Constitution & Political System - Solved Questions (2025-2018) | UPSC Topic Wise Previous Year Questions PDF Download
From 2018 to 2025, 50 questions with varying difficulty levels have been asked: 15 easy (30%), 25 medium (50%), and 10 hard (20%)—emphasis is generally given on topics such as Indian constitutional provisions, governance structures, and judicial processes across different years.
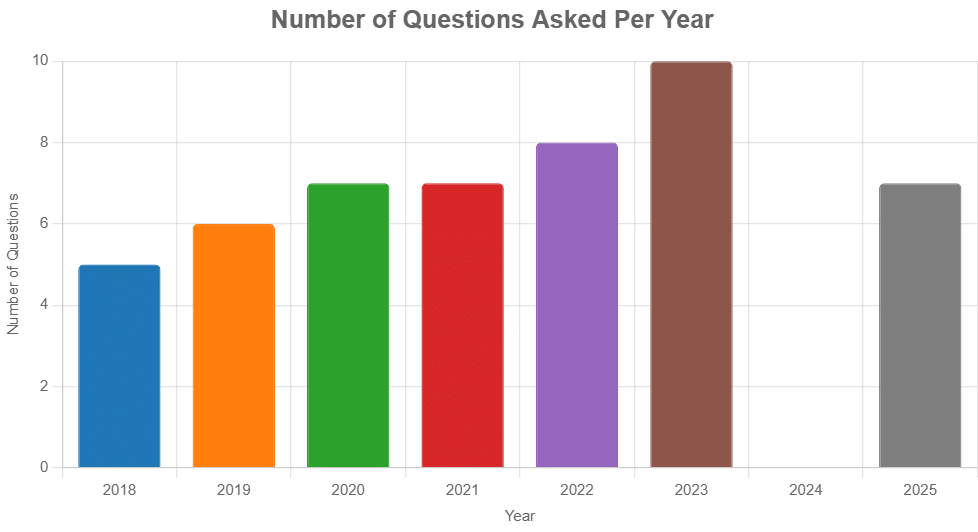 Question 1: With reference to India, consider the following:
Question 1: With reference to India, consider the following:
I. The Inter-State Council
II. The National Security Council
III. Zonal Councils
How many of the above were established as per the provisions of the Constitution of India? (2025)
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Among the listed bodies, only the Inter-State Council is constitutionally established. The others are created through statutory or executive measures.
I. Inter-State Council – Correct
Constituted under Article 263 of the Indian Constitution to promote coordination between the Centre and States.
II. National Security Council – Incorrect
Set up in 1998 via an executive order, not enshrined in the Constitution.
III. Zonal Councils – Incorrect
Formed under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, making them statutory but not constitutional bodies.
Question 2: With reference to the Indian polity, consider the following statements:
I. An Ordinance can amend any Central Act.
II. An Ordinance can abridge a Fundamental Right.
III. An Ordinance can come into effect from a back date.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2025)
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
An Ordinance is a temporary law enacted by the President (under Article 123) or Governor (under Article 213) when the legislature is not in session. It carries the same legal weight as a regular law but is subject to constitutional constraints.
Statement I: Correct
An Ordinance can amend any Central Act, similar to a law passed by Parliament, provided it complies with constitutional provisions.
Statement II: Incorrect
Ordinances cannot violate Fundamental Rights, as per Article 13(2) of the Constitution. Any provision that does so is void.
Statement III: Correct
Ordinances can be applied retrospectively, meaning they may take effect from a prior date.
Question 3: With reference to the Indian polity, consider the following statements:
I. The Governor of a State is not answerable to any court for the exercise and performance of the powers and duties of his/her office.
II. No criminal proceedings shall be instituted or continued against the Governor during his/her term of office.
III. Members of a State Legislature are not liable to any proceedings in any court in respect of anything said within the House.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2025)
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The Indian Constitution grants legal immunities and privileges to ensure the independent functioning of constitutional offices and legislative bodies.
Statement I: Correct
Under Article 361(1), the Governor is not accountable to any court for actions performed in their official capacity.
Statement II: Correct
Article 361(2) prohibits the initiation or continuation of criminal proceedings against a Governor during their term of office.
Statement III: Correct
Article 194(2) provides immunity to State Legislators for statements made or votes cast in the State Legislature or its committees.
Question 4: Consider the following statements:
I. If any question arises as to whether a Member of the House of the People has become subject to disqualification under the Tenth Schedule, the President’s decision in accordance with the opinion of the Council of Union Ministers shall be final.
II. There is no mention of the word 'political party' in the Constitution of India.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2025)
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Neither of the statements regarding the Tenth Schedule of the Indian Constitution is correct.
Statement I: Incorrect
The authority to decide on disqualification under the Tenth Schedule lies with the Speaker or Chairman of the respective House, not the President or the Union Council of Ministers.
Statement II: Incorrect
The term ‘political party’ is explicitly referenced in the Tenth Schedule, which governs the disqualification of members on grounds of defection.
Question 5: Consider the following pairs: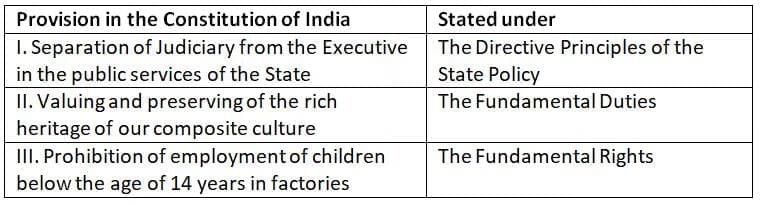
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched? (2025)
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Each of the following pairs accurately links a constitutional provision to its respective part in the Constitution of India.
Statement I: Directive Principles of State Policy – Correct
Article 50, under the Directive Principles of State Policy, mandates the separation of the judiciary from the executive in the public services of the State to ensure judicial independence.
Statement II: Fundamental Duties – Correct
Article 51A(f), part of the Fundamental Duties, requires citizens to value and preserve the rich heritage of India's composite culture.
Statement III: Fundamental Rights – Correct
Article 24, within the Fundamental Rights, prohibits the employment of children below the age of 14 years in hazardous occupations, such as factories or mines, to safeguard their well-being.
Thus, all three pairs are correctly matched with their respective constitutional provisions.
Question 6: Consider the following statements:
I. Panchayats at the intermediate level exist in all States.
II. To be eligible to be a Member of a Panchayat at the intermediate level, a person should attain the age of thirty years.
III. The Chief Minister of a State constitutes a commission to review the financial position of Panchayats at the intermediate levels and to make recommendations regarding the distribution of net proceeds of taxes and duties, leviable by the State, between the State and Panchayats at the intermediate level.
Which of the statements given above are not correct? (2025)
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Statement I: Incorrect
The Constitution of India does not mandate the establishment of intermediate-level Panchayats (Panchayat Samitis) in all states. States with a population below 20 lakh are exempt from creating this tier, as per the 73rd Constitutional Amendment. This allows smaller states flexibility in their Panchayati Raj structure.
Statement II: Incorrect
The minimum age for eligibility to become a member of a Panchayat is 21 years, as specified under the Panchayati Raj Acts of various states, aligning with the Representation of the People Act. The claim of a 30-year minimum age is inaccurate.
Statement III: Incorrect
The State Finance Commission is appointed by the Governor of the state, not the Chief Minister, as per Article 243-I of the Indian Constitution. The Governor is responsible for constituting the commission to review the financial position of Panchayats and make recommendations.
Question 7: Consider the following statements with regard to pardoning power of the President of India:
I. The exercise of this power by the President can be subjected to limited judicial review.
II. The President can exercise this power without the advice of the Central Government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2025)
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Statement I is correct because the President's pardoning power, while significant, is not absolute and can be subject to judicial review on limited grounds, such as if the decision is made with mala fide intent (bad faith) or is arbitrary.
Statement II is incorrect because the President is not strictly bound to act solely on the advice of the Council of Ministers when exercising the pardoning power. The President can exercise this power with some discretion, as it is a constitutional prerogative under Article 72 of the Indian Constitution, and not entirely dependent on the Council's advice.
Thus, only Statement I is correct.
Question 8: In essence, what does Due Process of Law' mean? (2023)
(a) The principle of natural justice.
(b) The procedure established by law.
(c) Fair application of law.
(d) Equality before law.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Due Process of Law:- Principle of Natural Justice in Due Process: The idea of due process is based on the principle of natural justice, which guarantees that legal processes are fair and just.
- Right to Present Defense: Due process requires that a person must have the chance to present their defense before any punishment is given.
- Protection of Life, Liberty, and Property: It ensures that no person can be deprived of their life, freedom, or property without following proper legal steps and protections.
- Due Process and Constitutional Rights: Due process safeguards people's constitutional rights and prevents arbitrary actions by authorities.
- Ensuring Fairness in Legal Proceedings: It controls the power of officials and guarantees fairness in legal cases.
- Dicey’s Rule of Law: According to A.V. Dicey, the rule of law in the English Constitution states that no one can be punished or lose their property unless they have broken a specific law that has been proven in a court.
- Connection to Natural Justice: The concept of due process is closely linked to the idea of natural justice, which demands fairness, proper legal procedures, and protection of individual rights.
Question 9: Which one of the following statements best reflects the Chief purpose of the 'Constitution' of a country? (2023)
(a) It determines the objective for the making of necessary laws.
(b) It enables the creation of political offices and a government.
(c) It defines and limits the powers of government.
(d) It secures social justice, social equality and social security.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The chief purpose of a constitution is to establish the fundamental principles, structure, and functions of a government and to define the rights and freedoms of individuals within a country. Constitutions serve as the supreme law of the land and provide a framework for governance, ensuring the balance of power, protecting individual rights, and guiding the functioning of the state.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Question 10: In India, which one of the following Constitutional Amendments was widely believed to be enacted to overcome the judicial interpretations of the Fundamental Rights? (2023)
(a) 1st Amendment
(b) 42nd Amendment
(c) 44th Amendment
(d) 86th Amendment
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
1st Constitutional Amendment Act, 1951:
- Issues involved in the cases included freedom of speech, acquisition of the Zamindari land, State monopoly of trade, etc.
- Added three more grounds of restrictions on freedom of speech and expression: public order, friendly relations with foreign states and incitement to an offense. Also, it made the restrictions ‘reasonable’ and thus, justiciable in nature.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Question 11: Consider the following organizations/bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above constitutional bodies?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) was initially constituted by the Central Govt by the National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993 and so far the Commission had been reconstituted 7 times up to 2016. The National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993 has been repealed through the National Commission for Backward Classes (Repeal) Act, 2018. The Commission has been accorded Constitutional Status and constituted through “The Constitution (One Hundred and Second Amendment) Act, 2018” Act.
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India was established on 12 October, 1993. The statute under which it is established is the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993 as amended by the Protection of Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2006.
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC), is a quasi- judicial commission in India which was set up in 1988 under the Consumer Protection Act of 1986.
- Law Commission of India is a non-statutory body and is constituted by a notification of the Government of India, Ministry of Law & Justice, Department of Legal Affairs with a definite terms of reference to carry out research in the field of law and the Commission makes recommendations to the Government (in the form of Reports) as per its terms of reference.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Question 12: With reference to Finance Bill and Money Bill in the Indian Parliament, consider the following statements: (2023)
- When the Lok Sabha transmits Finance Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it can amend or reject the Bill.
- When the Lok Sabha transmits Money Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it cannot amend or reject the Bill, it can only make recommendations.
- In the case of disagreement between the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha, there is no joint sitting for Money Bill, but a joint sitting becomes necessary for Finance Bill.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
There are two kinds of Finance Bills:
- Finance Bill (Money Bill)
- Finance Bill (Ordinary Bill)
- If the Finance Bill is not a Money Bill, the Rajya Sabha has the power to amend or reject it.
- For a Money Bill, the Rajya Sabha can only make recommendations within 14 days, and the Lok Sabha can choose to accept or ignore these suggestions.
- There is no arrangement for a joint sitting for a Money Bill as stated in Article 110. However, a joint sitting can be called for a Finance Bill (Ordinary Bill) to address any disagreements.
- Since the third statement is incorrect, the right answer is (b) Only two statements are correct.
Question 13: Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I: The Supreme Court of India has held in some judgements that the reservation policies made under Article 16(4) of the Constitution of India would be limited by Article 335 for maintenance of efficiency of administration.
Statement-II: Article 335 of the Constitution of India defines the term 'efficiency of administration'.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-1
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- In the past seven decades of constitutional jurisprudence on reservations, the Supreme Court of India has consistently referred to the notions of “efficiency” and “merit,” while adjudicating the validity of various reservation policies.
- The Court has held in several judgments (Indra Sawhney and others v Union of India and Others 1993; M Nagaraj and Others v Union of India and Others 2006) that the reservation policies made under Article 16(4)1 of the Constitution would be limited by Article 335 (2) which provides for “maintenance of efficiency of administration,”. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- This was done while the Constitution does not define the term “efficiency of administration.” Hence, statement 2 is not correct. While considering the claims of the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and the Scheduled Tribes (STs) in the making of appointments to public services and posts. This was done while the Constitution does not define the term “efficiency of administration.” Hence, option (c) is correct.
Question 14: Consider the following:
- Demographic performance
- Forest and ecology
- Governance reforms
- Stable government
- Tax and fiscal efforts
For the horizontal tax devolution, the Fifteenth Finance Commission used how many of the above as criteria other than population area and income distance? (2023)
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) All five
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
For the horizontal tax devolution, the Fifteenth Finance Commission used the following as criteria:
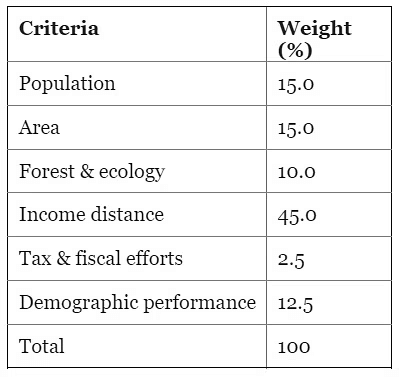
Hence, the correct answer is b.
Question 15: Consider the following statements in respect of the National Flag of India According to the Flag Code of India, 2002: (2023)
Statement-I: One of the standard sizes the National Flag of India of 600 mm × 400 mm.
Statement-II: The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the Flag shall be 3 : 2.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The standard sizes of national flag shall be as follows:
- Hence, statement 1 is incorrect.
- The National Flag shall be rectangular in shape. The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the flag shall be 3 : 2. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Question 16: Consider the following statements in respect of the Constitution Day:(2023)
Statement-I: The Constitution Day is celebrated on 26th November every year to promote constitutional values among citizens.
Statement-II: On 26th November, 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India set up a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar to prepare a Draft Constitution of India.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- It is celebrated on 26th November every year. It is also known as National Law Day. On this day in 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India formally adopted the Constitution of India that came into force on 26th January 1950. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- On 29 August, 1947, the Constituent Assembly set up a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar to prepare a Draft Constitution for India. Hence, statement 2 is incorrect.
- On 13 December 1946, the Constituent Assembly formally commenced its task of framing the Constitution of India. Jawaharlal Nehru moved the Objectives Resolution, which aimed to declare India as an Independent Sovereign Republic and create a Constitution to govern its future. The Resolution established general principles to guide the work of the Constituent Assembly. On January 22, 1947, the Constituent Assembly adopted the Resolution.
Question 17: Consider the following statements in respect of election to the President of India: (2023)
- The members nominated to either House of the Parliament or the Legislative Assemblies of States are also eligible to be included in the Electoral College.
- Higher the number of elective Assembly seats, higher is the value of vote of each MLA of that State.
- The value of vote of each MLA of Madhya Pradesh is greater than that of Kerala.
- The value of vote of each MLA of Puducherry is higher than that of Arunachal Pradesh because the ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry is greater as compared to Arunachal Pradesh.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The President is elected not directly by the people but by members of electoral college consisting of: 1. the elected members of both the Houses of Parliament; 2. the elected members of the legislative assemblies of the states; and 3. the elected members of the legislative assemblies of the Union Territories of Delhi and Puducherry1. Thus, the nominated members of both of Houses of Parliament, the nominated members of the state legislative assemblies, the members (both elected and nominated) of the state legislative councils (in case of the bicameral legislature) and the nominated members of the Legislative Assemblies of Delhi and Puducherry do not participate in the election of the President. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Is the value of vote of each elector the same?
- Answer: No. The value of votes of MLAs would differ from State to State as the value of each such vote is calculated by the process explained below. However, the value of votes of all MPs is the same. Statements 2 and 3 are not correct.
- Ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry = 471707/30 =
- 15,723.56.
- Ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Arunachal Pradesh = 467511/60 = 7,791.85.
The value of vote of each MLA of Puducherry is higher than that of Arunachal Pradesh because the ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry is greater as compared to Arunachal Pradesh. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
Question 18: If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
(a) This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
(b) This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
(c) This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
(d) The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Land Governance under the fifth Schedule area: Governor can make regulations with regard to the:
- Prohibition and restriction of transfer of land from and between Scheduled Tribes – almost every State in the country, and certainly all States with Scheduled Areas, have enacted legislations relating to prevention/prohibition of land transfer in Scheduled Areas by tribals to non- tribals, and in some cases, even the transfer of land between tribals inter-se is restricted. Hence, option (a) is correct.
- Regulation of allotment of land to tribals in Scheduled Areas.
- Regulation of moneylending in Scheduled Areas to tribals.
Question 19: Consider the following statements: (2022)
- A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India.
- When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent.
- A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The Constitution Amendment Bill can be reinstated by a minister or a private member and for this the prior approval of the President is not necessary. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The President is bound to assent to the bill. They can neither keep the bill with themselves nor send it to the Parliament for reconsideration. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It is mandatory to pass the Constitution Amendment Bill separately in each house. In case of disagreement between the two houses, there is no provision to pass the bill in the joint sitting of both the houses. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
Question 20: Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Constitution of India classifies the ministers into four ranks viz. Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State and Deputy Minister.
- The total number of ministers in the Union Government, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 percent of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Our constitution does not categorize ministers into four levels: Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State, and Deputy Minister. This classification comes from England, but it is not written in our constitution. Only the Council of Ministers is mentioned in Article 74.
- Therefore, statement 1 is incorrect.
- According to the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, the term Minister refers to a member of the Council of Ministers (which includes a member of the Cabinet), a Minister of State, a Deputy Minister, or a Parliamentary Secretary.
- The 91st amendment in 2003 states that the total number of ministers, including the Prime Minister, in the Council of Ministers cannot be more than 15% of the total members of the House of the People.
- Thus, statement 2 is correct.
- Article 74 states that a Council of Ministers, led by the Prime Minister, will help and advise the President in carrying out his responsibilities.
- The Council of Ministers includes Cabinet Ministers, Deputy Ministers, and Ministers of State.
- The term cabinet appears only once in the Indian constitution, specifically in Article 352 (3).
Question 21 : Which of the following is/are the exclusive power(s) of Lok Sabha? (2022)
- To ratify the declaration of Emergency
- To pass a motion of no-confidence against the Council of Ministers
- To impeach the President of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- It is the exclusive power of the Lok Sabha to pass a no-confidence motion against the Council of Ministers. When the Lok Sabha passes a no-confidence motion against the Council of Ministers, all the ministers, including the ministers of the Rajya Sabha, have to resign. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The resolution of the proclamation of emergency will be required to be passed by a majority of the total number of members of each House of Parliament and 2/3 majority of the members present and voting. A Declaration of National Emergency is placed before each House of Parliament and if it is not approved within a month, it does not remain in force, but once approved, it can remain in operation for six months. As a result, the Proclamation of Emergency is ratified by both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha. It is not the exclusive power of the Lok Sabha. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The impeachment motion of the President should be passed by a special majority (two- thirds) in the original house. The motion is then sent to the other house for consideration. The second house acts as an inspector. A Select Committee has been constituted to investigate the allegations against the President. Impeachment of the President of India comes under both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. It is not the exclusive power of Lok Sabha. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Question 22: With reference to anti-defection law in India, consider the following statements? (2022)
- The law specifies that a nominated legislator cannot join any political party within six months of being appointed to the House.
- The law does not provide any time-frame within which the presiding officer has to decide a defection case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- A public representative can be disqualified under the Anti-Defection Act if:
- An elected member voluntarily gives up the membership of a political party. An independent elected member joins a political party.
- A member votes against the party in the House.
- A member abstains from voting.
- After the expiry of six months, a nominated member joins a political party.
- Therefore, any nominated MLA can join any political party within six months of being appointed to the House but not after six months. Hence statement 1 is not correct. As per the law, the Speaker of the House has the power to decide the disqualification of the members.
- If any complaint is received regarding the party of the Speaker of the House, any other member elected by the House has the right to take a decision in this regard. Therefore, this law does not prescribe any time period within which the presiding officer has to decide the defection case. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Question 23: Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Attorney General of India and Solicitor General of India are the only officers of the Government who are allowed to participate in the meetings of the Parliament of India.
- According to the Constitution of India, the Attorney General of India submits his resignation when the Government which appointed him resigns.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- According to the Constitution, only the Attorney General can take part in the proceedings of both the Houses of Parliament or their joint sitting and any committee of the Parliament of which s/he may be named a member, but without a right to vote. In addition to the AG, there are other law officers of the Government of India. They are the solicitor general of India and additional solicitor general of India. They assist the Attorney General in carrying out official duties. The Constitution does not mention the solicitor general and additional solicitor general. Hence statement 1 not correct.
- The procedure and grounds for removal of the Attorney General are not mentioned in the Constitution. He holds office during the pleasure of the President (may be removed by the President at any time). Therefore, the Attorney General of India does not resign on the resignation of the government. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
Question 24: With reference to the writs issued by the Courts in India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Mandamus will not lie against a private organisation unless it is entrusted with a public duty.
- Mandamus will not lie against a Company even though it may be a Government Company.
- Any public minded person can be a petitioner to move the Court to obtain the writ of Quo Warranto.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Mandamus is issued to direct a public authority to do its duty. Mandamus is a judicial remedy in the form of an order from a court. It cannot be issued to compel an authority to do something against a statutory provision. Therefore, no mandate will be issued against any private organisation unless it has been entrusted with any public work. Hence option 1 is correct.
- Mandamus is issued by the court to a public official asking him to perform his official duties that he has failed or refused to perform. It can also be issued against any public body, a corporation, an inferior court, a tribunal or government for the same purpose. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The Supreme Court or High Court issues this writ to prevent illegal usurpation of public office by any person. Through this writ, the court examines the validity of a person's claim to public office. This writ empowers any person other than the aggrieved person to seek redress. Therefore, any public-prone person can be a petitioner to move the court to obtain a writ of right. Hence option 3 is correct.
Question 25: With reference to Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, consider the following statements: (2022)
- As per the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, the election of Deputy Speaker shall be held on such date as the Speaker may fix.
- There is a mandatory provision that the election of a candidate as Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha shall be from either the principal opposition party or the ruling party.
- The Deputy Speaker has the same power as of the Speaker when presiding over the sitting of the House and no appeal lies against his rulings.
- The well established parliamentary practice regarding the appointment of Deputy Speaker is that the motion is moved by the Speaker and duly seconded by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 2 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha: Like the Speaker, the Deputy Speaker is chosen by the Lok Sabha from among its own members.
- The election of the Deputy Speaker happens after the Speaker has been elected.
- The Speaker sets the date for the election of the Deputy Speaker. Therefore, Statement 1 is correct.
- If the Deputy Speaker's position becomes vacant, the Lok Sabha will elect someone else to fill that position.
- Until the 10th Lok Sabha, both the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker usually came from the ruling party. However, starting from the 11th Lok Sabha, it has been agreed that the Speaker will come from the ruling party (or alliance), while the Deputy Speaker will be from the main opposition party. Hence, Statement 2 is not correct.
- The Deputy Speaker takes over the duties of the Speaker when the Speaker's office is vacant.
- He also steps in as the Speaker when the Speaker is not present during the House session.
- In both situations, he has all the powers of the Speaker.
- The Deputy Speaker has the same authority as the Speaker when leading a House session, and there can be no appeals against his decisions. Therefore, Statement 3 is correct.
- He also leads the joint session of both Houses of Parliament if the Speaker is absent.
- Before noon on the day before the fixed date, any member can submit a written notice to the Secretary-General, proposing that another member be chosen as the Deputy Speaker. This notice must be seconded by another member and include a statement from the proposed member agreeing to serve as Deputy Speaker. Thus, Statement 4 is not correct.
Question 26: With reference to India, consider the following statements: [2021]
- When a prisoner makes out a sufficient case, parole cannot be denied to such prisoner because it becomes a matter of his/her right.
- State Governments have their own Prisoners Release on Parole Rules.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- The provision of Parole is a privilege/concession but not a right of any convicted prisoner. Hence, statement 1 is incorrect.
- States do have separate prison/parole rules because “prison and persons detained” is a state subject of the 7th schedule. So, statement 2 is correct.
- And, Option (b) is correct.
Question 27: Which one of the following in Indian polity is an essential feature that indicates that it is federal in character?
(a) The independence of judiciary is safeguarded.
(b) The Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units.
(c) The Union Cabinet can have elected representatives from regional parties.
(d) The Fundamental Rights are enforceable by Courts of Law
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Key features of federalism:
- There are two or more levels (or tiers) of government.
- Different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation and administration.
- The jurisdictions of the respective levels or tiers of government are specified in the constitution. So the existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
- The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be unilaterally changed by one level of government. Such changes require the consent of both the levels of government.
- Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of government.
- The highest court acts as an umpire if disputes arise between different levels of government in the exercise of their respective powers. The most important feature of the federal system adopted by the Indian Constitution is the principle that relations between the States and the centre would be based on cooperation. And for this, Independent Judiciary is the prerequisite. Hence, Option (a) is correct.
- Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial Autonomy.
Question 28: Which one of the following best defines the term ‘State’?
(a) A community of persons permanently occupying a definite territory independent of external control and possessing an organized government
(b) A politically organized people of a definite territory and possessing an authority to govern them, maintain law and order, protect their natural rights and safeguard their means of sustenance
(c) A number of persons who have been living in a definite territory for a very long time with their own culture, tradition and government
(d) A society permanently living in a definite territory with a central authority, an executive responsible to the central authority and an independent judiciary
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- In political science, the term “State” has a more specific and definite meaning- “word State means a community or society politically organized under one independent government within a definite territory.
- It alone has the prerogative of making laws. The lawmaking power derives from sovereignty, which is the most distinctive characteristic of the State.
Question 29: With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- There is only ‘one citizenship and one domicile’.
- A citizen by birth only can become the Head of State.
- A foreigner once granted the citizenship cannot be deprived of it under any circumstances.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The Citizenship Act offers other categories of citizenship like Citizenship by Registration (Section 5) and Citizenship by Naturalisation (Section 6). These are basically for foreigners who wish to settle in India and seek Indian citizenship or persons of Indian origin living abroad who want to return to India and live as citizens in this country. It says that if the registration or certificate of naturalization was obtained by “means of fraud, false representation or the concealment of a material fact; or that citizen has shown himself by act or speech to be disloyal or disaffected towards the Constitution of India as bylaw established; or that citizen has, during any war in which India may be engaged, unlawfully traded or communicated with an enemy; or that citizen has been ordinarily resident out of India for a continuous period of seven years”, that person’s citizenship can be cancelled.
Question 30: Which one of the following factors constitutes the best safeguard of liberty in a liberal democracy?
(a) A committed judiciary
(b) Centralization of powers
(c) Elected government
(d) Separation of powers
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
In the liberal approach which is inherent in democracy, all forms of power are rooted in the will of the people. This approach enhances the rule of law as one of the basic foundations of democracy; it affirms the separation of powers as a vehicle for their restraint, and it promotes individuals’ rights and freedoms as a prerequisite for their dignity.
Question 31: Under the Indian Constitution, concentration of wealth violates
(a) the Right to Equality
(b) the Directive Principles of State Policy
(c) the Right to Freedom
(d) the Concept of Welfare
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
PART IV (DIRECTIVE PRINCIPLES OF STATE POLICY)- Article 39- says that the operation of the economic system does not result in the concentration of wealth and means of production to the common detriment.
Question 32: What is the position of the Right to Property in India?
(a) Legal right available to citizens only
(b) Legal right available to any person
(c) Fundamental Right available to citizens only
(d) Neither Fundamental Right nor legal right
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- The Forty Fourth Constitutional Amendment, 1978, deleted Articles 19(1)(f) and 31 from Part III, the chapter on Fundamental Rights in the Constitution. Instead, it inserted Article 300A in a new chapter IV of Part XII of the Constitution, thereby depriving the ‘right to property’ of its ‘fundamental right’ status. Article 300A directs that - Persons not to be deprived of property save by authority of law.—No person shall be deprived of his property save by authority of law.
Question 33: A parliamentary system of government is one in which [2020-I]
(a) All political parties in the parliament are represented in the government
(b) The government is responsible to the parliament and can be remove by it
(c) The government is elected by the people and can be removed by them
(d) The government is chosen by the parliament but cannot be removed by it before completion of a fixed term
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Article 75: The ministers are collectively responsible to the Parliament in general and to the Lok Sabha in particular. The principle of collective responsibility implies that the Lok Sabha can remove the ministry (i.e., council of ministers headed by the prime minister) from office by passing a vote of no confidence.
- So, b is the right choice.
Question 34: Which part of the Constitution of India declares the ideal of Welfare state? [2020-I]
(a) Directive principles of state policy
(b) Fundamental rights
(c) Preamble
(d) Seventh schedule
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Directive principles of state policy are given in the Part IV of the Indian Constitution (Article 36→51). Within that, Article 38 mentioned about State to secure a social order for the promotion of welfare of the people.
Question 35: Consider the following statements: [2020-I]
1. The Constitution of India defines its ‘basic structure’ in terms of federalism, secularism, fundamental rights and democracy.
2. The Constitution of India provides for ‘judicial review’ to safeguard the ‘citizens’ liberties and to preserve the ideals on which the constitution is based.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Constitution of India does not define the term ‘basic structure’. It is a judicial tool that was invented by the Supreme Court of India in the Keshavananda Bharti vs State of Kerala (1973) landmark judgment.
- Even though, the Supreme Court invented the concept of Basic Structure in the aforementioned judgment, it did not define the same. However, it is only in the later judgments that the court has added various elements to the list of the basic structure of the Constitution.
- So, 1st statement is incorrect.
- Article 13 of the Indian Constitution deals with the ‘CONCEPT’ of Judicial Review however, it does not explicitly mentions the term judicial review. But assuming that question is asking in general sense, the answer should be “b”: Only 2nd statement correct.
Question 36: One common agreement between Gandhism and Marxism
is [2020-I]
(a) The final goal of a stateless society
(b) Class struggle
(c) Abolition of private property
(d) Economic determinism
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Stateless Society: A society which lacks formal institutions of government.
Gandhiji is a philosophical anarchist. Anarchist is one who is opposed to every type of state; Gandhian Ramrajya is that it is a self-regulating system where everyone is one’s
own ruler.
Marxism revolves a classless society and stateless society. Karl Marx had predicted that the proletariats will take control of the state and production, the, destroy all class
differences and class antagonisms, and finally resulting in the ‘withering Away of the State’. Thus, the end result will be a stateless society.
Thus, we can inform that both Gandhi & Marx aimed for Stateless society.
Question 37: The Preamble to the Constitution of India is [2020-I]
(a) A part of the Constitution but has no legal effect
(b) Not a part of the Constitution and has no legal effect either
(c) A part of the Constitution and has the same legal effect as any other part
(d) A part of the Constitution but has no legal effect independently of other parts
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
A.K. Gopalan vs State of Madras (1950): Supreme Court ruled that Preamble is not enforceable in a court of law.
Berubari Vs Union (1960): Supreme Court ruled that Preamble is not a part of the Indian Constitution however, it helps in interpretation of the clauses of the Constitution. Keshavananda Bharti vs State of Kerala (1973)→ Supreme Court ruled that the Preamble is a part of the Indian Constitution.
The combined effect of the 3 judgments has been that even though the Preamble is a part of the Constitution, but it is not enforceable in a court of law. However, the Preamble helps in ascertaining the vision of the Constitution and hence, independently, it is non-justiciable.
Question 38: With reference to the provisions contained in part IV of the constitution of India, which of the following statements is/ are correct? [2020-I]
1. They shall be enforceable by courts
2. They shall not be enforceable by any court
3. The principles laid down in this part are to influence the making of laws by the state
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Part-IV of the Indian Constitution deals with the Directive Principles of the State Policy (Article 36 to Article 51)
Article 37: Provisions of Part-IV shall not be enforceable by any court (Hence, 2nd statement is correct)
Article 37 of the Indian Constitution also states that it shall be the duty of the state to apply these principles in making laws as they are fundamental in the governance of the country. So, #3 is correct. So, by elimination, the answer is d.
Question 39: Other than the Fundamental Rights, which of the following parts of the Constitution of India reflect/reflects the principles and provisions of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)? [2020-I]
1. Preamble
2. Directive Principles of State Policy
3. Fundamental Duties
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Preamble to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights mentions about dignity of an individual. Preamble of Indian Constitution speaks about “EQUALITY of status and of opportunity; assuring the dignity of the individual and the unity and integrity” So #1 is correct.
Article 23 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights mentions about the Right to Work. Similar concept in Article 41 of the Indian Constitution, under the head of DPSPs. Article 29 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights mentions about duties. A similar concept that was inserted in the Indian Constitution by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1976 under Part IV-A of the Constitution (Article 51A).
Question 40: Consider the following statements: [2019-I]
1. The 44th Amendment to the Constitution of India introduced an Article placing the election of the Prime Minister beyond judicial review.
2. The Supreme Court of India struck down the 99th Amendment to the Constitution of India as being violative of the independence of the judiciary.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(b) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
"Keeping election of the Prime Minister beyond judicial review" is a wrong statement 99th Amendment had replaced the collegium system of appointing judges to the Supreme Court and High Courts with a new body called the National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC). In 2015, SC held "ultra vires" the 99th Constitutional Amendment Act and the NJAC Act. So, #2 is right. Answer B: only 2.
Question 41: Consider the following statements: [2019-I]
1. The motion to impeach a judge of the supreme court of India cannot be rejected by the speaker of the Lok Sabha as per the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.
2. The constitution of India defines and gives details of what constitutes 'incapacity and proved misbehaviour' of the judges of the Supreme Court of India.
3. The details of the process of the impeachment of the judges of the Supreme Court of India are given in the judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.
4. If the motion of the impeachment of a judge is taken up for voting, the law requires the motion to be backed by each house of the parliament and supported by a majority of total membership of that house and by not less than two-thirds of total members of that House present and voting.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Speaker/Chairman may admit the motion or refuse to admit motion for impeachment of SC Judges.
- The address to remove SC Judge must be supported by a special majority of each House of Parliament (ie, a majority of the total membership of that House and a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members of that House present and voting). So #4 is right, answer is C.
Question 42: Under which schedule of the Constitution of India can the transfer of tribal land to private parties for mining be declared null and void? [2019-I]
(a) Third Schedule
(b) Fifth Schedule
(c) Ninth Schedule
(d) Twelfth Schedule
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Fifth Schedule of the Constitution deals with the administration and control of scheduled areas. The Governor can make regulations to prohibit or restrict the transfer of land by or among members of the scheduled tribes. So, B is the right answer.
Question 43: With reference to the constitution of India, prohibition or limitations or provisions contained in ordinary laws cannot act as prohibitions or limitations on the constitutional powers under Article 142. It could mean which one of the following? [2019-I]
(a) The decisions taken by the Election Commision of India while discharging its duties can not be challenged in any court of law.
(b) The Supreme Court of India is not constrained in the exercise of its powers by laws made by the parliament.
(c) In the event of grave financial crises in the country, the President of India can declare Financial Emergency without the counsel from the cabinet.
(d) State Legislatures can not make laws on certain matters without the concurrence of the Union legislature.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Articles 124 to 147 in Part V of the Constitution deal with the organisation, independence, jurisdiction, powers, procedures and so on of the Supreme Court.
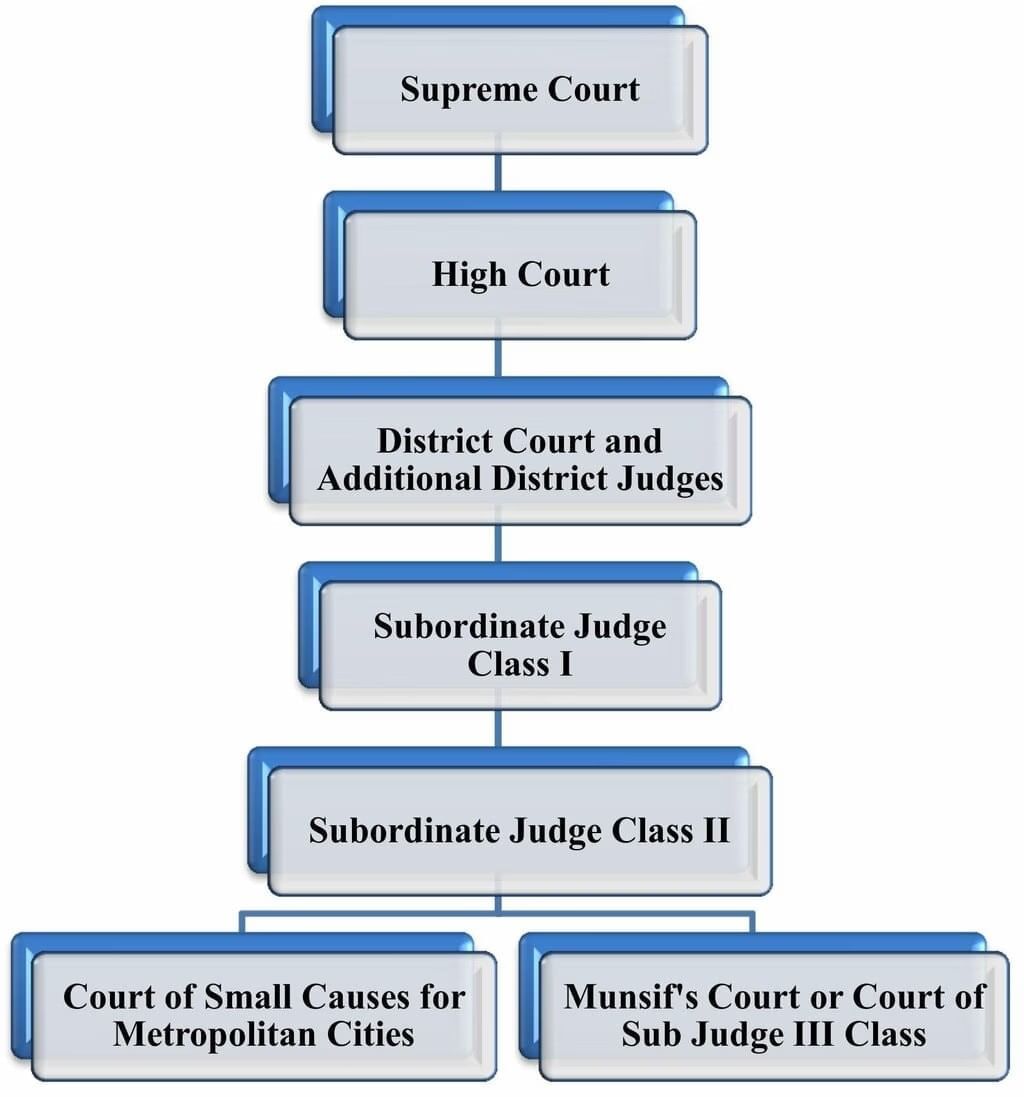
- 142 is an Article between 124-147 so, closest match is B: related to Supreme Court.
Question 44: Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017? [2019-I]
1. Pregnant women are entitled for three months predelivery and three months post-delivery paid leave
2. Enterprises with creches must allow the mother minimum six creche visits daily
3 Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1,2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
As per the bare act:
- In case of a woman who has two or more children, the maternity benefit will continue to be 12 weeks. If less than two children then she'll get 26 weeks paid leave.
- Every establishment with 50 or more employees to provide crèche facilities within a prescribed distance. The woman will be allowed four visits to the crèche in a day. So #2 is wrong. We are left with Answer C: only 3.
Question 45: With reference to the Constitution of India, consider the following statements: [2019-I]
1. No High Court shall have the jurisdiction to declare any central law to be constitutionally invalid.
2. An amendment to the Constitution of India cannot be called into question by the Supreme Court of India.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The Constitution itself confers the power of judicial review on the judiciary (both the Supreme Court as well as High Courts). Judicial review is the power of the judiciary to examine the constitutionality of legislative enactments and executive orders of both the Central and State governments. On examination, if they are found to be violative of the Constitution (ultra vires), they can be declared as illegal, unconstitutional and invalid (null and void) by the judiciary. So #1 is wrong.
I.R. Coelho case (2007), the Supreme Court ruled that there could not be any blanket immunity from judicial review of laws included in the Ninth Schedule. Thus #2 is also wrong. So, D: neither 1 nor 2 correct.
Question 46: Consider the following statements : [2018-I]
1. The Parliament of India can place a particular law in the Ninth Schedule of the Constitution of India
2. The validity of a law placed in the Ninth Schedule cannot be examined by any court and no judgement can be made on it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (a)
- First statement is correct. the 1st Amendment to the constitution (1951) had inserted new Articles 31A and 31B and the Ninth Schedule, thus securing the constitutional validity of zamindari abolition laws by, among other things, specifying that they could not be challenged on the grounds that they violated the Fundamental Rights. Subsequent governments have added other progressive laws in the same, to give them immunity from litigation. Government add the acts in the 9th schedule, 'via parliament' so first statement is right.
- In I.R. Coelho case(2007), the Supreme Court ruled that there could not be any blanket immunity from judicial review of laws included in the Ninth Schedule. So statement#2 is WRONG
Question 47: In the federation established by The Government on India Act of 1935. Residuary Power were given to the [2018-I]
(a) Federal Legislature
(b) Governor General
(c) Provincial Legislature
(d) Provincial Governors
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Residuary powers were in the hands of Governor General.
Question 48: Which one of the following reflects the nicest, appropriate relationship between law and liberty? [2018-I]
(a) If there are more laws, there is less liberty.
(b) If there are no laws, there is no liberty.
(c) If there is liberty, laws have to be made by the people.
(d) If laws are changed too often, liberty is in danger.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (b)
- Concept of Negative Liberty: Historically speaking, the term liberty was initially defined as absence of all restraints on an individual. John Stuart Mill, the nineteenth century English political philosopher, described, "Restraint as an evil". Mill was especially worried about the restraints coming from the state and society. From this concept, we can infer A: if there are more laws, there is less liberty.
- Concept of Positive Liberty: Since individuals live together in a society, complete absence of restraints would be neither possible nor desirable. It has been very aptly said that your liberty to swing your arm ends there where my nose begins. For liberty to be enjoyed by everyone, it should have reasonable restraints. The freedom of many requires restraint of law on the freedom of some. Later liberals supported the positive liberty. From this concept, we can infer B: if there are no laws, there is no liberty.
- So, as such, both A and B (and even D) seem "appropriate", but question also asks which one reflects both "appropriate" and "nicest"- Option B is the nicest of them three.
Question 49: Which of the following are regarded as the main features of the "Rule of Law"? [2018-I]
1. Limitation of powers
2. Equality before law
3. People's responsibility to the Government
4. Liberty and civil rights
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- This idea of rule of law implies that all individuals - rich and poor, men or women, forward or backward castes - are subjected to the same law. So, #2 is right. (Equality before the law)
- The principal role of the judiciary is to protect rule of law and ensure supremacy of law. It safeguards rights of the individual…and ensures that democracy does not give way to individual or group dictatorship. So, it also means #1 and #4 are right.
- Statement #3 is irrelevant, so by elimination we are left with Option (c)
Question 50: Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of Right to Life and Personal Liberty. Which of the following in the Constitution of India correctly and appropriately imply the above statement? [2018-I]
(a) Article 14 and the provisions under the 42nd Amendment to the Constitution
(b) Article 17 and the Directive Principles of State Policy in Part IV
(c) Article 21 and the freedoms guaranteed in Part. III
(d) Article 24 and the provisions under the 44th Amendment to the Constitution
 View Answer
View Answer 
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Supreme Court ruled that "the right to privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of the right to life and personal liberty under Article 21 and as a part of the freedoms guaranteed by Part III of the Constitution" so Option c is right.
Let's also look at the wrong options:
- Article 14- Gives the Right to Equality. 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act 1976, is known as mini constitution.
- Article 17- Related to the Abolition of Untouchability. It is part of Right to Equality. Part IV- Directive Principles of State Policy, does not have any mention about the Privacy.
- Article 24- Prohibition of employment of children in factories, et(c) 44th Constitution Amendment- 44th amendment of the Constitution was enacted by the Janata Government mainly to nullify some of the amendments made by the 42nd Amendment Act, 1976.
|
72 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Constitution & Political System - Solved Questions (2025-2018) - UPSC Topic Wise Previous Year Questions
| 1. What is the significance of the Constitution of India in the political system? |  |
| 2. How does the Indian political system ensure the separation of powers? |  |
| 3. What role do fundamental rights play in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. What are the main features of the Indian federal system? |  |
| 5. How does the process of constitutional amendment work in India? |  |






















