Common Diseases in Humans - 2 | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Some Diseases caused by Bacteria
Bacterial diseases are illnesses caused by pathogenic bacteria. Bacteria are diverse microorganisms, and while many bacteria are harmless or even beneficial, some can cause various diseases in humans
1. Typhoid
Typhoid is an infectious bacterial disease that mainly spreads through contaminated food or water. It can also spread due to poor hygienic conditions. The major symptoms of this disease are characterized by high fever, loss of appetite and diarrhoea. Salmonella typhi is the bacterium responsible for this disease and humans are the only carriers. The first case of typhoid fever was reported in the United States in the early 1900’s. Overall, about 21 million people are infected with this disease annually, and about 200,000 cases are fatal. Furthermore, scientists have identified 2 types of typhoid causing bacterium, namely:
- ST1
- ST2
Causes of Typhoid
Also called as “Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi”, this microbe is the causative agent for this disease. It is a gram-negative bacteria characterized by a thin cell wall and an outer membrane. The cells are reddish in colour, with some having black stains in the centre.
It is rod-shaped and grows in the small intestine of the human body. Human beings are the main hosts of these bacteria. This type of species can survive in environments which are rich in oxygen and also, they are found in sewage, water bodies and some eventually make their own on to food.
The bacteria enter the human body through the contaminated foods and water, where it then enters into the intestinal cells of the human body. Later, it passes through the bloodstream and destroys the lymphatic system and spreads throughout the body. This bacterium is mainly carried by the white blood cells present in the liver and also the bone marrow. There, they multiply and re-enter the blood cells, which in turn, causes a number of symptoms to appear in the later stages.
Symptoms of Typhoid
Patients affected with typhoid usually display the following symptoms: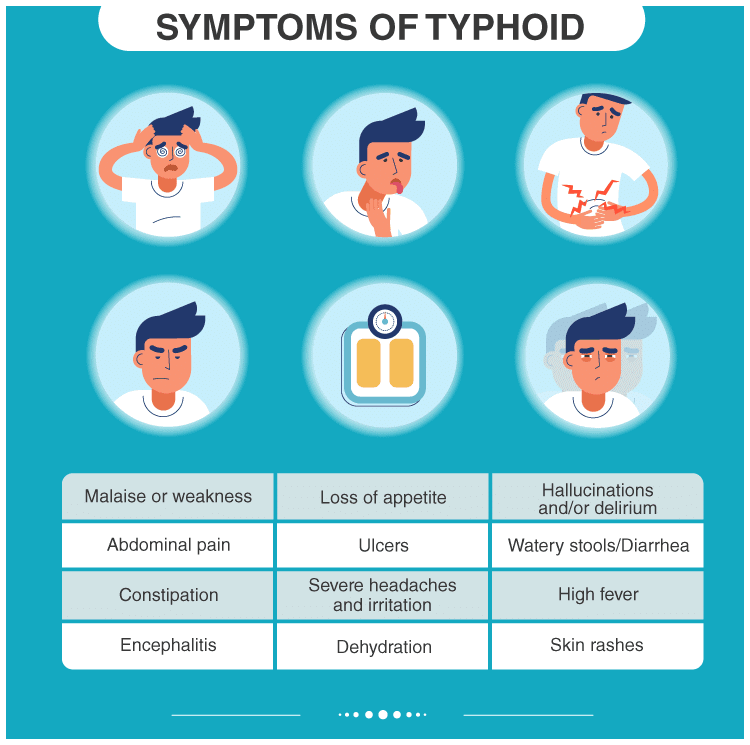
Treatment for Typhoid
Sanitation is one of the most important things that one can do to prevent the infection of such diseases. The other way would be the use of antibiotics that can kill the disease-causing germs. Also by maintaining good and hygienic food habits, one can get rid of diseases easily.
2. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a common disease that can have more than 30 different causes and symptoms. It is a highly contagious lung infection characterised by inflammation of air sacs in one or both the lungs. The air sacs get filled with fluid or pus resulting in fever, chills, cough and breathing difficulty. Let us have a look at the different types of pneumonia, its symptoms, treatment and how is it caused.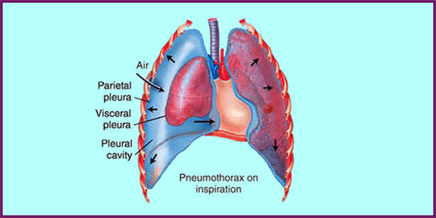
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a serious infection of lungs caused by various bacteria, viruses and fungi. It can be mild and sometimes even prove fatal. It affects people with weakened immune systems, older people above 65 years of age, infants and young children. Pneumonia can be bacterial, viral or mycoplasmic. It is a serious health issue and requires proper treatment.
Types of Pneumonia
Bacterial Pneumonia
- The most common bacteria causing pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae. It occurs in people with an existing lung disorder, and also those who drink excessively because of which they develop a weaker immune system. It also affects old people whose immunity weakens with increasing age.
Viral Pneumonia
- It is caused by various viruses such as the influenza virus. More than 1/3rd of the pneumonia cases are caused by viruses.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia
- This is known as atypical pneumonia and shows different symptoms. It is caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae and causes mild pneumonia that affects all age groups.
Other Pneumonia
- These are less common and can be caused by other infectious agents such as fungi.
How is Pneumonia Caused?
Pneumonia is caused by a variety of pathogens such as virus and bacteria. When these pathogens overpower our immune system, they cause pneumonia.
Pneumonia Symptoms
The common symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Coughing with greenish, yellow and sometimes blood in the mucus.
- Shortness of breath
- Fever with chills.
- Sweating
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Chest pain
Pneumonia Treatment
Antibiotics should be given to the patients for a speedy recovery. Pneumonia can be treated at home, but in severe cases, the patient needs to be hospitalized. Viral pneumonia has no specific treatment. It gets cured on its own. The patient needs to increase the fluid intake, take proper nutrition, take oxygen therapy for breathing problems and medicines for pain and cough-relief.
Pneumonia Prevention
Pneumonia can be prevented by the following steps:
1. Vaccination
A few types of pneumonia can be prevented by certain vaccinations. The vaccination status should be reviewed by the doctor even if you have already received a pneumonia vaccine. There are different vaccine for children below 2 years of age and between 2-5 years of age who are more at risk.
2. Practice Proper Hygiene
Wash your hands properly or use a proper sanitizer to prevent yourself from any pathogenic infections.
3. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and alcohol consumption weakens the immune system and makes it prone to infections. Quit these habits to maintain strong immunity and prevent yourself from any infections.
Key Points about Pneumonia
- Pneumonia is the infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses and fungi.
- It can be diagnosed through physical examinations, blood tests and tests for sputum.
- It ranges from mild to fatal.
- Pneumonia can be characterised by fever, chills, shortness of breath and chest pain.
- It can be treated by certain antibiotics.
3. Common Cold
What is Common Cold?
Cold or common cold is a disease diagnosed with a headache, runny nose, scratchy throat, fever and non-stop sneezing. It is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract, which primarily affects the nose and sometimes sinuses, ears, and bronchial tubes.
Causes of Common Cold
A common cold is caused by viruses. Some of them include –
- Rhinovirus – This one usually intrudes your system during early fall, spring, and summer. They are behind 10%-40% of colds. Even though these are the main common viruses which affect you, they would rarely make you seriously sick.
- Coronavirus – The virus affects the human system during winter and early spring. This virus is behind 20% of colds. There are more than 30 types of coronavirus, out of which only 3 or 4 ones are harmful.
- RSV and parainfluenza – These tiny organisms are behind severe infections like pneumonia, in young children.
Pneumonia is a lung infection with symptoms of a cough, fever, and breathing problem. Some more symptoms would include –
- A cough viz. mucus (sputum) from your lungs, which could be rusty or green or tinged with blood.
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Shaking and “teeth-chattering” chills
- Fast breathing and feeling short of breath
- Fast heartbeat
- Chest pain that often feels worse when you cough or breathe in
- Vomiting and Nausea
- Feeling very weak or tired

You could get infected by a cold infected person. When you touch surfaces or objects used by them, which contains germs and then to your nose or mouth, you are prone to get infected by the germs or virus.
You could get affected by it if you’re near a cold infected person, as their sneeze could contaminate the air which you breathe passively. When a virus attaches to the lining of the nose or throat, the infection of cold initiates. The immune system of the body sends out white blood cells (WBC) to attack this invader and this is how cold gets demolished.
Signs and Symptoms of Common Cold
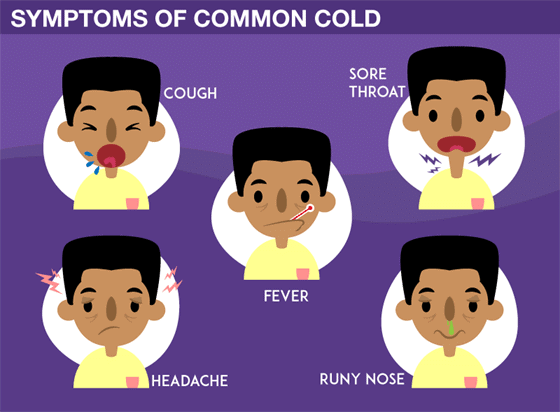
When cold strikes, the following symptoms are usually observed –
Primary Symptoms
- Scratchy or a sore throat
- Sneezing
- Stuffy nose
- A cough
- A Runny Nose
- Watery eyes
- Mucus draining from your nose into your throat
Secondary Symptoms
- High fever
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- A headache
- Loss of appetite
These symptoms indicate that you have flu rather than a common cold.
Prevention of Common Cold

It is practically impossible to completely prevent the spread of colds, but you can take certain measures to reduce the chances of getting cold.
- Wash your hands often – It is probably the best measure to prevent the transfer of cold or any kind of infection. Use sanitizer while being in any public places and also make it a point to wash hands before eating. Teach the importance of hand-wash to kids also.
- Avoid touching your face – Try not to touch face, mouth, nose & eye areas, when you are near to a person infected with cold.
- Control stress – People facing emotional stress regularly have a weaker immune system, which implies that they could catch a cold easily. So, reduce stress and live a healthy life.
- Cleanliness – Keep household surfaces like doorknobs, drawer pulls, keyboards, light switches, telephones, remote controls, countertops, and sinks clean. These are the places where viruses lie for hours after they are used by an infected person.
- Avoid Smoking – Cigarette smoke could raise the chances of susceptibility to colds and other infections. Avoid passive smoking as well.
- Drink sufficient amount of water – Drink water, juice, clear broth, warm lemon water, chicken soup, and other warm fluids. These will help you to stay away from cold or flu.
Myths About Common Cold
Note that getting chilly or wet doesn’t trigger the cold sickness. You get infected with cold only when you are more prone to. When you are extremely tired, under emotional distress, or have allergies to nose and throat symptoms, you easily catch a cold. Another myth states that your diet is the cause of such sickness or infection which is not true. Another hoax is when they say that you’re getting sick because your tonsils or adenoids are large.
Some Diseases caused by Fungi
Ringworm
Ringworm, also known as dermatophytosis, is a fungal infection of the skin. It can affect both humans and animals. The infection initially appears as red patches on the affected areas that later spreads to different areas of the body. It majorly affects the scalp, nails, feet, groin and beard.
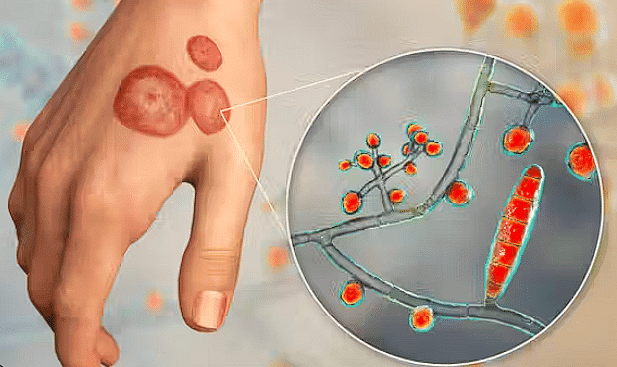
The ringworm fungus grows well in moist environment such as showers, bathroom floors and walls, swimming pools and also in between the skin folds. The vectors for this disease include pets such as cats and dogs. There are multiple forms of ringworm fungi, which affect different body parts.
Types of Ringworm
Ringworm is classified based on the part of the body it affects.
- Tinea capitis: This fungal infection affects the scalp. It is also known by the name of scalp ringworm. (Tinea: Technical term for ringworm.) (Capitis: Latin for “of the head“)
- Tinea corporis: This fungal infection might occur in any part of the body. Thus it is known as body ringworm. (Corporis: Latin for “of the body”)
- Tinea cruris: This fungal infection affects the skin around the inner thighs, buttocks, and groin. It is also known as the Jock itch. (Cruris: Latin for “of the leg”)
- Tinea pedis: This fungal infection affects both the foot, in between the fingernails and toenails. It is also known as Athlete’s foot. (Pedis: Latin for “of the foot”)
Causes of Ringworm
Ringworm can be caused by the following ways:
- It spreads by skin contact with an infected person.
- It spreads from pets and cows. One should wash hands properly after playing with the pets.
- The fungus causing ringworm might be found lingering on clothes, comb, towels and brushes.
- These fungi are mainly present in the spores of soil. Coming into contact with such soil will result in an infection.
Symptoms of Ringworm
Ringworm symptoms vary depending upon the site of infection. The following are the common characteristic symptoms of ringworm:
- The skin of the feet becomes swollen and itchy between the toes. The soles and heels of the feet may also be affected.
- Itchy, scaly red spots appear on the groin area.
- Ringworm appears like an itchy, scaly, inflamed bald spot on the scalp.
- Ringworm on nails appear to be thick and abnormal in colour and shape.
- In the beard, itchy, red spots appear on the chin, cheeks, and the upper neck.
Diagnosis of Ringworm
Identifying ringworm infection is very easy. It primarily depends on the location and appearance of certain abnormalities in the skin such as bumps, scaly skins etc. Below are common diagnostic procedures done by doctors to diagnose ringworms.
- A black-light (also called UV-A or Wood’s lamp) is used to illuminate affected areas on the body. Presence of the fungal infection will glow under the light.
- KOH exam- The scrapings of the infected skin is collected and mixed with the prepared potassium (K) hydroxide (OH) solution. The KOH tests detect the fungi by removing the unaffected cells and leaving the fungal cells aside. The test results are checked under the microscope to detect ringworms.
- Skin biopsy – A small section of skin tissue is cut and examined under a microscope to detect fungi. It can detect a range of infections and disorders
- Fungal culture: A large swab is brushed over the infected areas. These samples are then sent to a lab for analysis to identify the causative microbes. This procedure helps to determine the best course of treatment for the infection.
Ringworm Treatment
A variety of products to treat ringworm infections are available in the market, such as antifungal cream, lotion, and powder. Sometimes, even home remedies are very effective.
- The best antifungal creams used for this infection are miconazole or terbinafine, which should be applied twice in a day on the infected region until the symptoms withdraw
- Amphotericin B is a very powerful fungicide that is used in the most serious cases of fungal infections
- There are many home remedies which help to prevent and control the infections. Using talcum powder is recommended as it helps to control sweating
- Home remedies include neem, which is a particularly effective antimicrobial and antifungal agent
Ringworm Prevention
Following precautions is one of the best methods to avoid ringworms. And more than often, lifestyle choices and decisions affect how the disease is spread. For instance, obesity increases the risk of ringworm.
- Maintain cleanliness and hygiene.
- Wash hands with sanitizers.
- Wear clean ironed clothes.
- Avoid using communal pools.
- Wear loose-fitting cotton clothes to avoid the accumulation of sweat.
- The skin folds have to be kept clean regularly to avoid the accumulation of sweat and dirt between the creases.
- Having a shower twice a day is also recommended.
- Touching or scratching the itchy red patches would help to prevent it from spreading.
Ringworm is not a serious disease, but it is a sign of poor hygiene and a precursor to many other major diseases and infections.
Dengue
Dengue is a mosquito borne disease most common in tropical regions such as Asia and Caribbean. In India it first occurred in 1780 in Chennai and the first dengue epidemic occurred in Kolkata in 1963-1964. People of any age can be infected by the virus once bitten by an infected mosquito but children and adults with low immune systems are severely affected.
What is Dengue?
The Dengue virus causes a mosquito-borne infectious disease known as the dengue fever. Female mosquitoes, Aedes aegypti are responsible for spreading the dengue virus. Dengue mosquitos strike during the day and can be encountered almost everywhere (Both inside and outside the house). During the dawn and dusk hours, these mosquitoes are at their most active state. After 6 to 10 days, the signs may appear. Symptoms may occur 6 to 10 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
Dengue Symptoms
The Dengue symptoms generally appear after four to six days of infection and can last up to ten days.
- Strong fever with no warning
- Headaches that are serious
- Back of the eyes ache
- Joint discomfort that is excruciating
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
- Two or five days after the onset of the fever, rashes develop on the skin.
- Mild bruising (such a nose bleed, bleeding gums, or easy bruising)
How does dengue spread?
Humans contract dengue fever after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The dengue virus is spread by only a few mosquito species. What exactly is a vector? A vector is a medium that transports and transmits disease from one organism to another. Animals and microorganisms that spread viruses are known as vectors.
- Arthropods, which are invertebrate organisms with an external skeleton called an exoskeleton, are the most common vectors. Mosquitoes, ticks, lice, bees, and fleas are also arthropods. Ticks, for example, can spread Lyme disease, and mosquitoes can transmit yellow fever, malaria, and dengue fever.
- A mosquito becomes infected with the dengue virus when it bites a human who has the virus in his or her blood. By biting healthy humans, an infected mosquito will spread the virus to them. Dengue fever cannot be transmitted directly from one person to another, and mosquitoes are used for transmission.
What is Chickunguniya?
Chikungunya is a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes. It is caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV). It is generally found worldwide but specifically in Africa, Asia and India.How Does Chikungunya Spread?
Chikungunya virus is transmitted to people by the bite of an infected mosquito. Outbreaks have occurred in countries in Africa, Asia, the Americas, Europe, the Caribbean, India, and Pacific Oceans. There is a risk factor that the virus will spread to unaffected areas through infected travellers.
Symptoms of Chikungunya
- Symptoms usually arise 3&7 days after an infected mosquito bites you.
- The most common symptoms are found to be fever and joint pain.
- Other symptoms may include muscle pain, headache, joint swelling, or rash.
- Death from Chikungunya is exceptional.
- Most patients start recovery within a week. In some cases, joint pain can be severe and may even persist for months.
- Including infants infected around the time of birth, older adults (65 years), and people with medical conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart disease are more at risk of getting severely affected by the disease.
- Once a person has been infected, they are most likely to be protected from future infections
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Common Diseases in Humans - 2 - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are some common diseases caused by bacteria? |  |
| 2. What are some diseases caused by fungi? |  |
| 3. What is Dengue and how is it caused? |  |
| 4. What is Chikungunya and what are its symptoms? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions about common diseases in humans? |  |





















