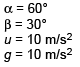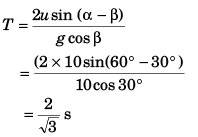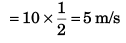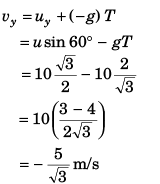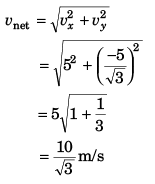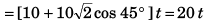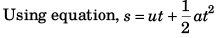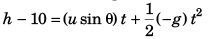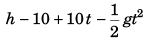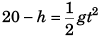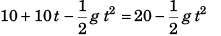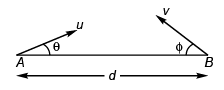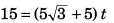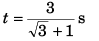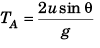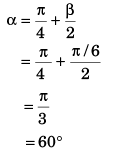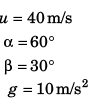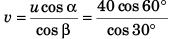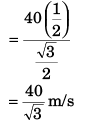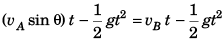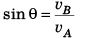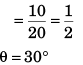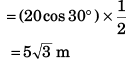DC Pandey Solutions: Projectile Motion - 2 | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 4.2
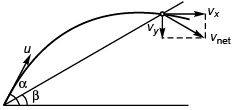
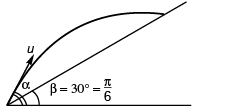
Ques 1: A particle is projected along an inclined plane as shown in figure. What is the speed of the particle when it collides at point A? (g = 10 m/s2)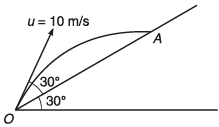
Ans: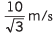
Sol: Time of flight
Using, v = u + at
vx = ux = u cos 60°
Q2: In the above problem what is the component of its velocity perpendicular to the plane when it strikes at A?
Ans: 5 m/s
Sol: Component of velocity perpendicular to plane
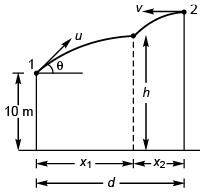
Ques 3: Two particles A and B are projected simultaneously from the two towers of height 10 m and 20 m respectively. Particle A is projected with an initial speed of 10√2 m/s at an angle of 45° with horizontal, while particle B is projected horizontally with speed 10 m/s. If they collide in air, what is the distance d between the towers?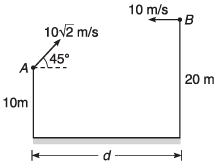
Ans: 20 m
Sol: Let the particle collide at time t.
x1 = (u cos θ) t
and x2 = vt
∴ d = x2 - x1
= (v + u cos θ) t
For vertical motion of particle 1:
i.e.,…(i)
or
For the vertical motion of particle 2:
i.e.,…(ii)
Comparing Eqs. (i) and (ii),
⇒ t = 1 s
∴ d = 20 m
Ques 4: Two particles A and B are projected from ground towards each other with speeds 10 m/s and 5√2 m/s at angles 30° and 45° with horizontal from two points separated by a distance of 15 m. Will they collide or not?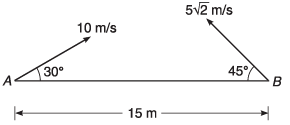
Ans: No
Sol: u = 10 m/s
v = 5√2 m/sθ = 30°
φ = 45°
d = 15 m
Let the particles meet (or are in the same vertical time t).
∴ d = (u cos θ) t + (v cos φ) t
⇒ 15 = (10 cos 30° + 5√2 cos 45°) t
or
or
= 1.009 s
Now, let us find time of flight of A and B
= 1 s
As TA < t, particle A will touch ground before the expected time t of collision.
∴ Ans: NO.
Ques 5: A particle is projected from the bottom of an inclined plane of inclination 30°. At what angle α (from the horizontal) should the particle be projected to get the maximum range on the inclined plane.
Ans: 60°
Sol: For range to be maximum
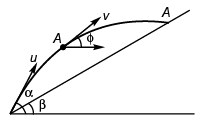
Ques 6: A particle is projected from the bottom of an inclined plane of inclination 30° with velocity of 40 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal. Find the speed of the particle when its velocity vector is parallel to the plane. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Ans: 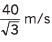
Sol: At point A velocity
of the particle will be parallel to the inclined plane.
∴ φ = β
vx = ux = u cos α
vx = v cos φ = v cos β
or u cos α = v cos β
⇒
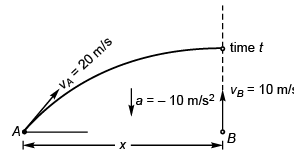
Ques 7: Two particles A and B are projected simultaneously in the directions shown in figure with velocities vA = 20 m/s and vB = 10 m/s respectively. They collide in air after 1/2 s.
Find:
(a) the angle θ
(b) the distance x.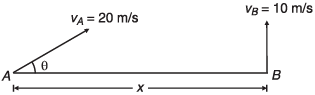
Ans: (a) 30°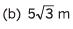
Sol: (a) At time t, vertical displacement of A
= Vertical displacement of B
i.e., vA sin θ = vB
∴ θ = 30°
(b) x = (vA cos θ) t
|
297 videos|953 docs|172 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Projectile Motion - 2 - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the formula for the maximum height reached by a projectile? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the range of a projectile? |  |
| 3. What factors affect the time of flight of a projectile? |  |
| 4. Can a projectile reach the same point from which it was launched? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the angle of projection in projectile motion? |  |