Concept of Azeotropes - NEET PDF Download
AZEOTROPES
Azeotropes are defined as a mixture of two liquids which has a constant composition in liquid and vapour phase at all temperatures.
- Azeotropes can’t be separated by fractional distillation, as the composition of vapour phase remains same after boiling.
- Because of uniform composition azeotropes are also known as Constant Boiling Mixtures.
Each azeotrope has a characteristic boiling point.
The boiling point of an azeotrope is either less than the boiling point temperatures of any of its constituents (a positive azeotrope), or greater than the boiling point of any of its constituents (a negative azeotrope).
There are two types of Azeotropes
- Maximum Boiling Azeotrope
- Minimum Boiling Azeotrope
(i) Maximum Boiling Azeotrope: Maximum Boiling Azeotrope is formed when we mix two non-ideal solutions at some specific composition, showing large negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
Examples:
- Nitric Acid (HNO3) (68%) and water (32%) form maximum boiling azeotrope at boiling temperature of 393.5 K
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) (20.24%) and water form maximum boiling azeotrope at boiling temperature of 373 K
(ii) Minimum Boiling Azeotrope: Minimum Boiling Azeotrope is formed when we mix two non-ideal solutions at some specific composition, which shows large positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
Example: Ethanol ( 95.5%) and water (4.5%) form minimum boiling azeotrope at boiling temperature of 351.5 K
Types of azeotrope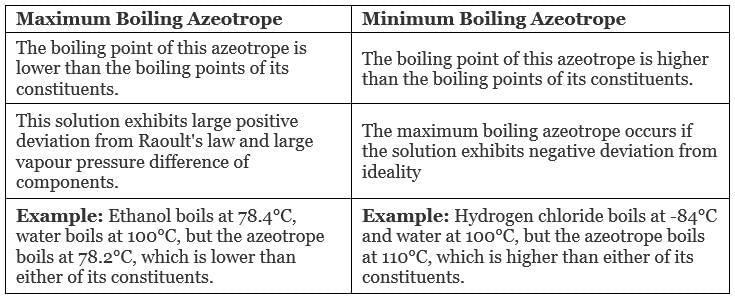
FAQs on Concept of Azeotropes - NEET
| 1. What are azeotropes? |  |
| 2. How are azeotropes different from regular mixtures? |  |
| 3. What causes the formation of azeotropes? |  |
| 4. Can azeotropes be broken or separated? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of azeotropes? |  |














