Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Practice Question Answers - Control and Coordination
True or False
Q1. Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland of the body.
Ans: True
The thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland and plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
Q2. Secondary sexual characters in males are influenced by testosterone.
Ans: True
Testosterone is the male sex hormone responsible for secondary sexual characters like facial hair, deep voice, and muscle growth.
Q3. Plant growth is promoted by abscisic acid.
Ans: False
Abscisic acid does not promote growth; instead, it inhibits growth and induces dormancy in seeds and buds.
Q4. Dendrites are the longest part of the neuron.
Ans: False
Dendrites are short, branched extensions that receive signals. The axon is the longest part of the neuron.
Q5. Gustatory receptors provide the sense of taste.
Ans: True
Gustatory receptors are found in taste buds on the tongue and are responsible for detecting different tastes.
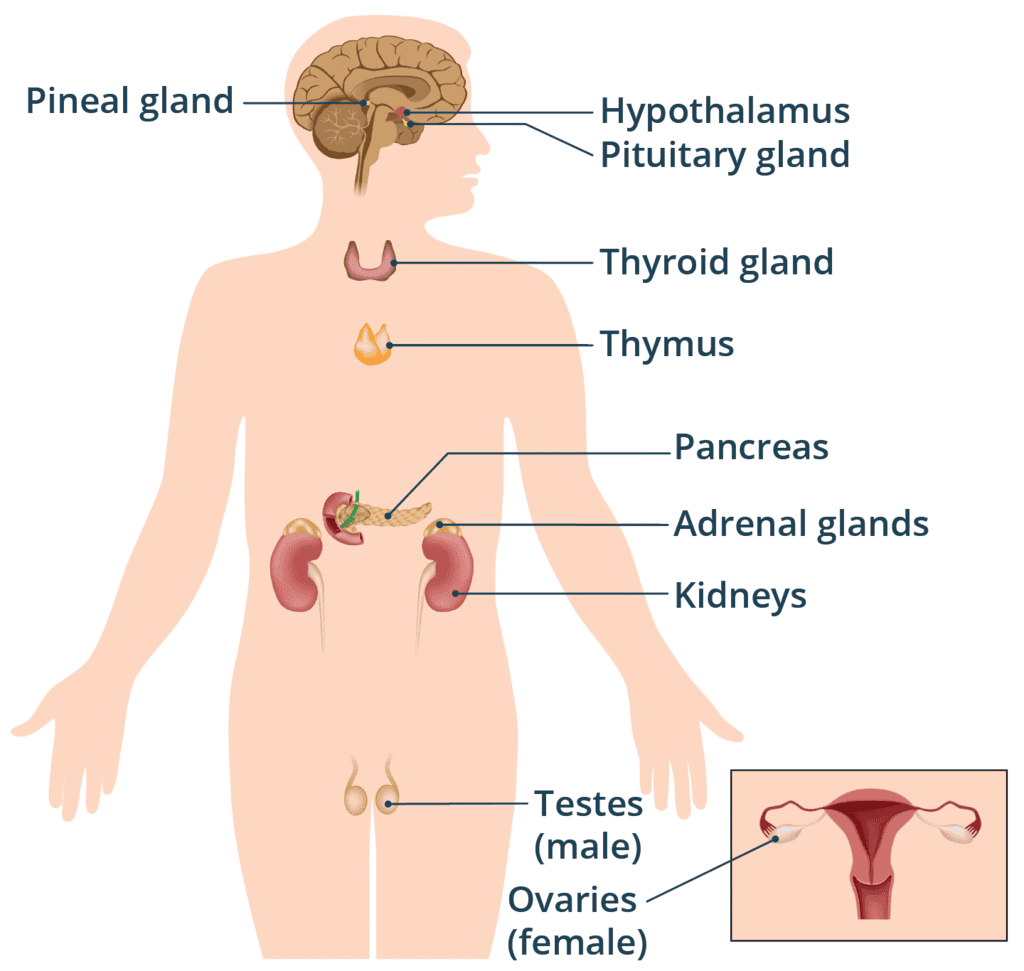
Q6. The adrenal gland is known as the master gland.
Ans: False
The pituitary gland is called the master gland, not the adrenal gland, because it controls other endocrine glands.
Q7. Pituitary gland is responsible for gigantism.
Ans: True
The pituitary gland secretes growth hormone. Over-secretion of this hormone during childhood leads to gigantism, a condition where a person grows abnormally tall.
Q8. The brain is responsible for regulating the heartbeat.
Ans: True
The brain, through the medulla, controls involuntary functions like heartbeat and breathing.
Q9. Secretion of exocrine glands is known as hormone.
Ans: False
Exocrine glands secrete substances like enzymes, saliva, or sweat, while hormones are secreted by endocrine glands.
Q10. Hypothalamus regulates the secretion of pituitary hormones.
Ans: True
The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland by releasing hormones that regulate its activity.
Fill in the blanks
Q1. Element __________ is essential for the synthesis of thyroxine.
Ans: Iodine
Iodine is an essential element required by the thyroid gland for the synthesis of thyroxine.
Q2. A __________ mechanism regulates the action of the hormones.
Ans: Feedback
The feedback mechanism controls hormone levels by increasing or decreasing their secretion based on the body's needs.
Q3. Secretion of ductless gland is called __________
Ans: Hormone
Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by ductless endocrine glands into the bloodstream.
Q4. __________ hormone regulates growth and development of the body.
Ans: Growth
Growth hormone, secreted by the pituitary gland, regulates the growth and development of the body.
Q5.The hormone which controls secondary sexual characters in male is __________
Ans: Testosterone
Testosterone, secreted by the testes, regulates the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Q6. The master gland in human body is__________
Ans: Pituitary
The pituitary gland is the master gland as it regulates other endocrine glands.
Q7. Hormones are __________ substances secreted in __________ quantities by __________
Ans: Chemical; Small; Endocrine glands
Hormones are chemical messengers secreted in small quantities by endocrine glands to regulate body functions.
Q8. The movement of a plant in response to light is called __________.
Ans: Phototropism
Phototropism is the growth movement of a plant toward or away from light. Shoots show positive phototropism by growing toward the light, while roots may show negative phototropism by growing away from it. This helps the plant maximize photosynthesis.
Q9. The movement of a part of the plant in response to light is called __________.
Ans: Phototropism
The bending or movement of plant parts in response to light is called phototropism.
Q10. The plant hormone responsible for phototropism is __________.
Ans:Auxin
Phototropism happens because the plant hormone auxin controls growth by accumulating more on the shaded side of the stem, making it bend towards light.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Practice Question Answers - Control and Coordination
| 1. What is the role of the nervous system in control and coordination? |  |
| 2. How do hormones contribute to control and coordination in the body? |  |
| 3. What are the main components of the human nervous system? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary actions? |  |
| 5. How do reflex actions work in terms of control and coordination? |  |