections for local bodies.
- Reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and women.
- Establishment of the State Election Commission to oversee local elections.
- Sharing of powers and resources between state and local governments.
These measures enhance the effectiveness of local governance and ensure that democracy is more participatory.
Q5. Explain the structure of the new Panchayati Raj institutions, both in rural and urban areas.
Ans: Rural Local Government is known as Panchayati Raj or democratic decentralisation. The structure includes:
- Each village or group of villages has a Gram Panchayat.
- The Panch, President, or Sarpanch is directly elected by the adult population of the village.
- The Panchayat operates under the supervision of the Gram Sabha, which includes all voters.
- A group of Gram Panchayats forms a Panchayat Samiti (also known as Block or Mandal).
- All Panchayat Samitis together create the Zilla Parishad, which consists of elected members, including Lok Sabha members and local MLAs.
- The Chairperson of the Zilla Parishad is its political head.
Urban Local Government consists of:
- Municipalities for towns and Municipal Corporations for larger cities.
- Both are governed by elected representatives.
- The political head of a Municipality is the Municipal Chairperson.
- The head of a Municipal Corporation is called the Mayor.
State governments must share certain powers and revenues with local bodies, though the extent of this varies by state.
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Civics Chapter 2 Question Answers - Federalism
| 1. What is federalism and how does it function in a government system? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of federalism? |  |
| 3. How does federalism affect the relationship between state and federal governments? |  |
| 4. What role does the Constitution play in establishing federalism in the United States? |  |
| 5. How does federalism impact the rights of citizens? |  |






















