UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > UPSC Mains: Internal Security & Disaster Management > Cyber Warfare
Cyber Warfare | UPSC Mains: Internal Security & Disaster Management PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cyber warfare |

|
| “Supply chain” cyber-attack |

|
| Pegasus Spyware |

|
| Disinformation |

|
| Cognitive hacking |

|
| Way Forward |

|
Cyber warfare
- Cyber warfare is computer- or network-based conflict involving politically motivated attacks by a nation-state on another nation-state. In these types of attacks, nation-state actors attempt to disrupt the activities of organizations or nation-states, especially for strategic or military purposes and cyber espionage.
- It involves the actions by a nation-state or international organization to attack and attempt to damage another nation’s computers or information networks through, for example, computer viruses or denial-of-service attacks.
Examples:
- In 2020, the United States (US) department of defence (DoD) exposed an information-stealing malware, Slothful Media, which they said was being used to launch cyberattacks against targets in India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Malaysia, Russia and Ukraine.
- The most notorious example is that of the misinformation campaign conducted by Russian bots during the 2016 US presidential elections.
- Societally, sowing disinformation through social media disinformation is also cyberwarfare. Russia has been particularly savvy in this field but recently, China has stepped up its game.
- Intellectual property (IP) rights are another avenue of strategic competition — in 2014, the US justice department indicted five Chinese military hackers and accused them of stealing secrets from US Steel, JP Morgan, Alcoa, Westinghouse Electrical Co., and United Steelworkers.
- Military cyberattacks are perhaps the most associated with cyberwarfare — the “Sandworm Team”, a group associated with Russian intelligence, has conducted attacks on government sectors in the US, Ukraine, Poland, and on the European Union and NATO.
- A well-documented cyberattack occurred in 2010 when a malware “Stuxnet” that was designed to damage Iran’s nuclear capability by making Iranian scientists and government think there were a series of internal engineering mishaps at their enrichment facility.
“Supply chain” cyber-attack
- In an increasingly digital and connected world, supply chain viruses and hackers could be the new face of cyber warfare. In the last week of 2020, news came in that Vietnam had been found to be the target of a sophisticated supply chain cyber-attack.
- In the second week of December 2020, the technology world was rocked by the news of a “supply chain” cyber-attack that had managed to infiltrate the networks and systems of multiple US government departments, tech majors like Microsoft and Cisco, and hundreds of big and small companies around the world working in sensitive areas.
- These are termed “supply chain” cyber-attacks because instead of attacking a target, the hackers rely on infecting one of its suppliers instead to gain access.
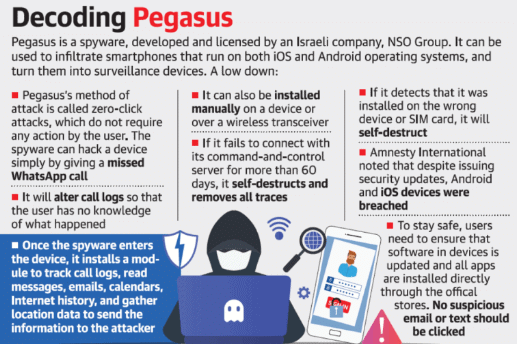
Pegasus Spyware
- Recently, it has been reported that Pegasus, the malicious software, has allegedly been used to secretly monitor and spy on an extensive host of public figures in India.
- As per claims, at least a 1,000 Indian phone numbers are in a list of potential targets of surveillance using the Pegasus spyware sold by Israeli company the NSO Group to “vetted governments” with the approval of the Israeli government.
What is a zero-click attack?
- A zero-click attack helps spyware like Pegasus gain control over a device without human interaction or human error.
- So, all awareness about how to avoid a phishing attack or which links not to click are pointless if the target is the system itself.
Disinformation
- Disinformation is an attack and compromise of our cognitive being. Here the information ecosystem is manipulated to create social discord, increase polarisation, and in some cases, influence the outcome of an election.
- Disinformation attacks use manipulated, miscontextualised, misappropriated information.
- Historically, the industry has treated these attacks independently, deployed different countermeasures, and even have separate teams working in silos to protect and defend against these attacks.
- For example, QAnon spread false information claiming that the U.S. 2020 presidential election was fraudulent, and conspiracy theorists burned down 5G towers because they believed it caused the novel coronavirus pandemic.
- COVID-19 disinformation campaigns had prevented people from wearing masks, using potentially dangerous alternative cures, and not getting vaccinated.
- Balancing the rights of speech with the dangers of disinformation is a challenge for policymakers and regulators.
Cognitive hacking
- Cognitive hacking is a cyberattack that seeks to manipulate the perception of people by exploiting their psychological vulnerabilities.
- Cognitive hacking is a threat from disinformation.
- Cognitive hacking attack attempts to change the target audience’s thoughts and actions, galvanise societies and disrupt harmony using disinformation.
- It exploits cognitive biases and shapes people by perpetuating their prejudices.
- The goal is to manipulate the way people perceive reality.
- The storming of the U.S. Capitol on January 6, 2021, is a prime example of the effects of cognitive hacking.
- Revolutions throughout history have used cognitive hacking techniques to overthrow governments and change society.
Way Forward
- The need to be aware of the nature of the cyber threat and take adequate precautionary measures, has become extremely vital.
- New technologies such as artificial intelligence, Machine learning and quantum computing, also present new opportunities.
- Nations that are adequately prepared and have made rapid progress in artificial intelligence and quantum computing have a clear advantage over states that lag behind in these fields.
- Pressure also needs to be put on officials in the public domain to carry out regular vulnerability assessments and create necessary awareness of the growing cyber threat.
- It is time that cybersecurity as a specialised discipline becomes an integral component of any IT syllabus being taught within our university systems as well as outside.
- Coordination among CERTs of different countries.
- Ensure that vulnerable sections of our society do not fall prey to the evil designs of cyber criminals.
- Understanding and implementing the global best practices of the cyber space.
- Need for India to move on from IT security to cyber security.
- Organisations that are hit by cyber-attacks must inform law enforcement immediately instead of worrying about their reputations.
- Important to have crisis management plans so that it helps to react in a given situation.
- A dedicated industry forum for cyber security should be set up to develop trusted indigenous solutions to check cyber-attacks.
The document Cyber Warfare | UPSC Mains: Internal Security & Disaster Management is a part of the UPSC Course UPSC Mains: Internal Security & Disaster Management.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
63 videos|114 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Cyber Warfare - UPSC Mains: Internal Security & Disaster Management
| 1. What is cyber warfare? |  |
Ans. Cyber warfare refers to the use of digital techniques and technologies to launch attacks on computer systems and networks, with the intention of causing damage or disruption to a target. It involves the use of hacking, malware, and other cyber tools to gain unauthorized access, steal information, or manipulate digital assets.
| 2. What is a "supply chain" cyber-attack? |  |
Ans. A supply chain cyber-attack is a type of cyber-attack that targets the vulnerabilities in the supply chain of an organization. It involves compromising the systems or software of a third-party vendor or supplier that is connected to the target organization's network. By exploiting these trusted relationships, attackers can gain unauthorized access to the target's systems and launch further attacks.
| 3. What is Pegasus Spyware? |  |
Ans. Pegasus Spyware is a highly sophisticated and powerful surveillance tool developed by the Israeli cybersecurity firm, NSO Group. It is designed to infect and secretly monitor mobile devices, allowing attackers to remotely access and control the device's functions, including calls, messages, and data. Pegasus has been associated with targeting journalists, activists, and political dissidents worldwide.
| 4. What is disinformation in the context of cyber warfare? |  |
Ans. Disinformation refers to the deliberate spread of false or misleading information with the intent to deceive or manipulate public opinion. In the context of cyber warfare, disinformation campaigns are often carried out by state-sponsored actors or hacktivist groups to sow discord, create confusion, or influence public sentiment. These campaigns may involve spreading fake news, creating bogus social media accounts, or conducting coordinated misinformation campaigns.
| 5. What is cognitive hacking? |  |
Ans. Cognitive hacking refers to the manipulation of human perception, cognition, or decision-making processes through psychological techniques in order to gain unauthorized access to information or systems. It exploits vulnerabilities in human psychology, such as cognitive biases, social engineering, or manipulation of trust, to deceive individuals and trick them into revealing sensitive information or granting access to secure systems.
Related Searches















