Current Electricity | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Categories of Current Electricity |

|
| Generation of Current Electricity |

|
| Contrasting Current Electricity and Static Electricity |

|
Introduction
Current electricity can be described as the movement of electrons from one part of a circuit to another.
Electromotive Force (EMF) and Voltage:
- When a wire connects two bodies with varying potentials, electrons move from Point 1 to Point 2 until both objects reach an equal potential, causing the current to cease. As long as there is a potential difference across a conductor, current will flow.
- Based on the aforementioned example, we can provide the following definitions:
- Definition of Electromotive Force: Electromotive force refers to the electric potential generated by an electrochemical cell or through alterations in the magnetic field.
- Definition of Voltage: Voltage is the disparity in electric potential between two points.
Categories of Current Electricity
There exist two categories of current electricity, namely:
- Direct Current (DC)
- Alternating Current (AC)
Direct Current
- Direct current refers to the flow of electricity in a consistent direction. It is characterized by a continuous movement of electrons from an area of high electron density to an area of low electron density. Direct current is commonly employed in various household devices and applications that rely on batteries.
Alternating Current
- Alternating current is a form of electricity that oscillates in both directions, constantly reversing the flow of charge. This bidirectional nature is achieved through sinusoidally varying currents and voltages that alternate their directions, resulting in a periodic back-and-forth motion of the current. The electrical outlets found in our homes and industries typically provide alternating current as the power supply.
Generation of Current Electricity
Current electricity can be generated by the following methods:
- By moving a metal wire through a magnetic field (Both alternating current and direct current can be generated by the following method)
- By a battery through chemical reactions (Direct current can be generated through this method)
Relative Motion Between Magnetic Field and Coil
Note that this setup must be a part of an electric circuit, otherwise the electrons have nowhere to go and current electricity won’t be generated.
The orientation of the magnetic field and the orientation of the wire will dictate the flow of electric current through the wire.
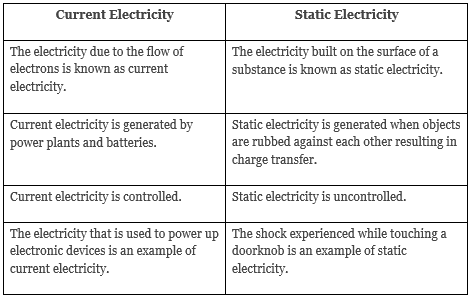
Contrasting Current Electricity and Static Electricity
In this segment, we will examine the distinctions between current electricity and static electricity:
Definition of Static Electricity:
- Static electricity pertains to the accumulation of electric charges on the surface of materials or substances. These charges remain stationary until they are grounded or discharged. This form of electricity arises from friction. Essentially, static electricity occurs when positive and negative charges become separated.
- Now, we will explore the various dissimilarities between static electricity and current electricity.
|
744 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|




















